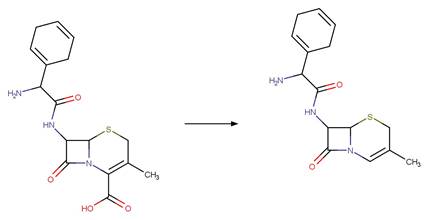
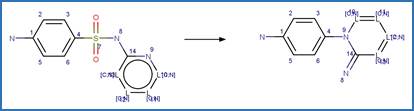
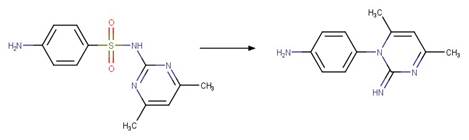
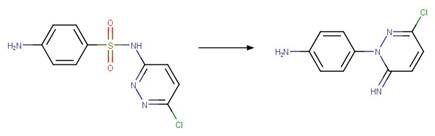
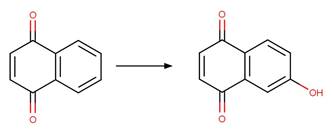
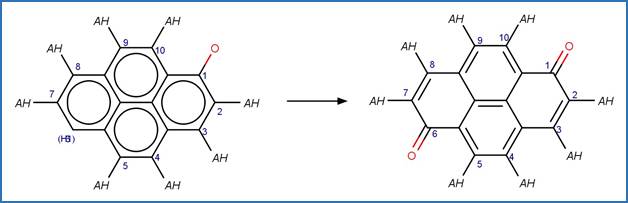
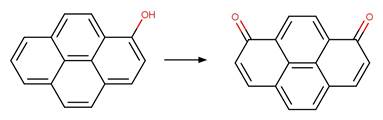
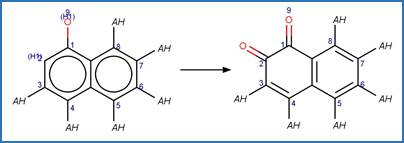
Version 1.3 of the Direct
Photolysis Reaction Library contains 155 reaction schemes:
Symbols and Notes. 6
Reaction Schemes. 7
Photorearrangement. 7
·
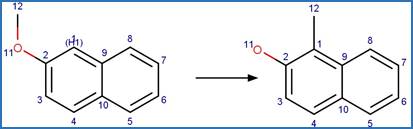
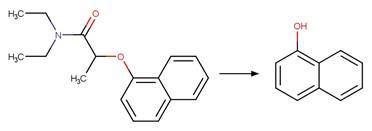
1-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C2). 7
·
1-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C4). 8
·
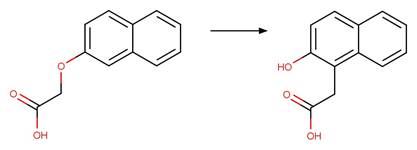
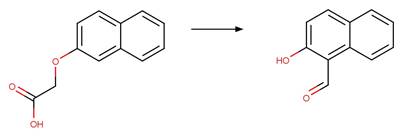
2-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C1). 9
·
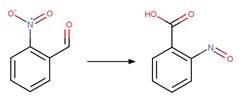
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde Photorearrangement. 10
·
Benzyl Phenyl Ether Photorearrangement
(o). 11
·
Benzyl Phenyl Ether Photorearrangement
(p). 12
·
Enone Steroid Photorearrangement to
Cyclopentenone. 13
·
Enone Steroid Photorearrangement to
Lumiketone. 14
·
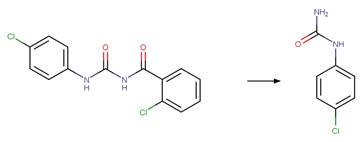
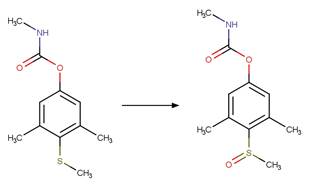
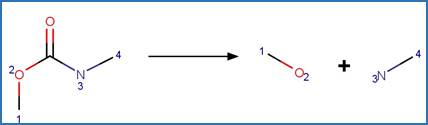
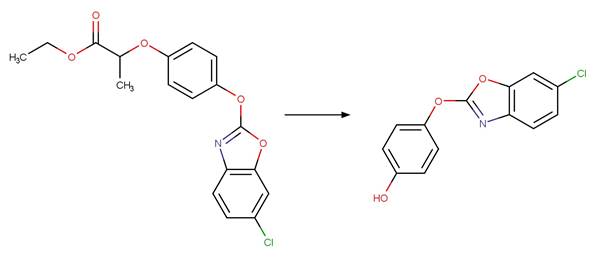
O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangement (o). 15
·
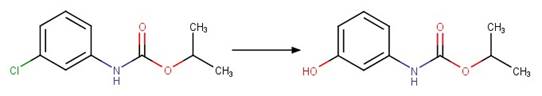
O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangement (p). 16
·
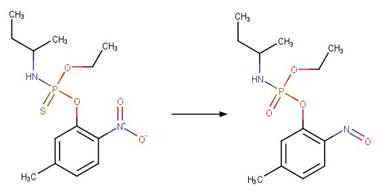
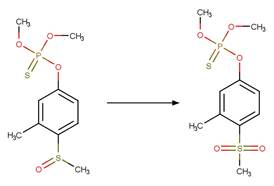
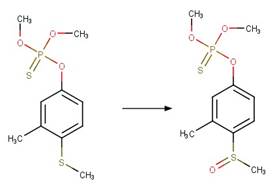
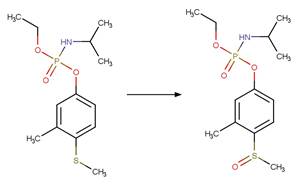
Organothiophosphorus Ester Photochemical
Oxygen Transfer. 17
·
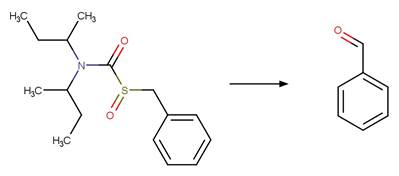
Organothiophosphorus Ester
Photorearrangement. 18
·
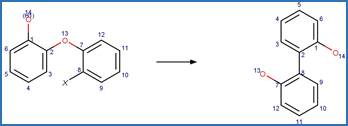
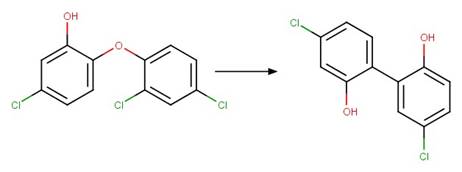
Phenoxyphenol Dehalogenative
Photorearrangement. 19
Photodissociation. 20
·
Aromatic Ketone Norrish II Photocleavage
(C1_C4). 20
·
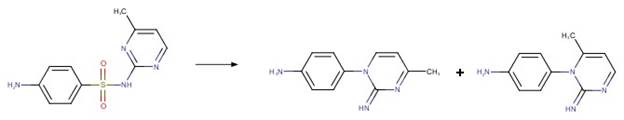
Aminobenzophenone Photochemical
N-dealkylation. 21
·
Benzyl Photodeamination to Alcohol 22
·
Benzyl Photodeamination to Carbonyl 23
·
Benzyl Thiocarbamate Photocleavage to
Carbonyl 25
·
Cyclohexanedione Oxime N-O Photocleavage. 26
·
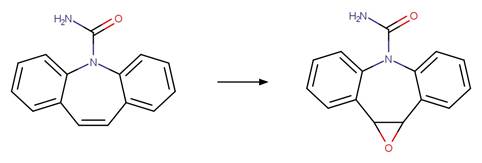
Diazepam Ring Photocleavage. 28
·
Dihydrophenanthrene Benzyl
Photodealkylation. 30
·
Dihydrophenanthrene Benzyl Oxidative
Photodealkylation. 31
·
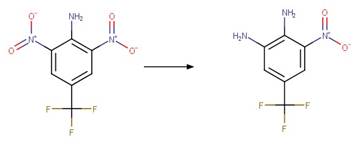
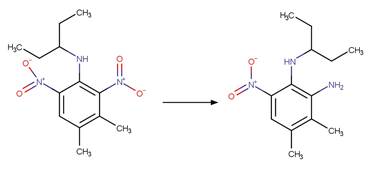
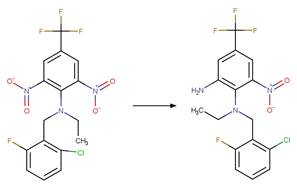
Dinitroaniline Photochemical
N-dealkylation. 32
·
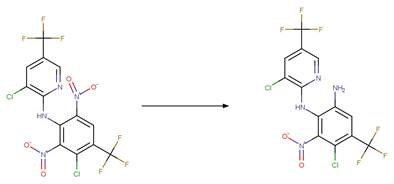
Fluoroquinolone Ethylenediamine
Photochemical N-dealkylation. 35
·
Fluoroquinolone Photochemical
N-dealkylation. 37
·
Fluoroquinolone Piperazine Photochemical
Bis N-dealkylation. 39
·
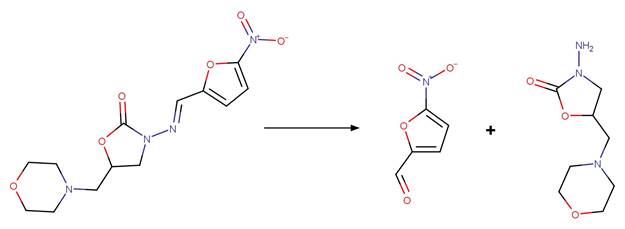
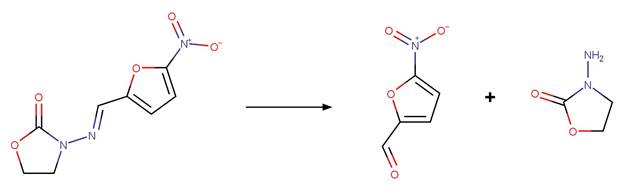
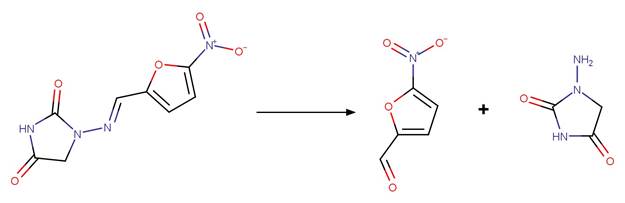
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to
Aldehyde. 41
·
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to Amide. 43
·
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to
Amidine. 45
·
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to
Carboxylic Acid. 47
·
Nitroenamine Photocleavage. 49
·
Nitroenamine Photocleavage to Carbonyl 50
·
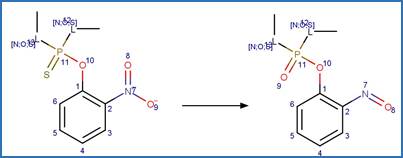
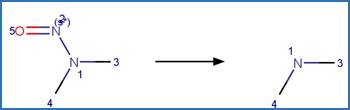
Nitrosamine N-C Photocleavage. 51
·
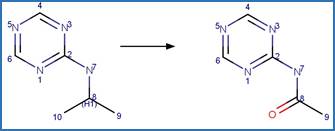
p-Aminobenzoic Acid Photochemical
N-dealkylation. 52
·
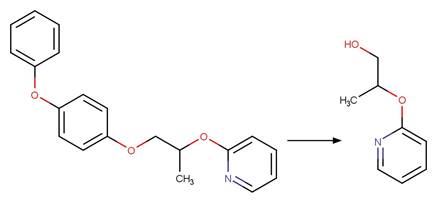
Phenoxyphenol Ether Photocleavage. 54
·
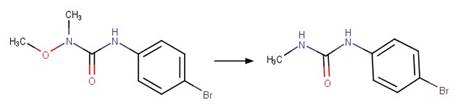
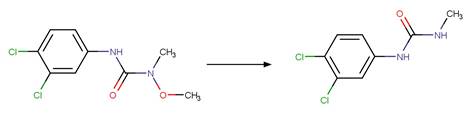
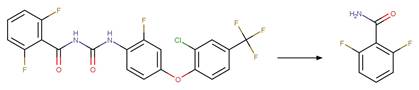
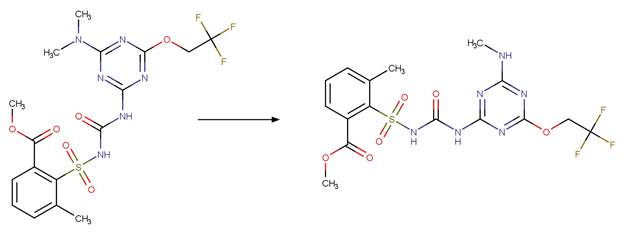
Phenylurea Photochemical N-dealkylation. 56
·
Phenylurea Photochemical
N-demethoxylation. 58
·
Phenylurea N-formyl Photocleavage. 59
·
Pyridinium Photochemical N-dealkylation. 60
·
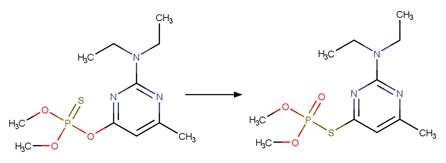
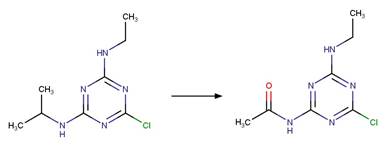
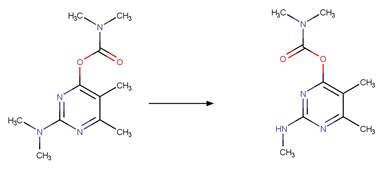
s-Triazine Side Chain Photochemical
N-dealkylation. 62
·
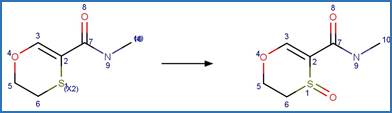
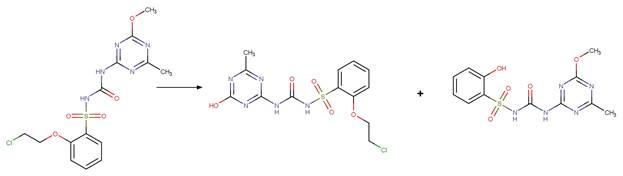
Sulfonamide N-C Photocleavage (6-5). 66
·
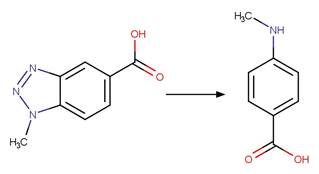
Tetracycline Photochemical N-dealkylation. 68
Photoelimination. 69
·
1_2_4-Triazine-5-one Photochemical
N-deamination. 69
·
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation. 70
·
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation
to Alcohol 72
·
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation
to Carbonyl 74
·
Aromatic Carboxylic Acid
Photodecarboxylation. 77
·
Aromatic Carboxylic Acid
Photodecarboxylation to Alcohol 81
·
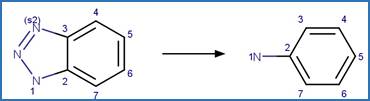
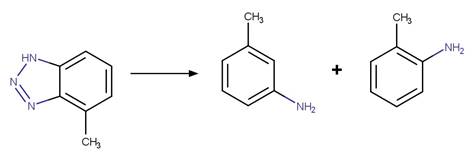
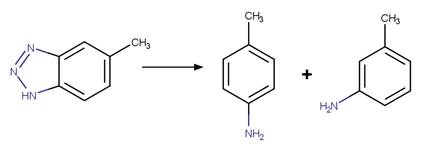
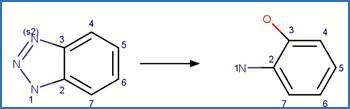
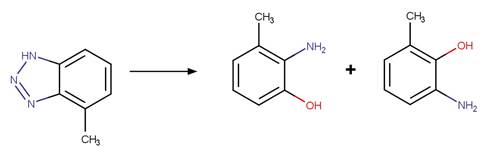
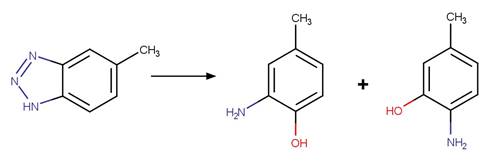
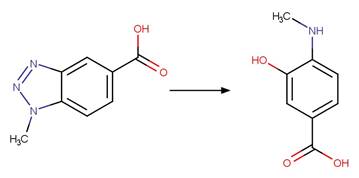
Benzotriazole Photodenitrogenation. 83
·
Benzotriazole Photodenitrogenation to
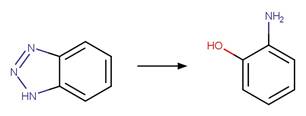
Phenol (o). 85
·
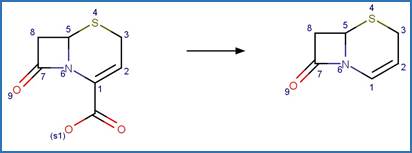
Cephem Photodecarboxylation. 87
·
Cyanohydrin Cyano Photoelimination to
Aldehyde. 89
·
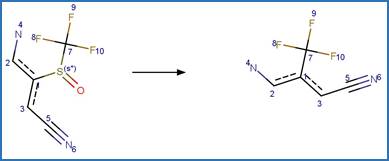
Fipronil Sulfoxide Photoextrusion. 90
·
Imidazolinone Amide Photoelimination. 91
·
Imidazolinone Photodecarbonylation. 92
·
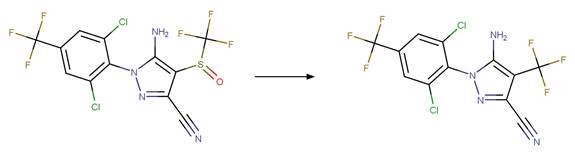
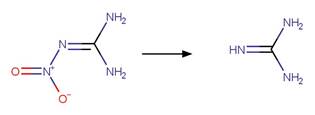
Nitroguanidine Photochemical
N-denitration. 94
·
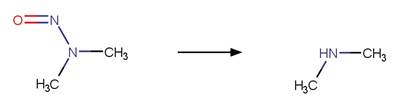
Nitrosamine N-N Photocleavage. 95
·
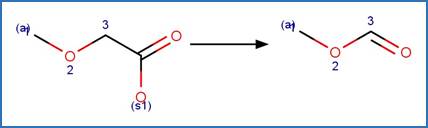
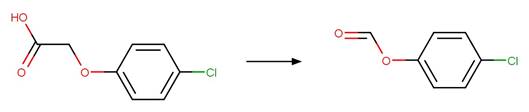
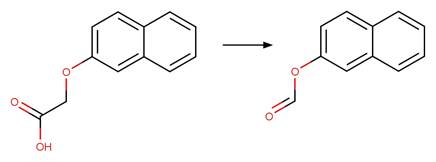
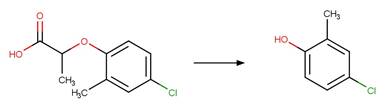
Phenoxyacetic Acid Photodecarboxylation. 96
·
Phenoxyacetic Acid Photodecarboxylation
to Carbonyl 97
·
Pyrrolinone Photodecarbonylation. 99
·
RDX Photochemical N-denitration to Imine. 100
·
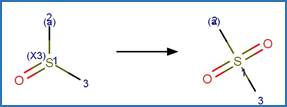
Sulfonamide SO2 Extrusion
Photorearrangement (6-6). 101
Photocyclization. 103
·
Acetanilide Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Pyrrolinone. 103
·
Acetanilide O-dealkyl Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Morpholinone. 104
·
Altrenogest Photocycloaddition. 106
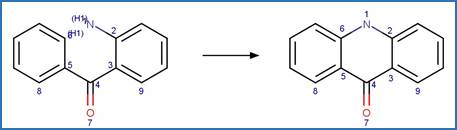
·
Aminobenzophenone Photocyclization to
Acridinone. 107
·
Anthranilic Diamide Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Oxazine. 108
·
Aromatic Ketone Norrish II
Photocyclization (C1_C4). 110
·
beta-Triketone Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Pyran. 111
·
Diarylethene Photocyclization to
Phenanthrene. 112
·
Diarylethene Photocyclization to
Phenanthrene (E isomer). 114
·
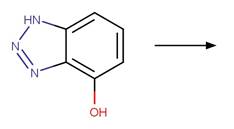
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to
Benzimidazole (NOHOH). 116
·
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to
Benzimidazole (NOHOH to NO). 116
·
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to
Benzimidazole (NO to N). 116
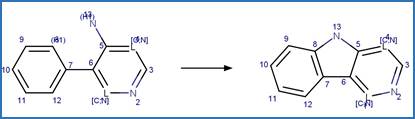
·
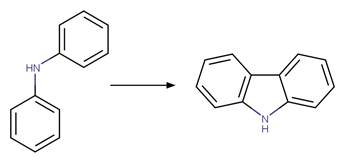
Diphenylamine Photocyclization to
Carbazole. 121
·
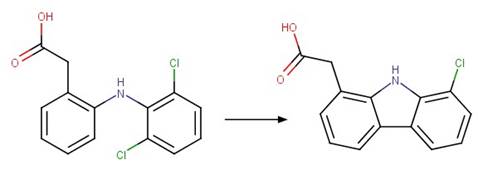
Diphenylamine Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Carbazole. 122
·
Fluoroquinolone Defluorinative
Photocyclization. 123
·
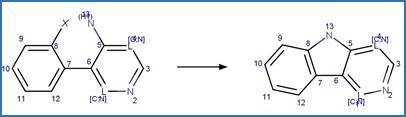
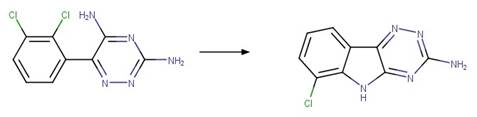
Lamotrigine Photocyclization to Carbazole. 124
·
Lamotrigine Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Carbazole. 125
·
o-Vinylbiphenyl Photocyclization to
Dihydrophenanthrene. 126
·
Phenoxyphenol Dehalogenative
Photocyclization to Dioxin. 128
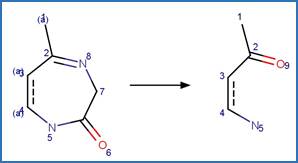
Photochemical Ring Contraction. 130
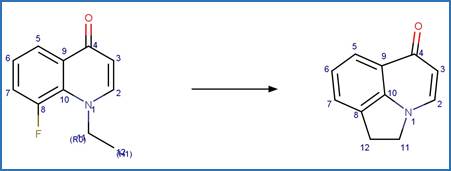
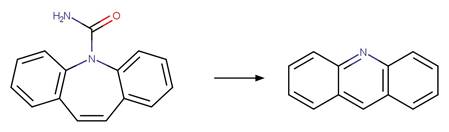
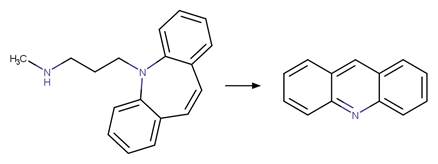
·
Zepine Photochemical Ring Contraction to
Acridine. 130
Photohydrolysis. 131
·
Aromatic Amine Photohydrolysis. 131
·
Aromatic Carbamate Photohydrolysis. 133
·
Aromatic Ether Photohydrolysis. 135
·
Aromatic Halide Photohydrolysis. 140
·
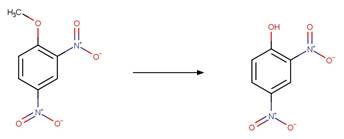
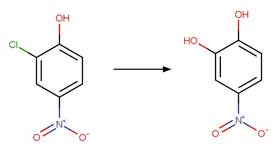
Aromatic Nitro Photohydrolysis. 147
·
Aromatic Sulfonate Photohydrolysis. 150
·
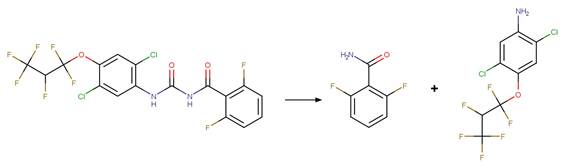
Benzoylphenylurea Amide Photohydrolysis. 152
·
Benzoylphenylurea Urea Photohydrolysis. 153
·
beta-Triketone alpha Photocleavage to
Carboxylic Acid. 155
·
Diphenyl Ether Photohydrolysis. 157
·
Fluoroquinolone Fluoride Photohydrolysis. 160
·
N-aryl Amide Photohydrolysis. 162
·
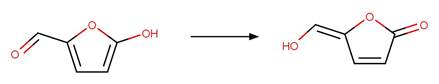
Nitrofuran Imine Photohydrolysis. 165
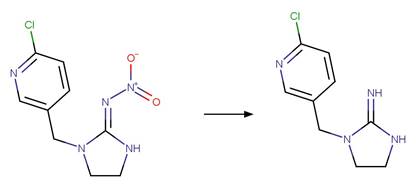
·
Nitroguanidine Imine Photohydrolysis. 167
·
Nitroguanidine Nitro Photohydrolysis. 169
·
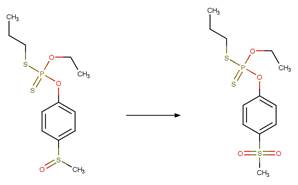
Organophosphorus Ester Photohydrolysis. 170
·
Pyrethroid Carboxylic Acid Ester
Photohydrolysis. 173
·
Pyrrolinone Halide Photohydrolysis. 174
·
Sulfonamide Photohydrolysis. 175
·
Sulfonamide S-C Photohydrolysis. 179
·
Sulfonylurea Photohydrolysis. 182
·
Sulfonylurea S-C Photohydrolysis. 184
·
Sulfonylurea S-N Photohydrolysis. 186
·
Trifluoromethyl Photohydrolysis. 188
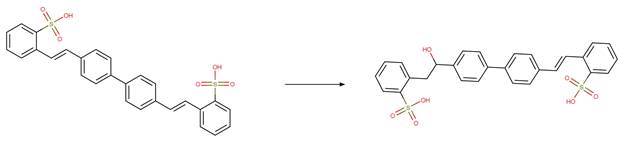
Photohydration. 192
·
Diarylethene Photohydration. 192
·
Dienone Steroid Photohydration (C5). 194
·
Dienone Steroid Photohydration (C9). 196
·
Enone Steroid Photohydration and
Photorearrangement to Spiro. 197
·
Trienone Steroid Photohydration (C10). 198
·
Trienone Steroid Photohydration (C12). 199
Photooxidation. 201
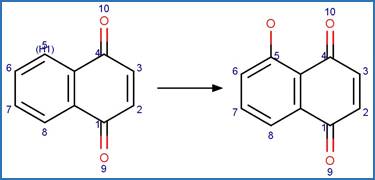
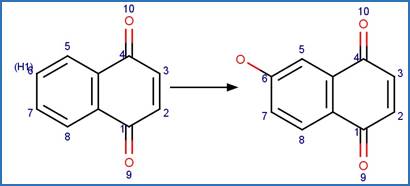
·
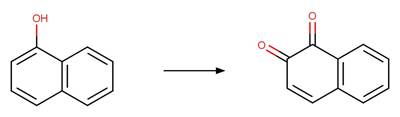
1_2-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation
(C4). 201
·
1_4-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation
(C5). 202
·
1_4-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation
(C6). 203
·
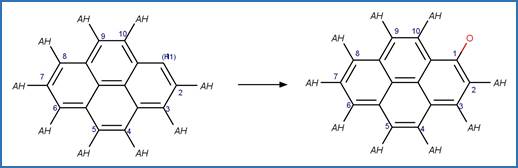
1-Hydroxypyrene Photooxidation to Quinone
(C1_C6). 204
·
1-Hydroxypyrene Photooxidation to Quinone
(C1_C8). 205
·
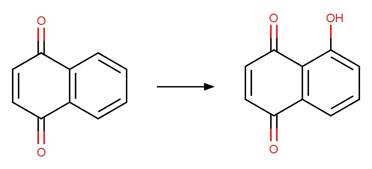
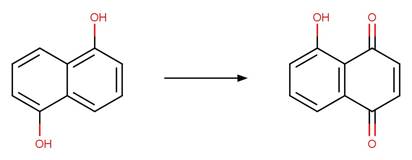
1-Naphthol Photooxidation to
1_2-Benzoquinone. 206
·
1-Naphthol Photooxidation to
1_4-Benzoquinone. 207
·
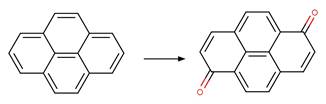
1-Naphthoxy Oxidative Photocleavage to
1_4-Benzoquinone. 208
·
Anthracene Photooxidation to Endoperoxide. 209
·
Aromatic Methyl Photooxidation to
Carboxylic Acid. 210
·
Aromatic Nitroso Photooxidation. 211
·
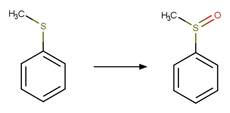
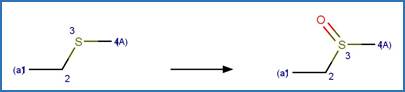
Aromatic Sulfoxide Photooxidation. 213
·
Aromatic Thioether Photooxidation. 215
·
Benzaldehyde Photooxidation to Carboxylic
Acid. 217
·
Benzyl Thio Photooxidation to Sulfoxide. 219
·
beta-Triketone alpha Photohydroxylation
(Dienol). 220
·
beta-Triketone alpha Photohydroxylation
(Keto) 221
·
beta-Triketone Photohydroxylation (Enol). 222
·
beta-Triketone Photohydroxylation (Keto) 223
·
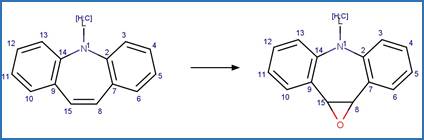
Carbamazepine Photoepoxidation. 224
·
Diarylethene Photooxidation. 225
·
Dihydrooxathiine Anilide Photooxidation
to Sulfoxide. 227
·
Dihydropyridine Photooxidation to
Pyridine. 228
·
Octahydrophenanthrene Benzyl
Photohydroxylation. 229
·
Octahydrophenanthrene Benzyl
Photooxidation to Ketone. 231
·
Organothiophosphorus Ester Photooxidation
to Oxon. 232
·
Phenylurea N-methyl Photooxidation to
N-formyl 234
·
Pyrene Aromatic Photohydroxylation. 235
·
s-Triazine Side Chain N-alkyl
Photooxidation to Carbonyl 236
·
s-Triazine Side Chain N-isopropyl
Photooxidation to Ketone. 237
·
Trienone Steroid Photooxidation to
Dialdehyde. 238
·
Trifluoroacetic Acid Photoformation. 239
Photoreduction. 240
·
Aromatic Photohydrodehalogenation. 240
·
Dinitroaniline Nitro Photoreduction. 243
·
Fluoroquinolone Photohydrodefluorination. 245
Secondary Dark Reaction. 247
·
12-OH Steroid Dehydration to Trienone. 247
·
5-OH Steroid Dehydration to Dienone. 249
·
Aldehyde Oxidation to Carboxylic Acid. 251
·
C-NCO Hydrolysis. 253
·
C-NNO2 Hydrolysis. 254
·
Dehydration of Geminal Diols. 255
·
Hydroxy Enal Tautomerization. 256
·
Nitro Amidine Hydrolysis. 257
Rank Assignment. 258
Rank Levels. 258
Rank of Individual Reaction Schemes. 258
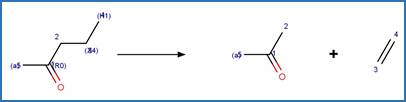
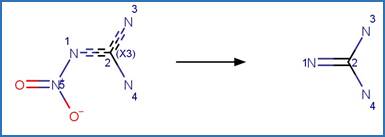
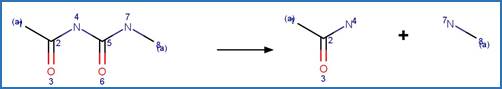
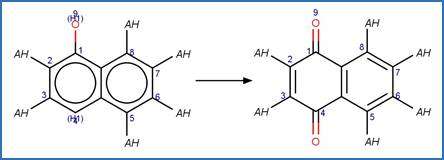
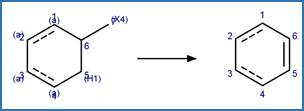
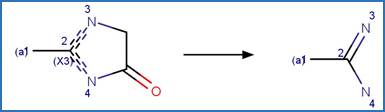
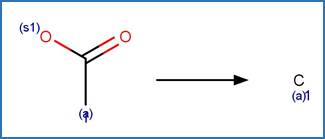
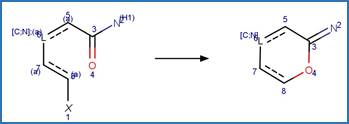
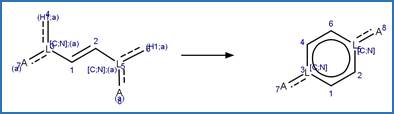
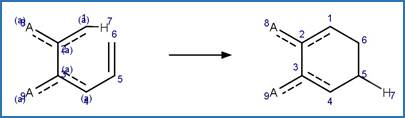
The reaction schemes
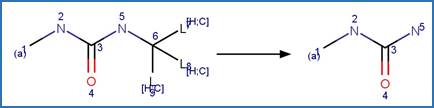
are encoded using the notation and structural query features (L, ~L, L1-X, etc)
from ChemAxon’s Marvin tools. Definitions of some common symbols used in the
reaction schemes are provided below:
·
L[a1;a2;…] is a list of possible atoms (a1, a2, …) that can
occupy the position within the fragment
·
~L![a1;a2;…] is a list of atoms (a1, a2, …) that cannot occupy
the position within the fragment
·
A is any atom except hydrogen
·
AH is any atom including hydrogen
·
X is any halogen atom (i.e. F, Cl, Br, X)
·
(A) indicates an aliphatic carbon atom
·
(a) indicates an aromatic carbon atom
·
(L1-N) indicates a string of atoms (acyclic or cyclic) of length
of N
·
(X#) indicates # connections (= substituents including hydrogen) are
attached to the atom
·
(H#) indicates at least # hydrogens are attached to the atom
·
(s#) indicates # non-hydrogen substituents are attached to the
atom
·
(s*) indicates the non-hydrogen substituent count is as drawn for
the atom
·
(R0) indicates the atom is not part of a ring
·
(R) indicate the atom is part of a ring
·
 is a single
bond
is a single
bond
·
 is a double
bond
is a double
bond
·
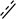 is an aromatic
bond unless otherwise stated underneath the reaction scheme to represent a single/aromatic
or a double/aromatic bond
is an aromatic
bond unless otherwise stated underneath the reaction scheme to represent a single/aromatic
or a double/aromatic bond
·
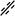 is a single or
double bond
is a single or
double bond
·
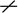 is a double cis
or trans bond
is a double cis
or trans bond
The associated
reactivity, selectivity, and exclusion rules are encoded using ChemAxon's
Chemical Terms Language. Definitions of the Chemical Terms functions used in
the reaction schemes can be referred from ChemAxon’s documentation: https://docs.chemaxon.com/display/docs/Available+Functions (accessed on Apr 29, 2020).
Other Notes:
·
The reference from European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reports
can be found on the official website and was not referred individually: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/publications
(accessed on Apr 29, 2020).
·
“XXX photo-product” as the compound name means that XXX was the
original compound photolyzed in the reference and the XXX photo-product and the
subsequent products were detected.
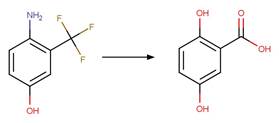
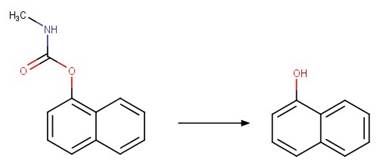
Scheme:
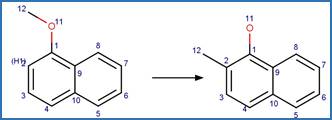
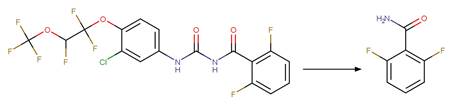
An exclusion rule is included to differentiate this scheme from
“O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangement (o)” by specifying that reactant atom 11
is not part of a carbamate functional group.
Examples:
Napropamide (Aguer et al. 1998, Chang
et al. 1991) (EFSA)
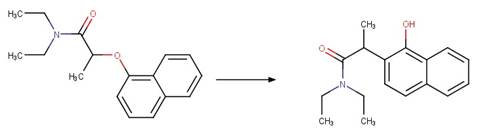
References:
Aguer, J.P.,
Boule, P., Bonnemoy, F. and Chezal, J.M. 1998. Phototransformation of
napropamide [n,n-diethyl-2-(1-naphthyloxy)propionamide] in aqueous solution:
Influence on the toxicity of solutions. Pestic. Sci. 54(3), 253-257.
Chang, L.L., Giang, B.Y., Lee, K.S. and Tseng, C.K. 1991.
Aqueous photolysis of napropamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 39(3), 617-621.
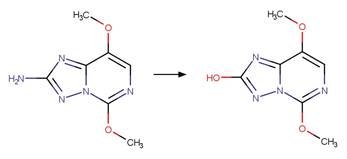
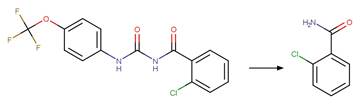
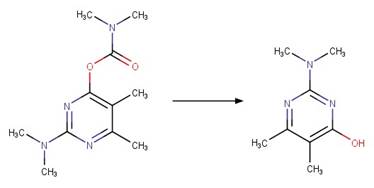
Scheme:
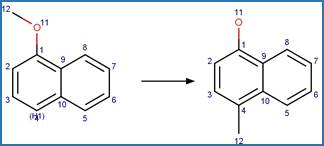
An exclusion
rule is included to differentiate the scheme from “O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangment
(p)” by specifying that reactant atom 11 is not part of a carbamate functional
group.
Examples:
Napropamide (Aguer et al. 1998, Chang
et al. 1991) (EFSA)

Reference:
Aguer, J.P.,
Boule, P., Bonnemoy, F. and Chezal, J.M. 1998. Phototransformation of
napropamide [n,n-diethyl-2-(1-naphthyloxy)propionamide] in aqueous solution:
Influence on the toxicity of solutions. Pestic. Sci. 54(3), 253-257.
Chang, L.L., Giang, B.Y., Lee, K.S. and Tseng, C.K. 1991.
Aqueous photolysis of napropamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 39(3), 617-621.
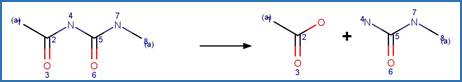
Scheme:
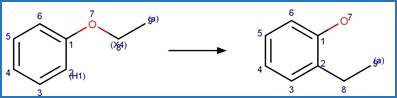
An exclusion
rule is included to exclude the counterexample dimoxystrobin by specifying that
reactant atom 9 is not part of a benzaldoxime functional group.
Examples:
Mandestrobin (Adachi et al. 2018) (EFSA)
Dimoxystrobin
(EFSA)
References:
Adachi, T., Suzuki, Y., Nishiyama, M., Kodaka, R., Fujisawa, T.
and Katagi, T. 2018. Photodegradation of strobilurin fungicide mandestrobin in
water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66(32), 8514-8521.
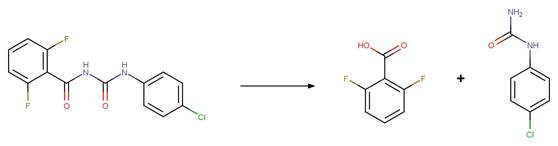
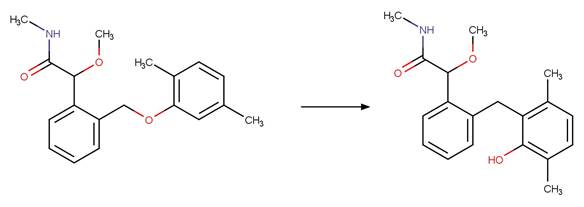
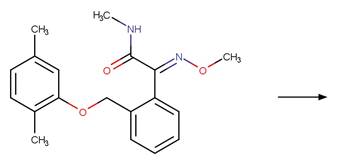
Scheme:
An exclusion
rule is included to exclude the counterexample dimoxystrobin by specifying that
reactant atom 9 is not part of a benzaldoxime functional group.
Examples:
Mandestrobin (Adachi et al. 2018) (EFSA)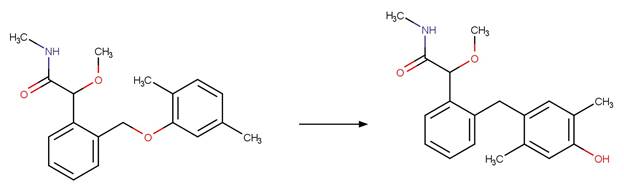
Dimoxystrobin
(EFSA)
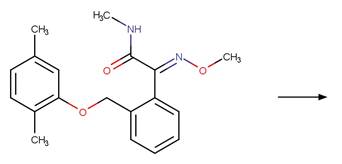
References:
Adachi, T., Suzuki, Y., Nishiyama, M., Kodaka, R., Fujisawa, T.
and Katagi, T. 2018. Photodegradation of strobilurin fungicide mandestrobin in
water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66(32), 8514-8521.
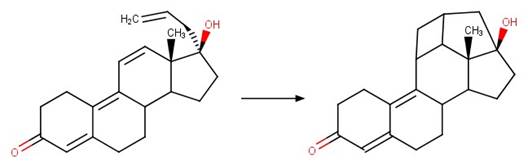
Scheme:
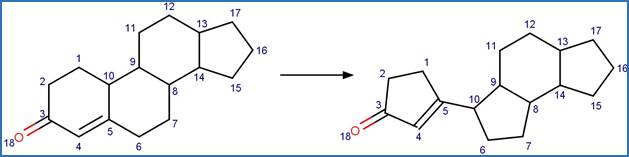
Examples:
Androstenedione
(Young et al. 2013)
Testosterone (Vulliet et al. 2010)
References:
Vulliet, E.,
Falletta, M., Marote, P., Lomberget, T., Païssé, J.-O. and Grenier-Loustalot,
M.-F. 2010. Light induced degradation of testosterone in waters. Sci. Total
Environ. 408(17), 3554-3559.
Young, R.B., Latch, D.E., Mawhinney, D.B., Nguyen, T.-H.,
Davis, J.C.C. and Borch, T. 2013. Direct photodegradation of androstenedione
and testosterone in natural sunlight: Inhibition by dissolved organic matter
and reduction of endocrine disrupting potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(15),
8416-8424.
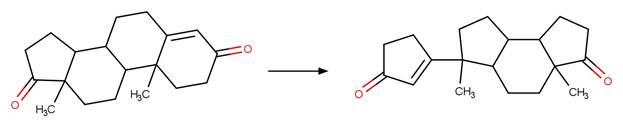
Scheme:
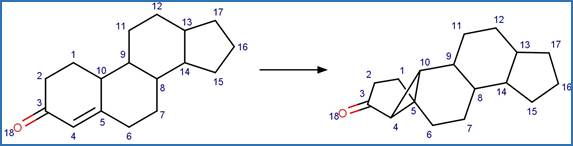
Examples:
Androstenedione
(Young et al. 2013)
Testosterone (Vulliet et al. 2010)
References:
Vulliet, E.,
Falletta, M., Marote, P., Lomberget, T., Païssé, J.-O. and Grenier-Loustalot,
M.-F. 2010. Light induced degradation of testosterone in waters. Sci. Total
Environ. 408(17), 3554-3559.
Young, R.B., Latch, D.E., Mawhinney, D.B., Nguyen, T.-H.,
Davis, J.C.C. and Borch, T. 2013. Direct photodegradation of androstenedione
and testosterone in natural sunlight: Inhibition by dissolved organic matter
and reduction of endocrine disrupting potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(15),
8416-8424.
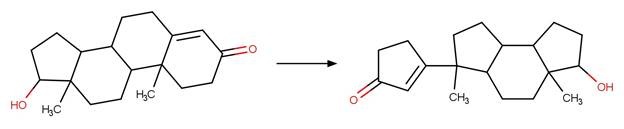
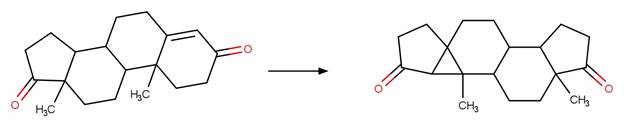
Scheme:
Examples:
Phenisopham (Passananti et al. 2014)
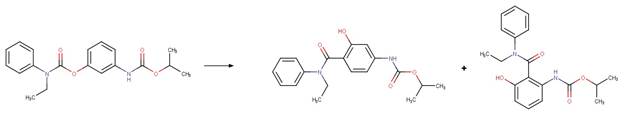
References:
Passananti, M., Lavorgna, M., Iesce, M.R., DellaGreca, M.,
Criscuolo, E., Parrella, A., Isidori, M. and Temussi, F. 2014. Chlorpropham and
phenisopham: Phototransformation and ecotoxicity of carbamates in the aquatic
environment. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 16(4), 823-831.
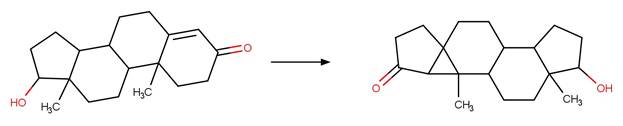
Scheme:

Examples:
Phenisopham (Passananti et al. 2014)

References:
Passananti, M., Lavorgna, M., Iesce, M.R., DellaGreca, M., Criscuolo,
E., Parrella, A., Isidori, M. and Temussi, F. 2014. Chlorpropham and
phenisopham: Phototransformation and ecotoxicity of carbamates in the aquatic
environment. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 16(4), 823-831.
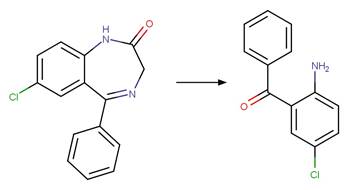
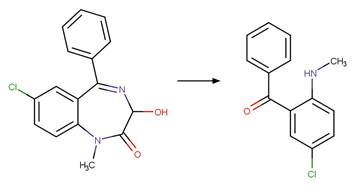
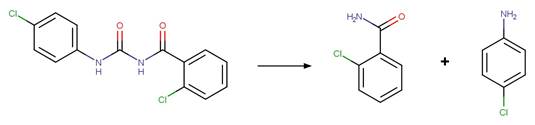
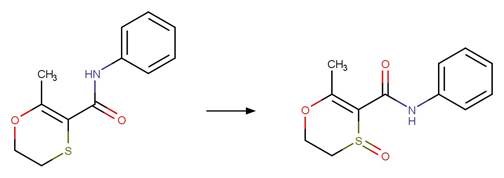
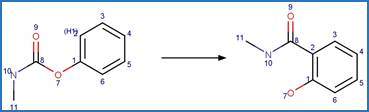
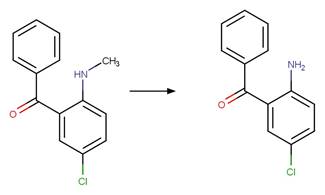
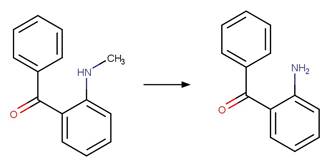
Scheme:
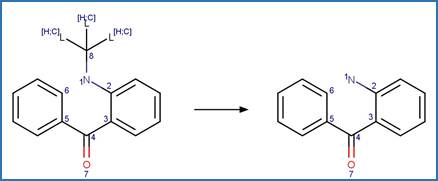
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
5-chloro-2-methylaminobenzophenone
(West and Rowland 2012)
Temazepam
photo-product (West and Rowland 2012)
References:
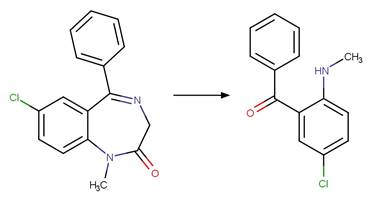
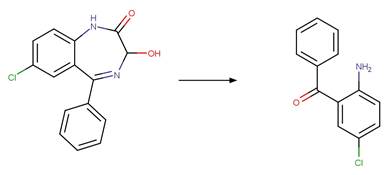
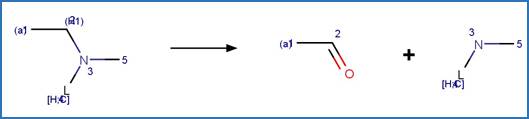
Scheme:
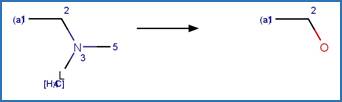
Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude the carbamate functional group at atom 3 and
(2) to constrain that the cleaved bond between reactant atom 2 and 3 is not
part of a ring.
Examples:
Rivastigmine (Temussi et al. 2012)

Imidacloprid (Wamhoff and Schneider 1999)
References:
Temussi, F.,
Passananti, M., Previtera, L., Iesce, M.R., Brigante, M., Mailhot, G. and
DellaGreca, M. 2012. Phototransformation of the drug rivastigmine: Photoinduced
cleavage of benzyl-nitrogen sigma bond. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 239,
1-6.
Wamhoff, H. and
Schneider, V. 1999. Photodegradation of imidacloprid. J. Agric. Food Chem.
47(4), 1730-1734.
West, C.E. and Rowland, S.J. 2012. Aqueous phototransformation
of diazepam and related human metabolites under simulated sunlight. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 46(9), 4749-4756.
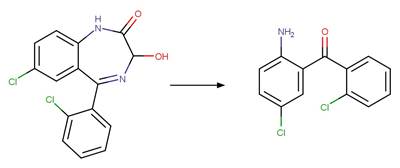
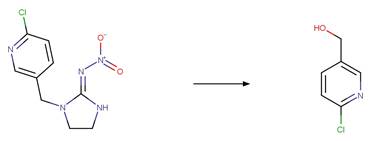
Scheme:
Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude the amide functional group at atom 3 and (2)
to constrain that the cleaved bond between reactant atom 2 and 3 is not part of
a ring.
Examples:
Rivastigmine (Temussi et al. 2012)
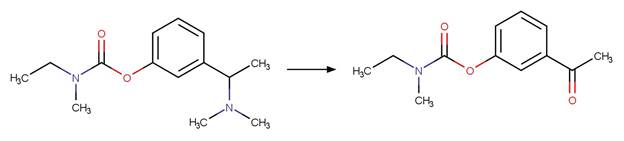
Imidacloprid (Moza et al. 1998)
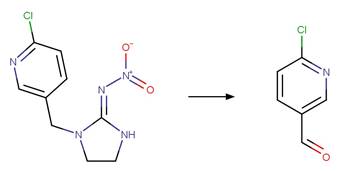
Methotrexate (Chatterji and Gallelli 1978)
The products are
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
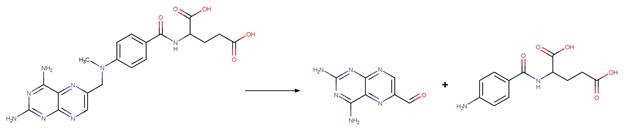
Folic acid (Saxby et al. 1983)
The products are
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
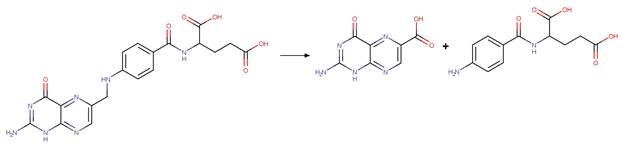
References:
Chatterji, D.C.
and Gallelli, J.F. 1978. Thermal and photolytic decomposition of methotrexate
in aqueous solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 67(4), 526-531.
Moza, P.N.,
Hustert, K., Feicht, E. and Kettrup, A. 1998. Photolysis of imidacloprid in
aqueous solution. Chemosphere 36(3), 497-502.
Saxby, M.J.,
Smith, P.R., Blake, C.J. and Coveney, L.V. 1983. The degradation of folic acid
in a model food system and in beer. Food Chem. 12(2), 115-126.
Temussi, F., Passananti, M., Previtera, L., Iesce, M.R.,
Brigante, M., Mailhot, G. and DellaGreca, M. 2012. Phototransformation of the drug
rivastigmine: Photoinduced cleavage of benzyl-nitrogen sigma bond. J.
Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 239, 1-6.
Scheme:
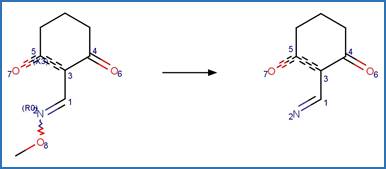
Examples:
Alloxydim (Sandín-España et al. 2013)

Clethodim (Sevilla-Morán et al. 2010)
Tralkoxydim
(EFSA)
References:
Sandín-España,
P., Sevilla-Morán, B., Calvo, L., Mateo-Miranda, M. and Alonso-Prados, J.L.
2013. Photochemical behavior of alloxydim herbicide in environmental waters.
Structural elucidation and toxicity of degradation products. Microchem. J.
106(Supplement C), 212-219.
Sevilla-Morán, B., Alonso-Prados, J.L., García-Baudín, J.M.
and Sandín-España, P. 2010. Indirect photodegradation of clethodim in aqueous
media. Byproduct identification by quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(5), 3068-3076.
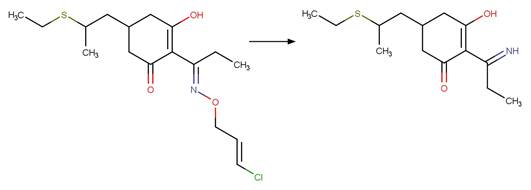
Scheme:
An exclusion rule is included to constrain that the cleaved
bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
5-[8-fluoro-4-isopropyl-2-(N-methylmethanesulfonamido)-5H,6H-benzo[h]quinazolin-6-yl]-3,5-dihydroxypentanoic
acid (Astarita et al. 2007)
References:
Astarita, A., DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Montanaro, S.,
Previtera, L. and Temussi, F. 2007. Polycyclic compounds by sunlight exposure
of the drug rosuvastatin in water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 187(2),
263-268.
Scheme:
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
5-[8-fluoro-4-isopropyl-2-(N-methylmethanesulfonamido)-5H,6H-benzo[h]quinazolin-6-yl]-3,5-dihydroxypentanoic
acid (Astarita et al. 2007)
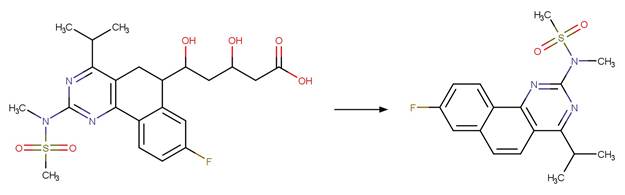
5-{3-fluoro-7-isopropyl-5H,6H-benzo[c]carbazol-5-yl}-3,5-dihydroxypentanoic
acid (Cermola et al. 2007)
References:
Astarita, A.,
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Montanaro, S., Previtera, L. and Temussi, F. 2007.
Polycyclic compounds by sunlight exposure of the drug rosuvastatin in water. J.
Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 187(2), 263-268.
Cermola, F., DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Montanaro, S.,
Previtera, L., Temussi, F. and Brigante, M. 2007. Irradiation of fluvastatin in
water: Structure elucidation of photoproducts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A:
Chem. 189(2), 264-271.
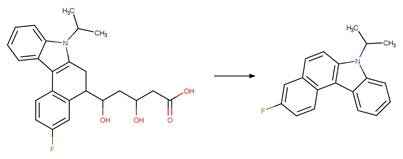
Scheme:
Examples:
Trifluralin (Leitis and Crosby 1974, Tagle
et al. 2005)(EFSA)
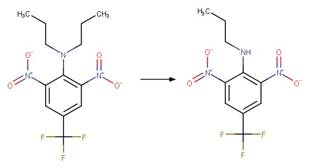
Pendimethalin (Dureja and Walia 1989, Pal
et al. 1991)

Butralin (Plimmer and Klingebiel 1974) (EFSA)
Benfluralin
(EFSA)
The products are
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
Oryzalin (EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
References:
Dureja, P. and
Walia, S. 1989. Photodecomposition of pendimethalin. Pestic. Sci. 25(2),
105-114.
Leitis, E. and
Crosby, D.G. 1974. Photodecomposition of trifluralin. J. Agric. Food Chem.
22(5), 842-848.
Pal, S., Moza,
P.N. and Kettrup, A. 1991. Photochemistry of pendimethalin. J. Agric. Food
Chem. 39(4), 797-800.
Plimmer, J.R. and
Klingebiel, U.I. 1974. Photochemistry of
n-sec-butyl-4-tert-butyl-2,6-dinitroaniline. J. Agric. Food Chem. 22(4),
689-693.
Tagle, M.G.S., Laura Salum, M., Bujan, E.I. and Arguello,
G.A. 2005. Time evolution and competing pathways in photodegradation of
trifluralin and three of its major degradation products. Photochemical &
Photobiological Sciences 4(11), 869-875.
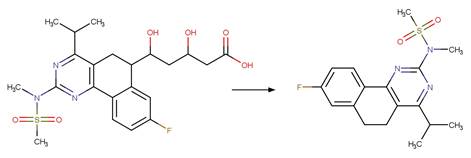
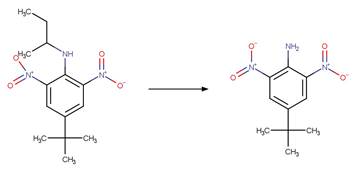
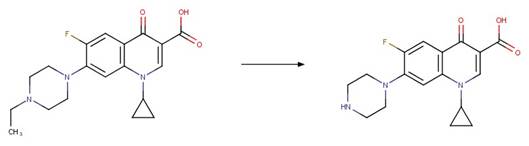
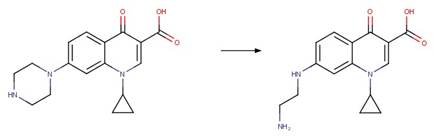
Scheme:
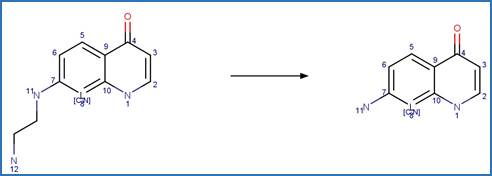
An exclusion
rule is included to distinguish this scheme from “Fluoroquinolone Piperazine Photochemical
bis N-dealkylation” by specifying that reactant atom 11 is not part of the full
piperazine ring.
Examples:
Enrofloxacin
photo-product (Burhenne et al. 1997), ciprofloxacin
photo-product (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)
Danofloxacin
photo-product (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)

Gatifloxacin (Ge et al. 2018)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
References:
Baena-Nogueras,
R.M., González-Mazo, E. and Lara-Martín, P.A. 2017. Photolysis of antibiotics
under simulated sunlight irradiation: Identification of photoproducts by
high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(6), 3148-3156.
Burhenne, J.,
Ludwig, M., Nikoloudis, P. and Spiteller, M. 1997. Primary photoproducts and
half-lives. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 4(1), 10-15.
Ge, L., Halsall, C., Chen, C.-E., Zhang, P., Dong, Q. and
Yao, Z. 2018. Exploring the aquatic photodegradation of two ionisable
fluoroquinolone antibiotics – gatifloxacin and balofloxacin: Degradation
kinetics, photobyproducts and risk to the aquatic environment. Sci. Total
Environ. 633, 1192-1197.
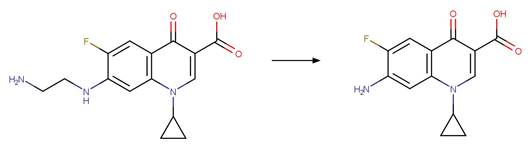
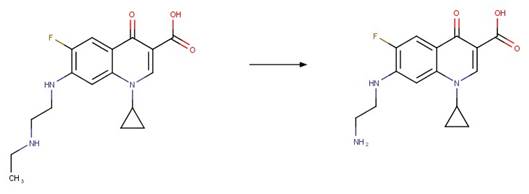
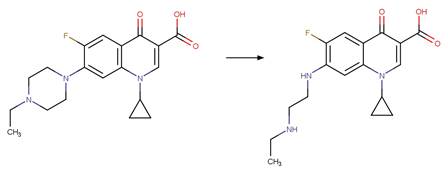
Scheme:
A reactivity
rule is included to distinguish this scheme from “Fluoroquinolone Piperazine Photochemical
bis N-dealkylation” and “Fluoroquinolone Piperazine Photochemical N-dealkylation”
by specifying that the shortest path between reactant atom 11 and 13 is 4
bonds.
Examples:
Enrofloxacin (Wammer et al. 2013)
Enrofloxacin
photo-product (Sturini et al. 2010)
Difloxacin (Kusari et al. 2009)
Danofloxacin (Ge et al. 2010)
References:
Ge, L., Chen, J.,
Wei, X., Zhang, S., Qiao, X., Cai, X. and Xie, Q. 2010. Aquatic photochemistry
of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of
main water constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(7), 2400-2405.
Kusari, S.,
Prabhakaran, D., Lamshöft, M. and Spiteller, M. 2009. In vitro residual
anti-bacterial activity of difloxacin, sarafloxacin and their photoproducts
after photolysis in water. Environ. Pollut. 157(10), 2722-2730.
Sturini, M.,
Speltini, A., Maraschi, F., Profumo, A., Pretali, L., Fasani, E. and Albini, A.
2010. Photochemical degradation of marbofloxacin and enrofloxacin in natural
waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(12), 4564-4569.
Wammer, K.H., Korte, A.R., Lundeen, R.A., Sundberg, J.E.,
McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2013. Direct photochemistry of three
fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water
Res. 47(1), 439-448.
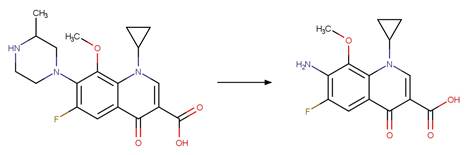
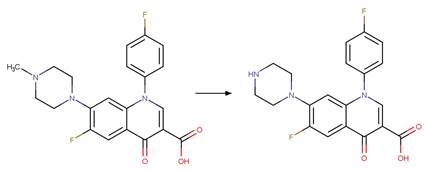
Scheme:
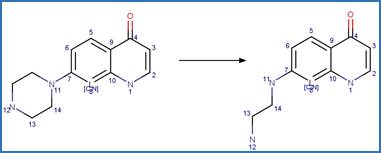
Examples:
Ciprofloxacin
photo-product (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)
Enrofloxacin (Burhenne et al. 1997)
Danofloxacin (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)

References:
Baena-Nogueras,
R.M., González-Mazo, E. and Lara-Martín, P.A. 2017. Photolysis of antibiotics
under simulated sunlight irradiation: Identification of photoproducts by
high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(6), 3148-3156.
Burhenne, J., Ludwig, M., Nikoloudis, P. and Spiteller, M.
1997. Primary photoproducts and half-lives. Environmental Science and Pollution
Research 4(1), 10-15.
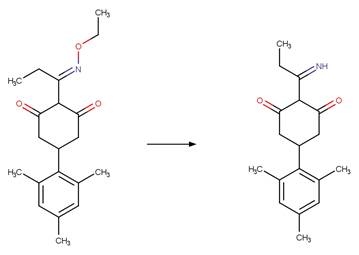
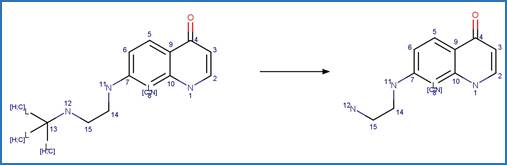
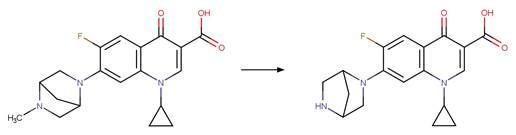
Scheme:
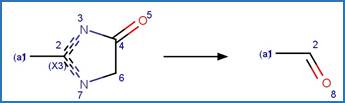
Examples:
Imazapic (Christiansen et al. 2015, Harir et al. 2007b)

Imazamox (Harir et al. 2007a)
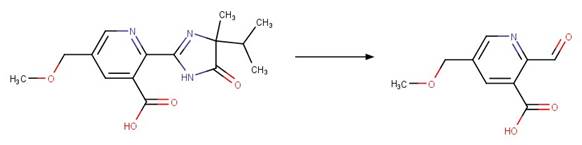
Imazapyr (Quivet et al. 2004)
References:
Christiansen, A.,
Peterson, A., Anderson, S.C., Lass, R., Johnson, M. and Nienow, A.M. 2015.
Analysis of the photodegradation of the imidazolinone herbicides imazamox,
imazapic, imazaquin, and imazamethabenz-methyl in aqueous solution. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 63(50), 10768-10777.
Harir, M.,
Frommberger, M., Gaspar, A., Martens, D., Kettrup, A., El Azzouzi, M. and
Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007a. Characterization of imazamox degradation by-products
by using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and high-resolution fourier
transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 389(5),
1459-1467.
Harir, M.,
Gaspar, A., Frommberger, M., Lucio, M., Azzouzi, M.E., Martens, D., Kettrup, A.
and Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007b. Photolysis pathway of imazapic in aqueous
solution: Ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry analysis of intermediates. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 55(24), 9936-9943.
Quivet, E., Faure, R., Georges, J., Païssé, J.O. and
Herbreteau, B. 2004. Kinetic studies of imazapyr photolysis and
characterization of the main photoproducts. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 86(4),
197-206.
Scheme:
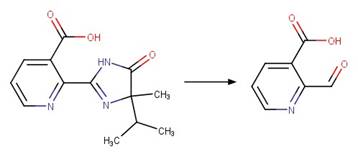
Examples:
Imazapic (Harir et al. 2007b)
Imazamox (Harir et al. 2007a)
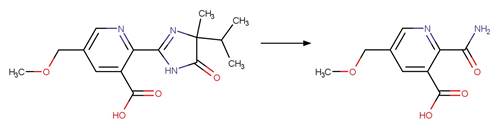
Imazapyr (Mallipudi et al. 1991)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.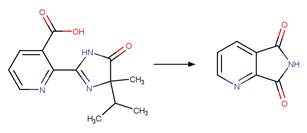
Imazaquin (Barkani et al. 2005) (EFSA)

p-imazamethabenz-methyl
(Brigante et al. 2007)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.

References:
Barkani, H.,
Catastini, C., Emmelin, C., Sarakha, M., El Azzouzi, M. and Chovelon, J.M.
2005. Study of the phototransformation of imazaquin in aqueous solution: A
kinetic approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 170(1), 27-35.
Brigante, M.,
Emmelin, C., Ferronato, C., Greca, M.D., Previtera, L., Paisse, J.O. and
Chovelon, J.-M. 2007. Effect of positional isomerism on the abiotic degradation
of pesticides: Case of m- and p-imazamethabenz-methyl. Chemosphere 68(3),
464-471.
Harir, M.,
Frommberger, M., Gaspar, A., Martens, D., Kettrup, A., El Azzouzi, M. and
Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007a. Characterization of imazamox degradation by-products
by using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and high-resolution fourier
transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.
389(5), 1459-1467.
Harir, M.,
Gaspar, A., Frommberger, M., Lucio, M., Azzouzi, M.E., Martens, D., Kettrup, A.
and Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007b. Photolysis pathway of imazapic in aqueous
solution: Ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry analysis of intermediates. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 55(24), 9936-9943.
Mallipudi, N.M., Stout, S.J., DaCunha, A.R. and Lee, A.H.
1991. Photolysis of imazapyr (ac 243997) herbicide in aqueous media. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 39(2), 412-417.
Scheme:
Examples:
Imazapic (Harir et al. 2007b)
Imazamox (Harir et al. 2007a)

Imazapyr (Quivet et al. 2004)
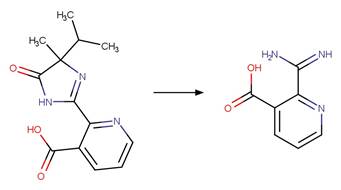
References:
Harir, M.,
Frommberger, M., Gaspar, A., Martens, D., Kettrup, A., El Azzouzi, M. and Schmitt-Kopplin,
P. 2007a. Characterization of imazamox degradation by-products by using liquid
chromatography mass spectrometry and high-resolution fourier transform ion
cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 389(5), 1459-1467.
Harir, M.,
Gaspar, A., Frommberger, M., Lucio, M., Azzouzi, M.E., Martens, D., Kettrup, A.
and Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007b. Photolysis pathway of imazapic in aqueous
solution: Ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry analysis of intermediates. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 55(24), 9936-9943.
Quivet, E., Faure, R., Georges, J., Païssé, J.O. and
Herbreteau, B. 2004. Kinetic studies of imazapyr photolysis and
characterization of the main photoproducts. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 86(4),
197-206.
Scheme:

Examples:
Imazamox (Harir et al. 2007)
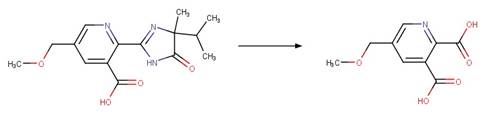
Imazaquin (Barkani et al. 2005) (EFSA)
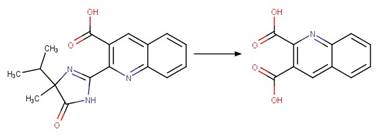
Imazapyr (Mallipudi et al. 1991, Quivet
et al. 2004)
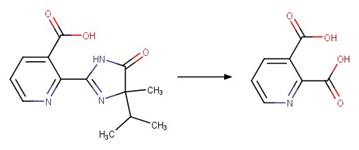
References:
Barkani, H.,
Catastini, C., Emmelin, C., Sarakha, M., El Azzouzi, M. and Chovelon, J.M.
2005. Study of the phototransformation of imazaquin in aqueous solution: A
kinetic approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 170(1), 27-35.
Harir, M.,
Frommberger, M., Gaspar, A., Martens, D., Kettrup, A., El Azzouzi, M. and
Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007. Characterization of imazamox degradation by-products
by using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and high-resolution fourier
transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.
389(5), 1459-1467.
Mallipudi, N.M.,
Stout, S.J., DaCunha, A.R. and Lee, A.H. 1991. Photolysis of imazapyr (ac
243997) herbicide in aqueous media. J. Agric. Food Chem. 39(2), 412-417.
Quivet, E., Faure, R., Georges, J., Païssé, J.O. and
Herbreteau, B. 2004. Kinetic studies of imazapyr photolysis and
characterization of the main photoproducts. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 86(4),
197-206.
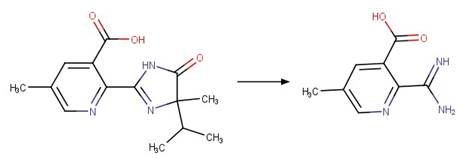
Scheme:

A reactivity
rule is included to ensure the correct valence of product atom 1.
Examples:
Nitenpyram (Ezell et al. 2019)

References:
Ezell, M.J., Wang, W., Shemesh, D., Ni, A., Gerber, R.B. and
Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. 2019. Experimental and theoretical studies of the
environmental sensitivity of the absorption spectra and photochemistry of
nitenpyram and analogs. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry 3(9), 2063-2075.
Scheme:
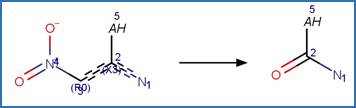
Examples:
Nitenpyram (Todey et al. 2018)
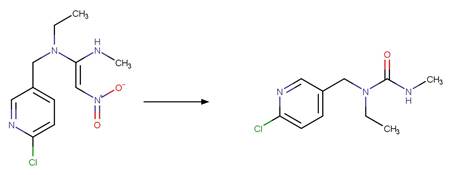
Nithiazine (Kleier et al. 1985)
References:
Kleier, D.,
Holden, I., Casida, J.E. and Ruzo, L.O. 1985. Novel photoreactions of an
insecticidal nitromethylene heterocycle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 33(5), 998-1000.
Todey, S.A., Fallon, A.M. and Arnold, W.A. 2018.
Neonicotinoid insecticide hydrolysis and photolysis: Rates and residual
toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 37(11), 2797-2809.
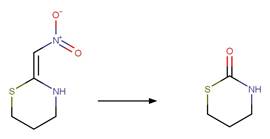
Scheme:
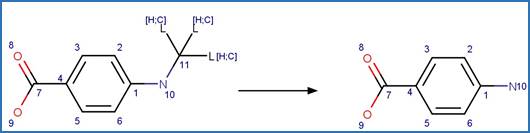
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
octyldimethyl
PABA (Sakkas et al. 2003)
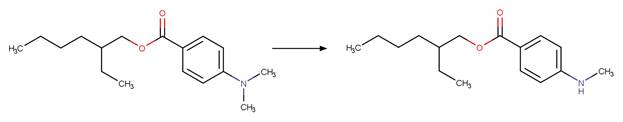
1-methyl-5-carboxylic
acid-benzotriazole photo-product (Weidauer et al. 2016)
N-methyl-4-aminobenzoic
acid (Chatterji and Gallelli 1978)
References:
Chatterji, D.C.
and Gallelli, J.F. 1978. Thermal and photolytic decomposition of methotrexate
in aqueous solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 67(4), 526-531.
Sakkas, V.A.,
Giokas, D.L., Lambropoulou, D.A. and Albanis, T.A. 2003. Aqueous photolysis of
the sunscreen agent octyl-dimethyl-p-aminobenzoic acid: Formation of
disinfection byproducts in chlorinated swimming pool water. J. Chromatogr. A
1016(2), 211-222.
Weidauer, C., Davis, C., Raeke, J., Seiwert, B. and
Reemtsma, T. 2016. Sunlight photolysis of benzotriazoles – identification of
transformation products and pathways. Chemosphere 154, 416-424.
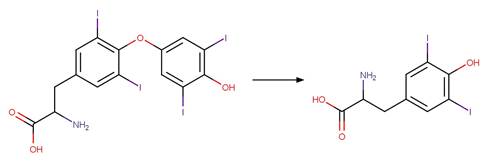
Scheme:

Examples:
Triclosan (Kliegman et al. 2013)
6-OH-PBDE 99 (Erickson et al. 2012)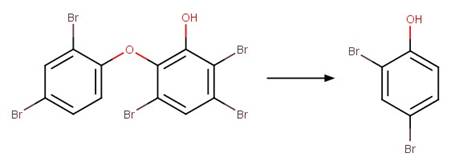
6-Cl-triclosan (Buth et al. 2009)
References:
Buth, J.M.,
Grandbois, M., Vikesland, P.J., McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2009. Aquatic
photochemistry of chlorinated triclosan derivatives: Potential source of
polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28(12), 2555-2563.
Erickson, P.R.,
Grandbois, M., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2012. Photochemical formation of
brominated dioxins and other products of concern from hydroxylated
polybrominated diphenyl ethers (oh-pbdes). Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(15),
8174-8180.
Kliegman, S., Eustis, S.N., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K.
2013. Experimental and theoretical insights into the involvement of radicals in
triclosan phototransformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(13), 6756-6763.
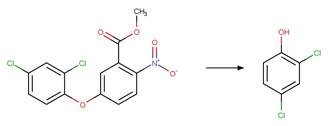
Scheme:
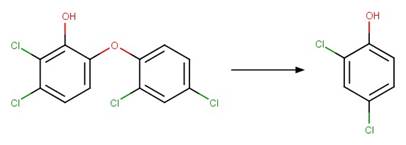
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
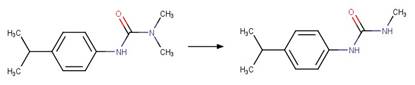
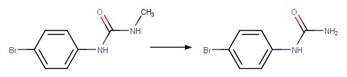
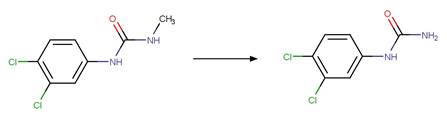
Examples:
Metoxuron (Boulkamh et al. 2001)
Diuron (Jirkovský et al. 1997)
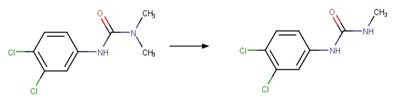
Isoproturon (Dureja et al. 1991)
Metobromuron
photo-product (Rosen and Strusz 1968)
Linuron
photo-product (Rosen et al. 1969)
References:
Boulkamh, A.,
Harakat, D., Sehili, T. and Boule, P. 2001. Phototransformation of metoxuron
[3-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea] in aqueous solution. Pest
Manage. Sci. 57(12), 1119-1126.
Dureja, P.,
Walia, S. and Sharma, K.K. 1991. Photolysis of isoproturon in aqueous solution.
Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 34(1), 65-71.
Jirkovský, J.,
Faure, V. and Boule, P. 1997. Photolysis of diuron. Pestic. Sci. 50(1), 42-52.
Rosen, J.D. and
Strusz, R.F. 1968. Photolysis of 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 16(4), 568-570.
Rosen, J.D., Strusz, R.F. and Still, C.C. 1969. Photolysis
of phenylurea herbicides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 17(2), 206-207.
Scheme:
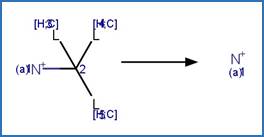
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
1-butyl-4-methylpyridinium
(Calza et al. 2017)
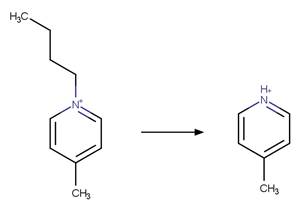
1-ethylpyridinium
(Calza et al. 2017)
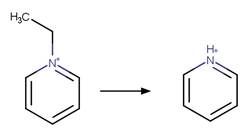
1-(3-cyanopropyl)pyridinium
(Calza et al. 2017)
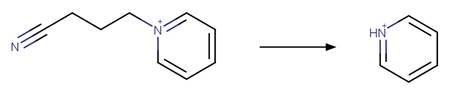
References:
Calza, P., Noè, G., Fabbri, D., Santoro, V., Minero, C., Vione,
D. and Medana, C. 2017. Photoinduced transformation of pyridinium-based ionic
liquids, and implications for their photochemical behavior in surface waters.
Water Res. 122, 194-206.
Scheme:
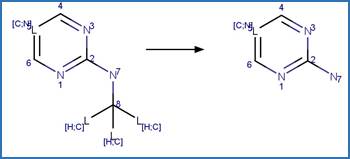
An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
desethyl
atrazine (Torrents et al. 1997)
desisopropyl
atrazine (Torrents et al. 1997)
Hexazinone
photo-product (Rhodes 1980)

Cybutryne (Okamura et al. 1999)
triflusulfuron-methyl
(EFSA)
Pirimicarb (Pirisi et al. 1996) (EFSA)
Bupirimate
(EFSA)
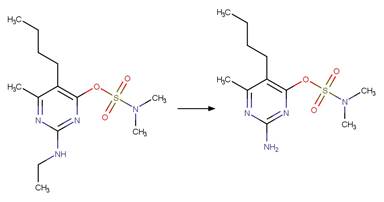
Terbuthylazine
(EFSA)
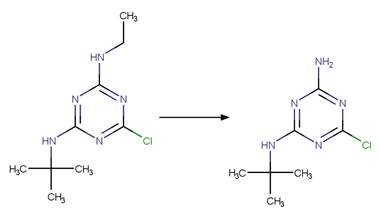
Dicyclanil (Goutailler et al. 2002)
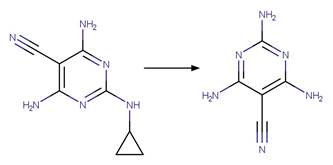
References:
Goutailler, G.,
Guillard, C., Faure, R. and Païssé, O. 2002. Degradation pathway of dicyclanil
in water in the presence of titanium dioxide. Comparison with photolysis. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 50(18), 5115-5120.
Okamura, H.,
Aoyama, I., Liu, D., Maguire, J., Pacepavicius, G.J. and Lau, Y.L. 1999.
Photodegradation of irgarol 1051 in water. Journal of Environmental Science and
Health, Part B 34(2), 225-238.
Pirisi, F.M.,
Cabras, P., Garau, V.L., Melis, M. and Secchi, E. 1996. Photodegradation of
pesticides. Photolysis rates and half-life of pirimicarb and its metabolites in
reactions in water and in solid phase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 44(8), 2417-2422.
Rhodes, R.C.
1980. Studies with carbon-14-labeled hexazinone in water and bluegill sunfish.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 28(2), 306-310.
Torrents, A., Anderson, B.G., Bilboulian, S., Johnson, W.E.
and Hapeman, C.J. 1997. Atrazine photolysis: Mechanistic investigations
of direct and nitrate-mediated hydroxy radical processes and the influence of
dissolved organic carbon from the chesapeake bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31(5),
1476-1482.
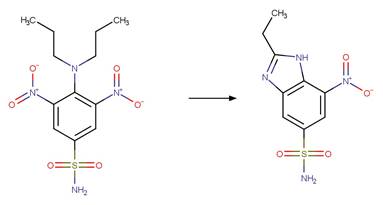
Scheme:
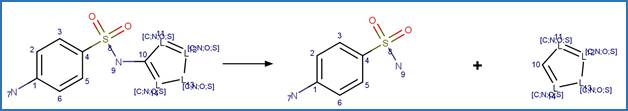
Examples:
Sulfamethoxazole
(Boreen et al. 2004)

Sulfisoxazole (Boreen et al. 2004)
Sulfamethizole (Boreen et al. 2004)
Sulfathiazole (Boreen et al. 2004)

N-acetyl
sulfamethoxazole (Bonvin et al. 2013)
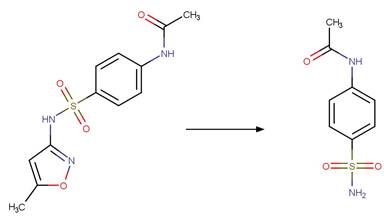
References:
Bonvin, F.,
Omlin, J., Rutler, R., Schweizer, W.B., Alaimo, P.J., Strathmann, T.J.,
McNeill, K. and Kohn, T. 2013. Direct photolysis of human metabolites of the
antibiotic sulfamethoxazole: Evidence for abiotic back-transformation. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 47(13), 6746-6755.
Boreen, A.L., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2004.
Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: Sulfa
drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups. Environ. Sci. Technol.
38(14), 3933-3940.
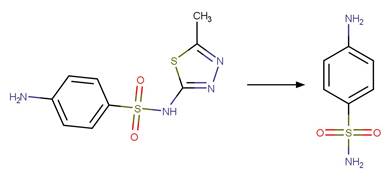
Scheme:

An exclusion
rule is included to constrain that the cleaved bond is not part of a ring.
Examples:
Chlortetracycline
(Chen et al. 2012)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.

References:
Chen, Y., Li, H., Wang, Z., Tao, T., Wei, D. and Hu, C. 2012.
Photolysis of chlortetracycline in aqueous solution: Kinetics, toxicity and
products. Journal of Environmental Sciences 24(2), 254-260.
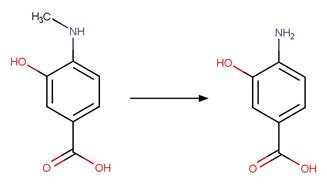
Scheme:
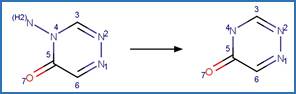
Examples:
Metamitron (Kouras-Hadef et al. 2011, Palm et al. 1997) (EFSA)
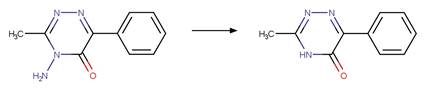
Metribuzin
(EFSA)

References:
Kouras-Hadef, S.,
de Sainte-Claire, P., ter Halle, A., Amine-Khodja, A. and Richard, C. 2011. The
role of triplet state keto–enol tautomerism in the photodeamination of
metamitron. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 115(50), 14397-14406.
Palm, W.U., Millet, M. and Zetzsch, C. 1997. Photochemical
reactions of metamitron. Chemosphere 35(5), 1117-1130.
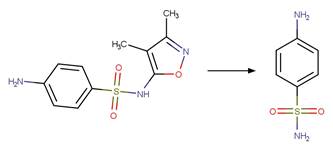
Scheme:

Examples:
Diclofenac (Agüera et al. 2005)
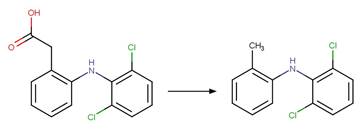
Ketoprofen (Koumaki et al. 2015)
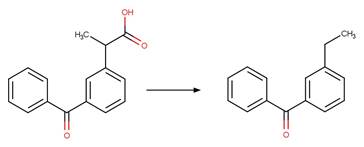
1-naphthaleneacetic
acid (Crosby and Tang 1969) (EFSA)
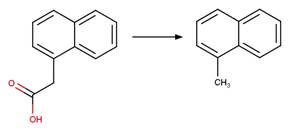
Benoxaprofen (Navaratnam et al. 1985)
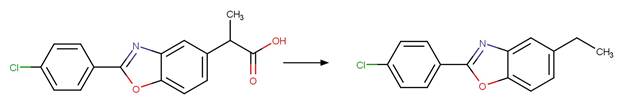
Naproxen (Moore and Chappuis 1988)
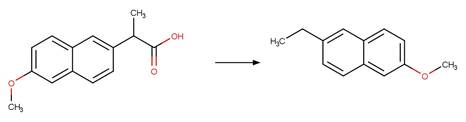
Indomethacin (Temussi et al. 2011)

References:
Agüera, A., Pérez
Estrada, L.A., Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Malato, S. and Fernández-Alba, A.R.
2005. Application of time-of-flight mass spectrometry to the analysis of phototransformation
products of diclofenac in water under natural sunlight. J. Mass Spectrom.
40(7), 908-915.
Crosby, D.G. and
Tang, C.-S. 1969. Photodecomposition of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 17(6), 1291-1293.
Koumaki, E.,
Mamais, D., Noutsopoulos, C., Nika, M.-C., Bletsou, A.A., Thomaidis, N.S.,
Eftaxias, A. and Stratogianni, G. 2015. Degradation of emerging contaminants
from water under natural sunlight: The effect of season, ph, humic acids and
nitrate and identification of photodegradation by-products. Chemosphere 138,
675-681.
Moore, D.E. and
Chappuis, P.P. 1988. A comparative study of photochemistry of the non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs, naproxen, benoxaprofen and indomethacin. Photochem.
Photobiol. 47(2), 173-180.
Navaratnam, S.,
Hughes, J.L., Parsons, B.J. and Phillips, G.O. 1985. Laser flash and
steady-state photolysis of benoxaprofen in aqueous solution. Photochem.
Photobiol. 41(4), 375-380.
Temussi, F., Cermola, F., DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R.,
Passananti, M., Previtera, L. and Zarrelli, A. 2011. Determination of
photostability and photodegradation products of indomethacin in aqueous media.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 56(4), 678-683.
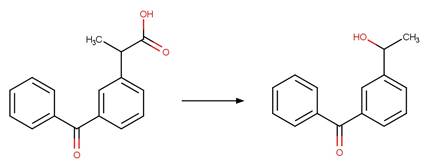
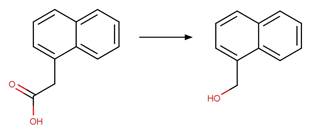
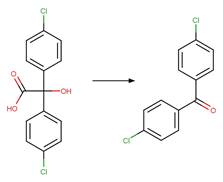
Scheme:
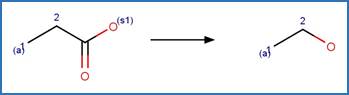
Examples:
Ibuprofen (Jacobs et al. 2011)

Ketoprofen (Koumaki et al. 2015)
1-naphthaleneacetic
acid (Crosby and Tang 1969) (EFSA)
4,4'-dichlorobenzilic
acid (Ware et al. 1980)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
Carprofen (Chen et al. 2003)

References:
Chen, F.A., Wang,
P.Y., Wen, K.C., Chen, C.Y. and Wu, A.B. 2003. Photolysis of nsaids. Ii. Online
lc-ms determination of photodegradants from carprofen. J. Food Drug Anal.
11(3), 186-190.
Crosby, D.G. and
Tang, C.-S. 1969. Photodecomposition of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 17(6), 1291-1293.
Jacobs, L.E.,
Fimmen, R.L., Chin, Y.-P., Mash, H.E. and Weavers, L.K. 2011. Fulvic acid
mediated photolysis of ibuprofen in water. Water Res. 45(15), 4449-4458.
Koumaki, E.,
Mamais, D., Noutsopoulos, C., Nika, M.-C., Bletsou, A.A., Thomaidis, N.S.,
Eftaxias, A. and Stratogianni, G. 2015. Degradation of emerging contaminants
from water under natural sunlight: The effect of season, ph, humic acids and
nitrate and identification of photodegradation by-products. Chemosphere 138,
675-681.
Ware, G.W., Crosby, D.G. and Giles, J.W. 1980.
Photodecomposition of dda. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9(2), 135-146.
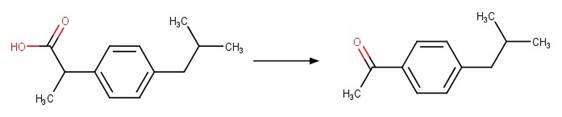
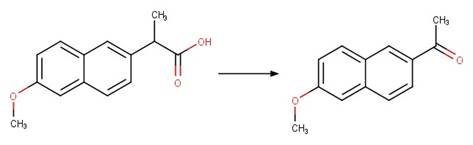
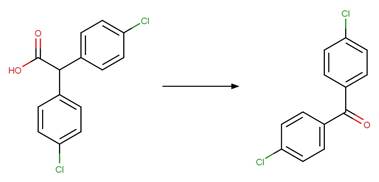
Scheme:
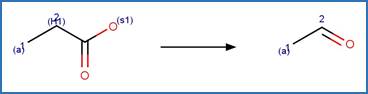
Examples:
Ibuprofen (Jacobs et al. 2011)
Naproxen (Packer et al. 2003)
Ketoprofen (Kotnik et al. 2016)
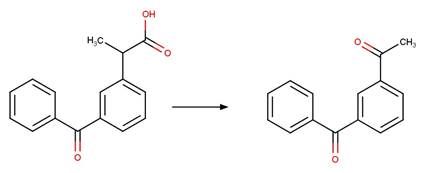
Diclofenac (Agüera et al. 2005)
1-naphthaleneacetic
acid (Crosby and Tang 1969) (EFSA)
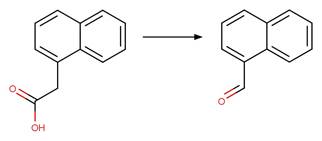
2,2'-bis(4-chlorophenyl)acetic
acid (Ware et al. 1980)
References:
Agüera, A., Pérez
Estrada, L.A., Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Malato, S. and Fernández-Alba, A.R.
2005. Application of time-of-flight mass spectrometry to the analysis of
phototransformation products of diclofenac in water under natural sunlight. J.
Mass Spectrom. 40(7), 908-915.
Crosby, D.G. and
Tang, C.-S. 1969. Photodecomposition of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 17(6), 1291-1293.
Jacobs, L.E.,
Fimmen, R.L., Chin, Y.-P., Mash, H.E. and Weavers, L.K. 2011. Fulvic acid
mediated photolysis of ibuprofen in water. Water Res. 45(15), 4449-4458.
Kotnik, K.,
Kosjek, T., Žegura, B., Filipič, M. and Heath, E. 2016. Photolytic fate
and genotoxicity of benzophenone-derived compounds and their photodegradation
mixtures in the aqueous environment. Chemosphere 147, 114-123.
Packer, J.L.,
Werner, J.J., Latch, D.E., McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2003. Photochemical
fate of pharmaceuticals in the environment: Naproxen, diclofenac, clofibric
acid, and ibuprofen. Aquat. Sci. 65(4), 342-351.
Ware, G.W., Crosby, D.G. and Giles, J.W. 1980.
Photodecomposition of dda. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9(2), 135-146.
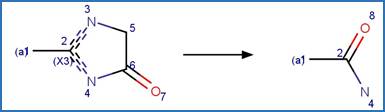
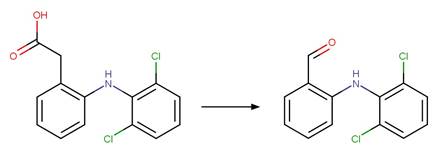
Scheme:
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not connected to an
imidazolinone functional group through an aromatic bond.
Examples:
flutolanil
photo-product (o-phthalic acid) (Lam et al. 2005)
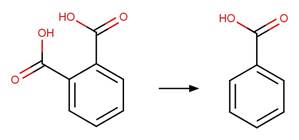
flutolanil
photo-product (2‐trifluoromethylbenzoic acid) (Lam et al. 2005)

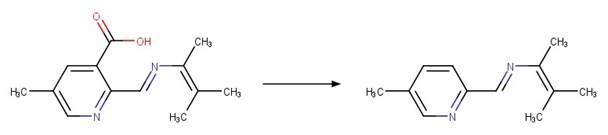
Imazapic photo-product
(Christiansen et al. 2015)
Imazaquin photo-product
1 (Christiansen et al. 2015)
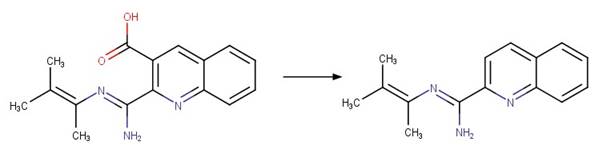
Imazaquin photo-product
2 (Barkani et al. 2005)
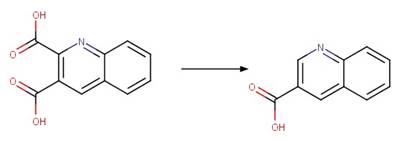
Imazapyr photo-product
(Quivet et al. 2004)
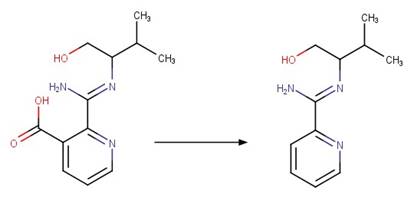
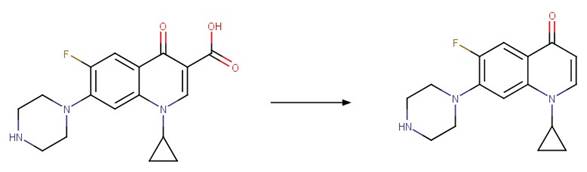
Ciprofloxacin (Ge et al. 2010)
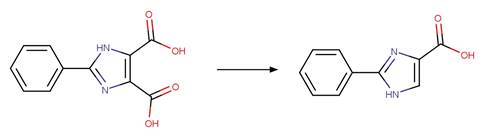
2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic
acid photo-product (Zhang et al. 2010)
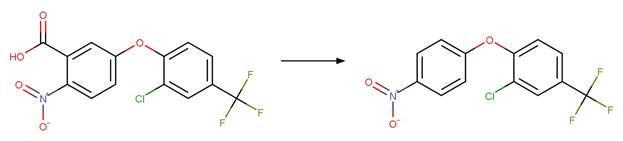
Acifluorfen (Vialaton and Richard 2002)
quinmerac (Pinna and Pusino 2012)
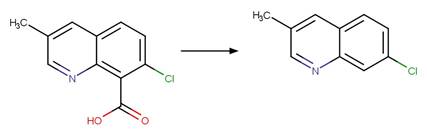
References:
Barkani, H.,
Catastini, C., Emmelin, C., Sarakha, M., El Azzouzi, M. and Chovelon, J.M.
2005. Study of the phototransformation of imazaquin in aqueous solution: A
kinetic approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 170(1), 27-35.
Christiansen, A.,
Peterson, A., Anderson, S.C., Lass, R., Johnson, M. and Nienow, A.M. 2015.
Analysis of the photodegradation of the imidazolinone herbicides imazamox,
imazapic, imazaquin, and imazamethabenz-methyl in aqueous solution. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 63(50), 10768-10777.
Ge, L., Chen, J.,
Wei, X., Zhang, S., Qiao, X., Cai, X. and Xie, Q. 2010. Aquatic photochemistry
of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of
main water constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(7), 2400-2405.
Lam, M.W., Young,
C.J. and Mabury, S.A. 2005. Aqueous photochemical reaction kinetics and
transformations of fluoxetine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(2), 513-522.
Pinna, M.V. and
Pusino, A. 2012. Direct and indirect photolysis of two quinolinecarboxylic
herbicides in aqueous systems. Chemosphere 86(6), 655-658.
Quivet, E., Faure,
R., Georges, J., Païssé, J.O. and Herbreteau, B. 2004. Kinetic studies of
imazapyr photolysis and characterization of the main photoproducts. Toxicol.
Environ. Chem. 86(4), 197-206.
Vialaton, D. and
Richard, C. 2002. Phototransformation of aromatic pollutants in solar light:
Photolysis versus photosensitized reactions under natural water conditions.
Aquat. Sci. 64(2), 207-215.
Zhang, S., Chen, J., Qiao, X., Ge, L., Cai, X. and Na, G.
2010. Quantum chemical investigation and experimental verification on the
aquatic photochemistry of the sunscreen 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(19), 7484-7490.
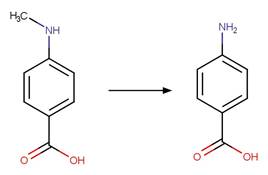
Scheme:
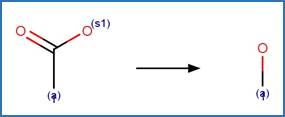
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not connected to an
imidazolinone functional group through an aromatic bond.
Examples:
Gentisic acid (McConville et al. 2016)
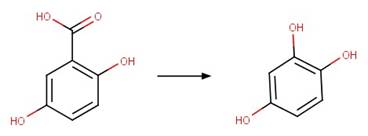
Imazaquin
photo-product (Christiansen et al. 2015)
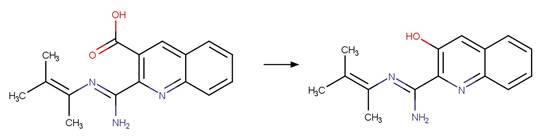
4-aminobenzoic
acid (Shaw et al. 1992)
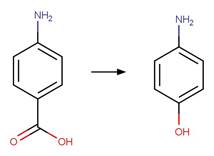
References:
Christiansen, A.,
Peterson, A., Anderson, S.C., Lass, R., Johnson, M. and Nienow, A.M. 2015.
Analysis of the photodegradation of the imidazolinone herbicides imazamox,
imazapic, imazaquin, and imazamethabenz-methyl in aqueous solution. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 63(50), 10768-10777.
McConville, M.B.,
Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016. Direct photolysis rates and transformation
pathways of the lampricides tfm and niclosamide in simulated sunlight. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Shaw, A.A., Wainschel, L.A. and Shetlar, M.D. 1992. The
photochemistry of p-aminobenzoic acid. Photochem. Photobiol. 55(5), 647-656.
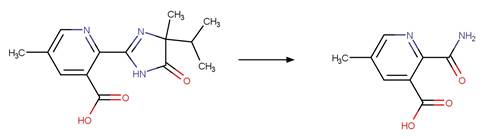
Scheme:

Examples:
Cyphenothrin (Suzuki et al. 2017)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
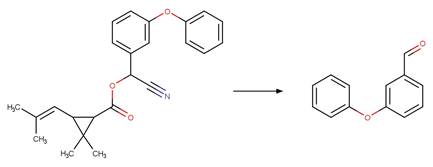
References:
Suzuki, Y., Yoshida, M., Sugano, T., Shibata, A., Kodaka, R.,
Fujisawa, T. and Katagi, T. 2017. Behavior of cyphenothrin in aquatic
environment. J. Pestic. Sci. 42(2), 17-24.
Scheme:
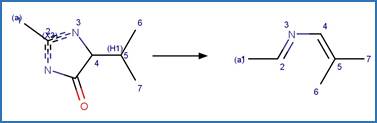
Examples:
Imazapic (Harir et al. 2007b)
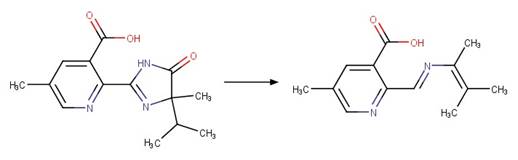
Imazamox (Harir et al. 2007a)
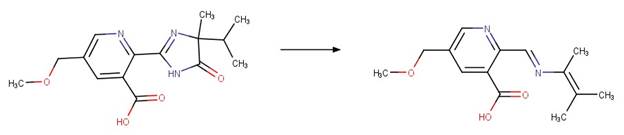
References:
Harir, M.,
Frommberger, M., Gaspar, A., Martens, D., Kettrup, A., El Azzouzi, M. and
Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007a. Characterization of imazamox degradation by-products
by using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and high-resolution fourier
transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.
389(5), 1459-1467.
Harir, M., Gaspar, A., Frommberger, M., Lucio, M., Azzouzi,
M.E., Martens, D., Kettrup, A. and Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2007b. Photolysis
pathway of imazapic in aqueous solution: Ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry
analysis of intermediates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55(24), 9936-9943.
Scheme:
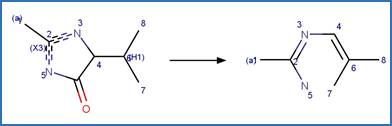
Examples:
Imazamox (Christiansen et al. 2015)

Imazapic (Christiansen et al. 2015)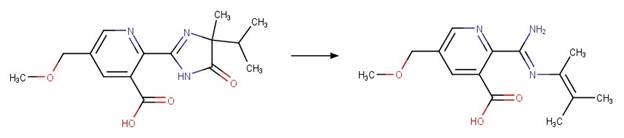
Imazaquin (Christiansen et al. 2015)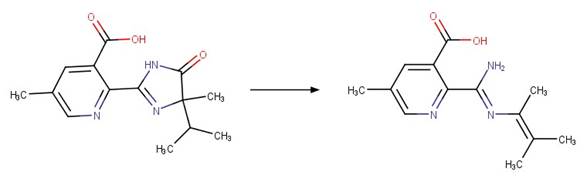
References:
Christiansen, A., Peterson, A., Anderson, S.C., Lass, R.,
Johnson, M. and Nienow, A.M. 2015. Analysis of the photodegradation of the imidazolinone
herbicides imazamox, imazapic, imazaquin, and imazamethabenz-methyl in aqueous
solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(50), 10768-10777.
Scheme:
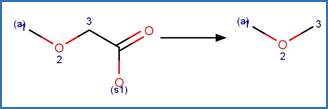
Examples:
Bezafibrate (Cermola et al. 2005)
fenofibric acid
(Cermola et al. 2005)
References:
Cermola, M., DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Previtera, L., Rubino,
M., Temussi, F. and Brigante, M. 2005. Phototransformation of fibrate drugs in
aqueous media. Environ. Chem. Lett. 3(1), 43-47.
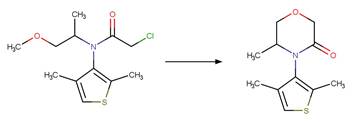
Scheme:
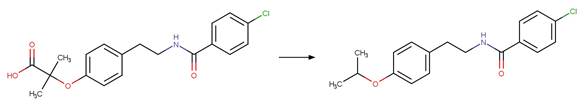
Examples:
Benoxacor
photo-product (Kral et al. 2019)
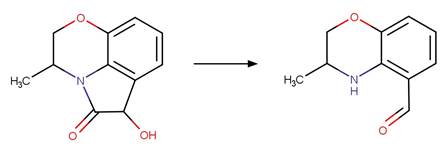
References:
Kral, A.E., Pflug, N.C., McFadden, M.E., LeFevre, G.H., Sivey,
J.D. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2019. Photochemical transformations of
dichloroacetamide safeners. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53(12), 6738-6746.
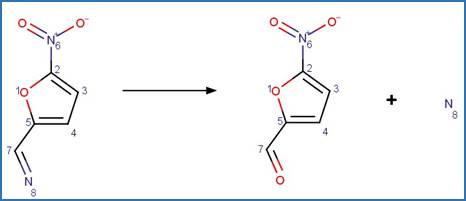
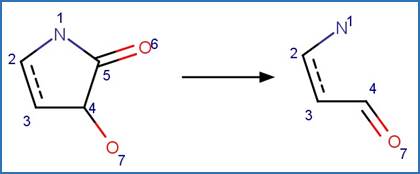
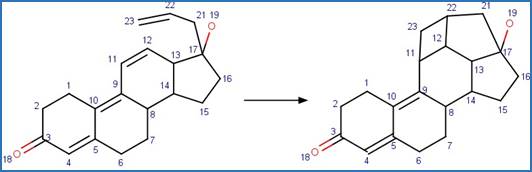
Scheme:
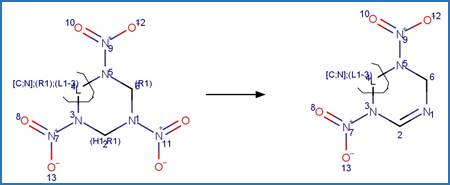
Examples:
hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine
(RDX) (Hawari et al. 2002)
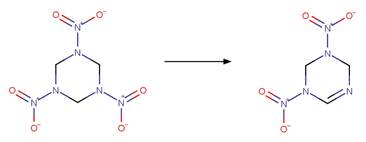
References:
Hawari, J., Halasz, A., Groom, C., Deschamps, S., Paquet, L.,
Beaulieu, C. and Corriveau, A. 2002. Photodegradation of rdx in aqueous
solution: A mechanistic probe for biodegradation with rhodococcus sp.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(23), 5117-5123.
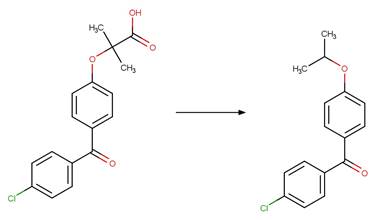
Scheme:
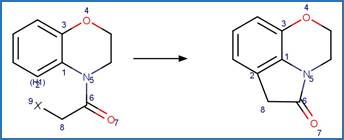
Examples:
Benoxacor (Kral et al. 2019)
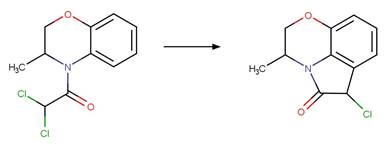
References:
Kral, A.E., Pflug, N.C., McFadden, M.E., LeFevre, G.H., Sivey,
J.D. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2019. Photochemical transformations of
dichloroacetamide safeners. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53(12), 6738-6746.
Scheme:
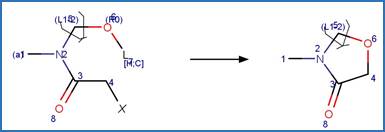
Examples:
Metolachlor (Dimou et al. 2005)

Alachlor (Chiron et al. 1995)

Dimethenamid (EFSA)
References:
Chiron, S.,
Barceló, D., Abian, J., Ferrer, M., Sanchez-Baeza, F. and Messeguer, A. 1995.
Comparative photodegradation rates of alachlor and bentazone in natural water
and determination of breakdown products. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14(8),
1287-1298.
Dimou, A.D., Sakkas, V.A. and Albanis, T.A. 2005.
Metolachlor photodegradation study in aqueous media under natural and simulated
solar irradiation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(3), 694-701.
Scheme:
Examples:
Altrenogest (Wammer et al. 2016)
References:
Wammer, K.H., Anderson, K.C., Erickson, P.R., Kliegman, S.,
Moffatt, M.E., Berg, S.M., Heitzman, J.A., Pflug, N.C., McNeill, K.,
Martinovic-Weigelt, D., Abagyan, R., Cwiertny, D.M. and Kolodziej, E.P. 2016.
Environmental photochemistry of altrenogest: Photoisomerization to a bioactive
product with increased environmental persistence via reversible photohydration.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(14), 7480-7488.
Scheme:
Examples:
Chlorantraniliprole
(Sharma et al. 2014) (EFSA)

Cyantraniliprole
(Sharma et al. 2014) (EFSA)

References:
Sharma, A.K., Zimmerman, W.T., Singles, S.K., Malekani, K.,
Swain, S., Ryan, D., McQuorcodale, G. and Wardrope, L. 2014. Photolysis of
chlorantraniliprole and cyantraniliprole in water and soil: Verification of
degradation pathways via kinetics modeling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(28),
6577-6584.
Scheme:

Examples:
Benzobicyclon
hydrolysate (Williams et al. 2018)
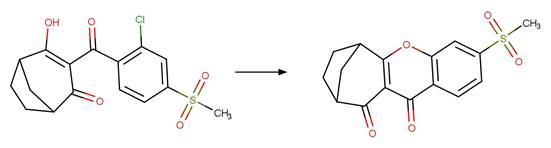
Sulcotrione (ter Halle et al. 2008)
References:
ter Halle, A.,
Wiszniowski, J., Hitmi, A., Ledoigt, G., Bonnemoy, F., Bonnet, J.L., Bohatier,
J. and Richard, C. 2008. Photolysis of the herbicide sulcotrione: Formation of
a major photoproduct and its toxicity evaluation. Pest Manage. Sci. 65(1),
14-18.
Williams, K.L., Kaur, R., McFall, A.S., Kalbfleisch, J.,
Gladfelder, J.J., Ball, D.B., Anastasio, C. and Tjeerdema, R.S. 2018. Aqueous
photolysis of benzobicyclon hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66(22),
5462-5472.
Scheme:

A reactivity
rule is included to ensure that no unreasonably fused products are formed by
specifying that the shortest pathway between product atom 7 and 8 is 5 bonds.
Examples:
Tamoxifen (DellaGreca et al. 2007)
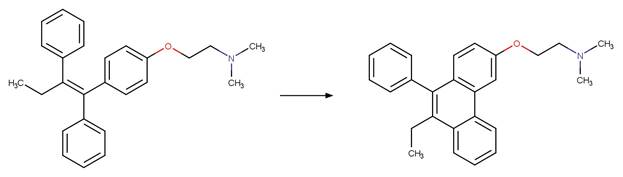
Atorvastatin
photo-product (Cermola et al. 2006)
References:
Cermola, F.,
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Montanaro, S., Previtera, L. and Temussi, F. 2006.
Photochemical behavior of the drug atorvastatin in water. Tetrahedron 62(31),
7390-7395.
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Isidori, M., Nardelli, A.,
Previtera, L. and Rubino, M. 2007. Phototransformation products of tamoxifen by
sunlight in water. Toxicity of the drug and its derivatives on aquatic
organisms. Chemosphere 67(10), 1933-1939.
Scheme:
A reactivity
rule is included to ensure that no unreasonably fused products are formed by
specifying that the shortest pathway between product atom 7 and 8 is 5 bonds.
Examples:
Diethylstilbestrol
(Xu et al. 2017)
Tamoxifen (DellaGreca et al. 2007)
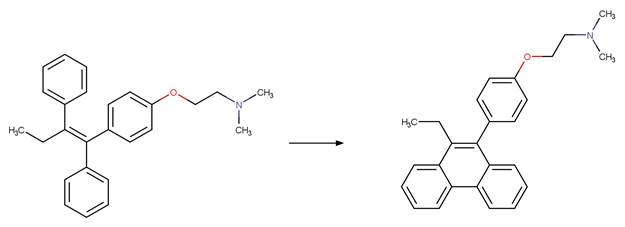
References:
DellaGreca, M.,
Iesce, M.R., Isidori, M., Nardelli, A., Previtera, L. and Rubino, M. 2007.
Phototransformation products of tamoxifen by sunlight in water. Toxicity of the
drug and its derivatives on aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 67(10), 1933-1939.
Xu, B., Li, K., Qiao, J., Liungai, Z., Chen, C. and Lu, Y.
2017. Uv photoconversion of environmental oestrogen diethylstilbestrol and its
persistence in surface water under sunlight. Water Res. 127, 77-85.
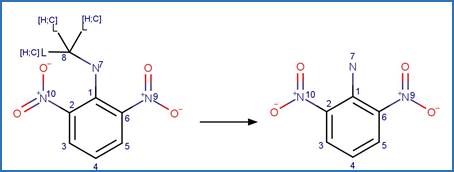
Scheme:
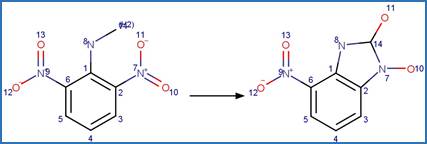
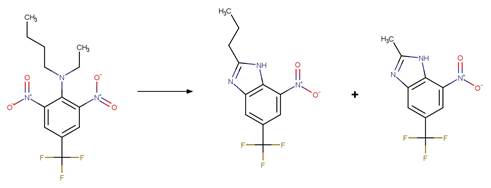
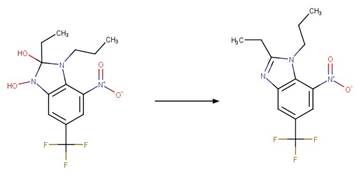
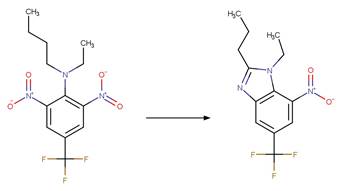
Scheme:
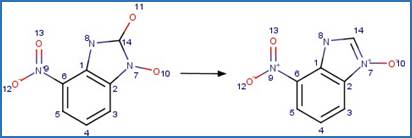
Scheme:
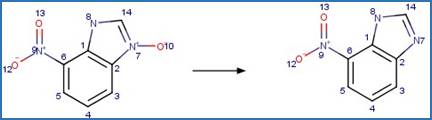
Because of a
software bug in Metabolizer, a direct cyclization reaction cannot be performed
on dinitroaniline compounds. Therefore, three sequential/consecutive reaction
schemes were created to perform the overall cyclization reaction. The following
examples are for any of the three schemes or their combinations.
Examples:
Trifluralin (Leitis and Crosby 1974, Tagle
et al. 2005)
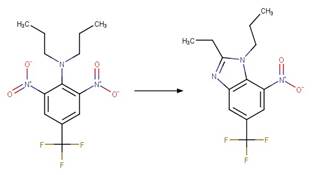
Trifluralin (Leitis and Crosby 1974)
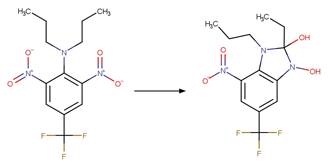
2-ethyl-4-nitro-3-propyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3-benzodiazole-1,2-diol
(Leitis and Crosby 1974)
Trifluralin photo-product
(Tagle et al. 2005)

Benfluralin
(EFSA)
Benfluralin
(EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.

Ethalfluraline
(EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
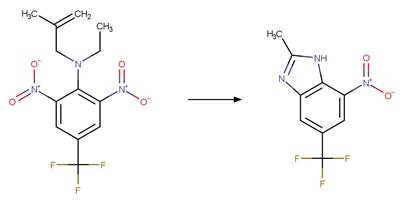
Ethalfluraline
(EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
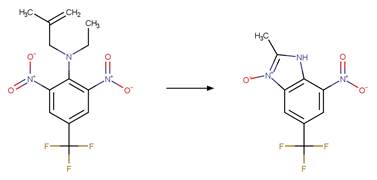
Flumetralin
(EFSA)
The products are
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
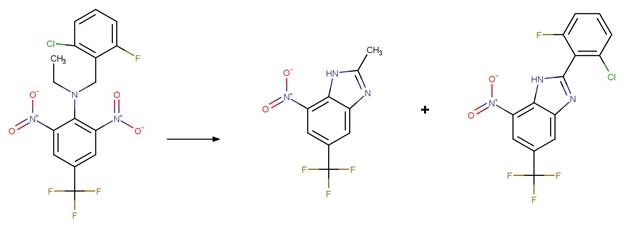
Oryzalin (EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.

References:
Leitis, E. and
Crosby, D.G. 1974. Photodecomposition of trifluralin. J. Agric. Food Chem.
22(5), 842-848.
Tagle, M.G.S., Laura Salum, M., Bujan, E.I. and Arguello,
G.A. 2005. Time evolution and competing pathways in photodegradation of
trifluralin and three of its major degradation products. Photochemical &
Photobiological Sciences 4(11), 869-875.
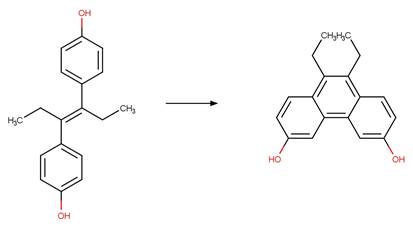
Scheme:
A reactivity
rule is included to ensure that no unreasonably fused products are formed by
specifying that the shortest path between product atom 8 and 9 is 3 bonds.
Examples:
Fluvastatin (Jarmużek et al. 2017)

Rosuvastatin (Astarita et al. 2007)
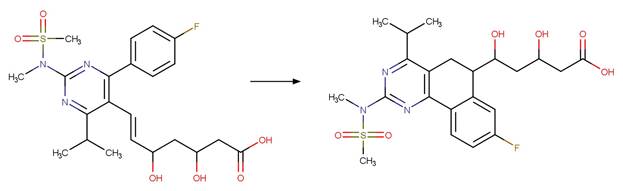
References:
Astarita, A.,
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Montanaro, S., Previtera, L. and Temussi, F. 2007.
Polycyclic compounds by sunlight exposure of the drug rosuvastatin in water. J.
Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 187(2), 263-268.
Jarmużek, D., Pedzinski, T., Hoffmann, M., Siodła,
T., Salus, K. and Pluskota-Karwatka, D. 2017. Experimental and theoretical
studies on fluvastatin primary photoproduct formation. PCCP 19(33),
21946-21954.
Scheme:

A reactivity
rule is included to ensure that no unreasonably fused products are formed by
specifying that the shortest pathway between product atom 3 and 12 is 4 bonds.
Examples:
Triclosan (Latch et al. 2003)
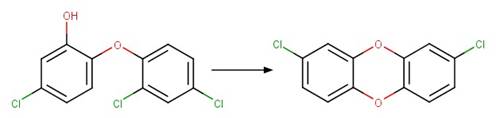
6-OH-PBDE 99 (Erickson et al. 2012)
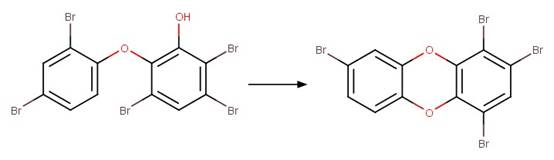
6-Cl-triclosan (Buth et al. 2009)
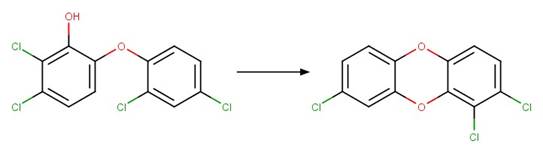
3-Cl-6-OH PBDE
47 (Steen et al. 2009)
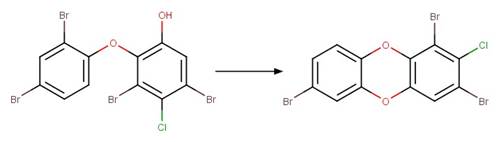
2’-HO PBDE 28 (Zhang et al. 2016)

References:
Buth, J.M.,
Grandbois, M., Vikesland, P.J., McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2009. Aquatic
photochemistry of chlorinated triclosan derivatives: Potential source of polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28(12), 2555-2563.
Erickson, P.R.,
Grandbois, M., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2012. Photochemical formation of
brominated dioxins and other products of concern from hydroxylated
polybrominated diphenyl ethers (oh-pbdes). Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(15),
8174-8180.
Latch, D.E.,
Packer, J.L., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2003. Photochemical conversion of
triclosan to 2,8-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aqueous solution. J. Photochem.
Photobiol. A: Chem. 158(1), 63-66.
Steen, P.O.,
Grandbois, M., McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2009. Photochemical formation of
halogenated dioxins from hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers (oh-pbdes)
and chlorinated derivatives (oh-pbcdes). Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(12), 4405-4411.
Zhang, Y.-n., Xie, Q., Sun, G., Yang, K., Song, S., Chen,
J., Zhou, C. and Li, Y. 2016. Effects of dissolved organic matter on
phototransformation rates and dioxin products of triclosan and 2′-ho-bde-28 in estuarine water.
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 18(9), 1177-1184.
Scheme:

Examples:
Carbamazepine (De Laurentiis et al. 2012)
Desipramine
photo-product (Gros et al. 2015)
References:
De Laurentiis,
E., Chiron, S., Kouras-Hadef, S., Richard, C., Minella, M., Maurino, V.,
Minero, C. and Vione, D. 2012. Photochemical fate of carbamazepine in surface
freshwaters: Laboratory measures and modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(15),
8164-8173.
Gros, M., Williams, M., Llorca, M., Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.,
Barceló, D. and Kookana, R.S. 2015. Photolysis of the antidepressants
amisulpride and desipramine in wastewaters: Identification of transformation
products formed and their fate. Sci. Total Environ. 530-531, 434-444.
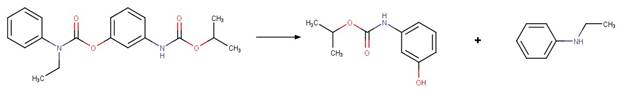
Scheme:
A reactivity
rule is included to ensure that at least one of the reactant atom 1 and 4 is
aromatic.
Examples:
Phenisopham (Passananti et al. 2014)
Pirimicarb (Pirisi et al. 1996) (EFSA)
Carbaryl (Brahmia and Richard 2003)
Diethofencarb
(EFSA)

References:
Brahmia, O. and
Richard, C. 2003. Phototransformation of carbaryl in aqueous solution:
Laser-flash photolysis and steady-state studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A:
Chem. 156(1), 9-14.
Passananti, M.,
Lavorgna, M., Iesce, M.R., DellaGreca, M., Criscuolo, E., Parrella, A.,
Isidori, M. and Temussi, F. 2014. Chlorpropham and phenisopham:
Phototransformation and ecotoxicity of carbamates in the aquatic environment.
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 16(4), 823-831.
Pirisi, F.M., Cabras, P., Garau, V.L., Melis, M. and Secchi,
E. 1996. Photodegradation of pesticides. Photolysis rates and half-life of
pirimicarb and its metabolites in reactions in water and in solid phase. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 44(8), 2417-2422.
Scheme:
A reactivity
rule is included to specify that reactant atom 3 is a chain atom. An exclusion
rule is included to exclude the carboxylic acid ester functional group by
specifying that reactant atom 2 is not a carbonyl carbon.
Examples:
Fluoxetine (Lam et al. 2005)
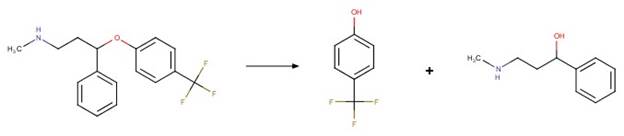
Oxyfluorfen (Ying and Williams 1999)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.

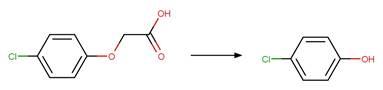
4-chlorophenoxyacetic
acid (Crosby and Wong 1973)
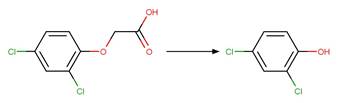
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic
acid (Crosby and Tutass 1966)
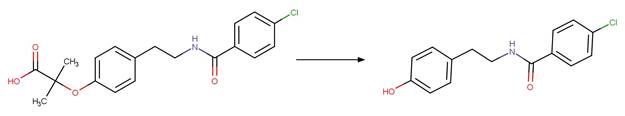
Bezafibrate (Cermola et al. 2005)
2,4-dinitroanisole
(Halasz et al. 2018)
Mecoprop (Meunier and Boule 2000)
Triasulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
Penoxsulam
photo-product (Jabusch and Tjeerdema 2006)

Napropamide (Aguer et al. 1998)
fenoxaprop-p-ethyl
(EFSA)
pyriproxyfen
(EFSA)
Fenazaquin (EFSA)

References:
Aguer, J.P.,
Boule, P., Bonnemoy, F. and Chezal, J.M. 1998. Phototransformation of
napropamide [n,n-diethyl-2-(1-naphthyloxy)propionamide] in aqueous solution:
Influence on the toxicity of solutions. Pestic. Sci. 54(3), 253-257.
Cermola, M.,
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Previtera, L., Rubino, M., Temussi, F. and Brigante,
M. 2005. Phototransformation of fibrate drugs in aqueous media. Environ. Chem.
Lett. 3(1), 43-47.
Crosby, D.G. and
Tutass, H.O. 1966. Photodecomposition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 14(6), 596-599.
Crosby, D.G. and
Wong, A.S. 1973. Photodecomposition of p-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 21(6), 1049-1052.
Halasz, A.,
Hawari, J. and Perreault, N.N. 2018. New insights into the photochemical
degradation of the insensitive munition formulation imx-101 in water. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 52(2), 589-596.
Jabusch, T.W. and
Tjeerdema, R.S. 2006. Photodegradation of penoxsulam. J. Agric. Food Chem.
54(16), 5958-5961.
Lam, M.W., Young,
C.J. and Mabury, S.A. 2005. Aqueous photochemical reaction kinetics and
transformations of fluoxetine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(2), 513-522.
Meunier, L. and
Boule, P. 2000. Direct and induced phototransformation of mecoprop [2‐(4‐chloro‐2‐methylphenoxy)propionic
acid] in aqueous solution. Pest Manage. Sci. 56(12), 1077-1085.
Vulliet, E., Emmelin,
C., Grenier-Loustallot, M.F., Païssé, O. and Chovelon, J.M. 2002. Simulated
sunlight-induced photodegradations of triasulfuron and cinosulfuron in aqueous
solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(5), 1081-1088.
Ying, G.G. and Williams, B. 1999. The degradation of
oxadiazon and oxyfluorfen by photolysis. Journal of Environmental Science and
Health, Part B 34(4), 549-567.
Scheme:

An exclusion
rule is added to differentiate this scheme from “Fluoroquinolone Fluoride Photohydrolysis”
by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not part of a quinolone functional group.
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not connected to a
benzoylphenylurea functional group.
Examples:
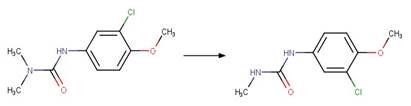
Chlorpropham (Passananti et al. 2014)
Niclosamide
photo-product (McConville et al. 2016)

Niclosamide
photo-product (McConville et al. 2016)
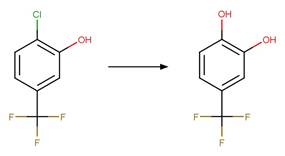
2-chloro-5-trifluoromethylphenol
(Young et al. 2008)
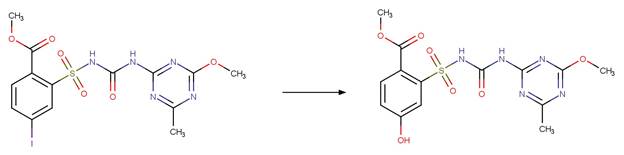
iodosulfuron-methyl
(Brigante et al. 2005)
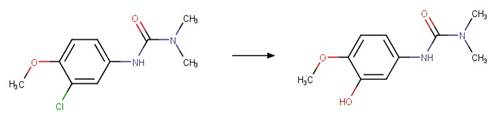
Metoxuron (Boulkamh et al. 2001)
Diuron (Jirkovský et al. 1997)
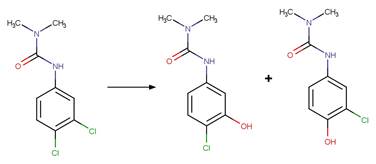
Linuron (Rosen et al. 1969)
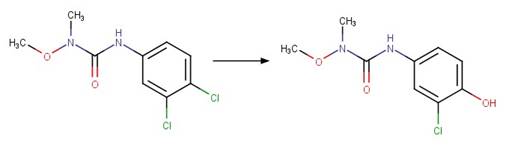
Monuron (Rosen et al. 1969)
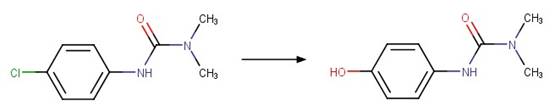
Metobromuron (Rosen and Strusz 1968)
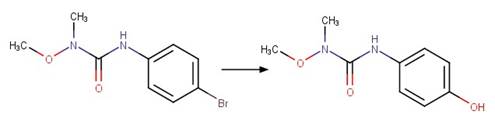
Atrazine (Torrents et al. 1997)
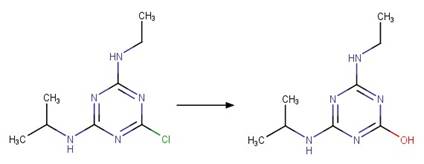
Des-ethyl
atrazine (Torrents et al. 1997)
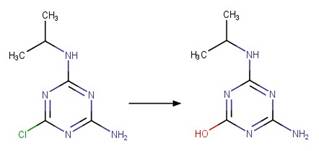
Chlorpropham (Guzik 1978)
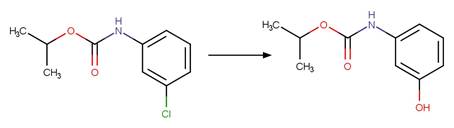
Terbuthylazine
(EFSA)
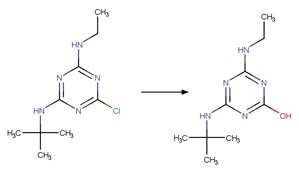
6-chlorobenzoxazolon
(a metabolite of fenoxaprop-p-ethyl) (EFSA report on fenoxaprop-p-ethyl)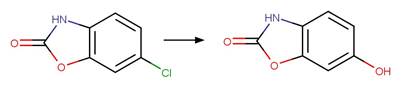
Bromoxynil (Machado et al. 1995)
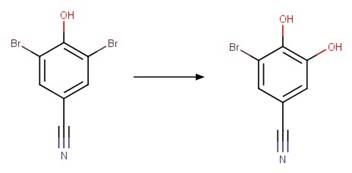
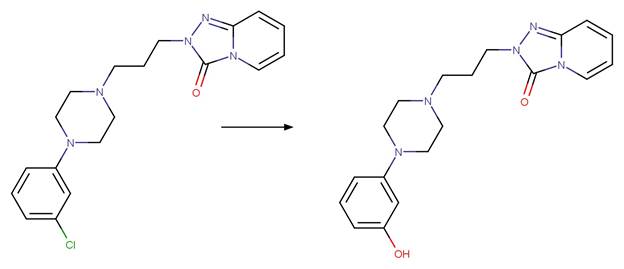
Trazodone (DellaGreca et al. 2008)
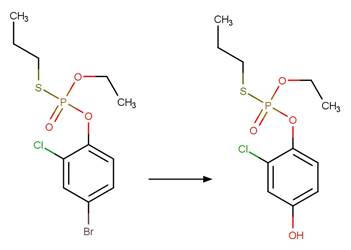
Profenofos (Zamy et al. 2004)
Diclofenac
photo-product (Eriksson et al. 2010)
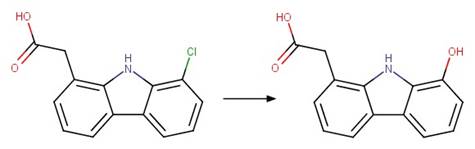
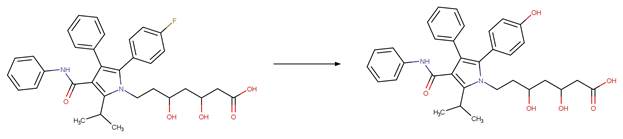
Sarafloxacin (Ge et al. 2010)
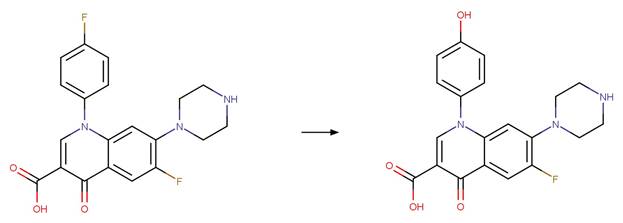
Atorvastatin (Lam and Mabury 2005)
References:
Boulkamh, A.,
Harakat, D., Sehili, T. and Boule, P. 2001. Phototransformation of metoxuron
[3-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea] in aqueous solution. Pest
Manage. Sci. 57(12), 1119-1126.
Brigante, M.,
Emmelin, C., Previtera, L., Baudot, R. and Chovelon, J.M. 2005. Abiotic
degradation of iodosulfuron-methyl-ester in aqueous solution. J. Agric. Food
Chem. 53(13), 5347-5352.
DellaGreca, M.,
Iesce, M.R., Previtera, L., Rubino, M., Barone, V. and Crescenzi, O. 2008.
Phototransformation of the drug trazodone in aqueous solution. J. Photochem.
Photobiol. A: Chem. 199(2), 353-357.
Eriksson, J.,
Svanfelt, J. and Kronberg, L. 2010. A photochemical study of diclofenac and its
major transformation products. Photochem. Photobiol. 86(3), 528-532.
Ge, L., Chen, J.,
Wei, X., Zhang, S., Qiao, X., Cai, X. and Xie, Q. 2010. Aquatic photochemistry
of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of
main water constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(7), 2400-2405.
Guzik, F.F. 1978.
Photolysis of isopropyl 3-chlorocarbanilate in water. J. Agric. Food Chem.
26(1), 53-55.
Jirkovský, J.,
Faure, V. and Boule, P. 1997. Photolysis of diuron. Pestic. Sci. 50(1), 42-52.
Lam, M.W. and
Mabury, S.A. 2005. Photodegradation of the pharmaceuticals atorvastatin,
carbamazepine, levofloxacin, and sulfamethoxazole in natural waters. Aquat.
Sci. 67(2), 177-188.
Machado, F.,
Collin, L. and Boule, P. 1995. Photolysis of bromoxynil
(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) in aqueous solution. Pestic. Sci. 45(2),
107-110.
McConville,
M.B., Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016. Direct photolysis rates and
transformation pathways of the lampricides tfm and niclosamide in simulated
sunlight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Passananti, M.,
Lavorgna, M., Iesce, M.R., DellaGreca, M., Criscuolo, E., Parrella, A.,
Isidori, M. and Temussi, F. 2014. Chlorpropham and phenisopham:
Phototransformation and ecotoxicity of carbamates in the aquatic environment.
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 16(4), 823-831.
Rosen, J.D. and
Strusz, R.F. 1968. Photolysis of 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 16(4), 568-570.
Rosen, J.D.,
Strusz, R.F. and Still, C.C. 1969. Photolysis of phenylurea herbicides. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 17(2), 206-207.
Torrents, A.,
Anderson, B.G., Bilboulian, S., Johnson, W.E. and Hapeman, C.J. 1997. Atrazine
photolysis: Mechanistic investigations of direct and nitrate-mediated
hydroxy radical processes and the influence of dissolved organic carbon from
the chesapeake bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31(5), 1476-1482.
Young, C., J.,
Gómez Biagi, R., F., Hurley, M., D., Wallington, T., J. and Mabury, S., A.
2008. Paint solvent to food additive: An environmental route of dehalogenation
for 4‐chlorobenzotrifluoride.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27(11), 2233-2238.
Zamy, C., Mazellier, P. and Legube, B. 2004.
Phototransformation of selected organophosphorus pesticides in dilute aqueous
solutions. Water Res. 38(9), 2305-2314.
Scheme:

Two relative reasoning exclusion
rules are included by specifying (1) reactant atom 1 is not part of a
dinitroaniline functional group and (2) reactant atom 1 is not part of a
nitrofuran imine functional group.
Examples:
3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol
(McConville et al. 2016)

4-nitrocatechol
(McConville et al. 2016)
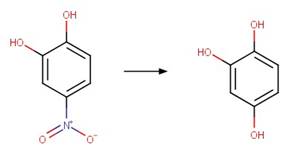
Oxyfluorfen (Ying and Williams 1999) (EFSA)
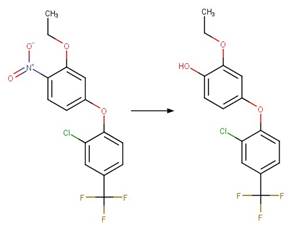
Parathion-methyl
(Araújo et al. 2013)
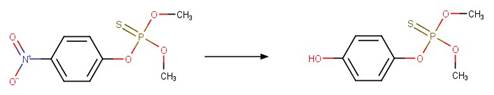
2,4-dinitroanisole
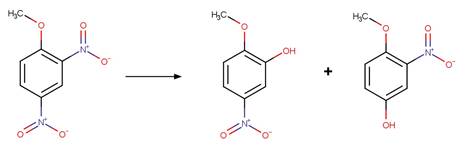
(Halasz et al. 2018)
2,4-dinitrophenol
(Hawari et al. 2015)
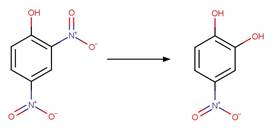
3‐nitro‐4,5‐dihydro‐1H‐1,2,4‐triazol‐5‐one
(NTO) (Halasz et al. 2018)
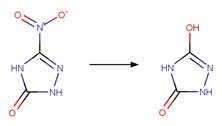
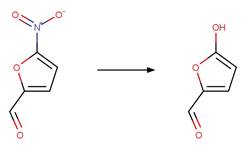
Nitrofuraldehyde
(Edhlund et al. 2006)
References:
Araújo, T.M.R.,
Canela, M.C. and Miranda, P.C.M.L. 2013. Photochemical nitro-nitrite
rearrangement in methyl parathion decay under tropical conditions. Journal of
Environmental Science and Health, Part B 48(4), 251-259.
Edhlund, B.L.,
Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2006. Aquatic photochemistry of nitrofuran
antibiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40(17), 5422-5427.
Halasz, A.,
Hawari, J. and Perreault, N.N. 2018. New insights into the photochemical
degradation of the insensitive munition formulation imx-101 in water. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 52(2), 589-596.
Hawari, J.,
Monteil-Rivera, F., Perreault, N.N., Halasz, A., Paquet, L., Radovic-Hrapovic,
Z., Deschamps, S., Thiboutot, S. and Ampleman, G. 2015. Environmental fate of 2,4-dinitroanisole
(dnan) and its reduced products. Chemosphere 119, 16-23.
McConville, M.B.,
Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016. Direct photolysis rates and transformation
pathways of the lampricides tfm and niclosamide in simulated sunlight. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Ying, G.G. and Williams, B. 1999. The degradation of
oxadiazon and oxyfluorfen by photolysis. Journal of Environmental Science and
Health, Part B 34(4), 549-567.
Scheme:

Examples:
5‐(dimethylsulfamoyl)‐2‐methylquinolin‐8‐yl
benzenesulfonate (Kageyama et al. 2009)
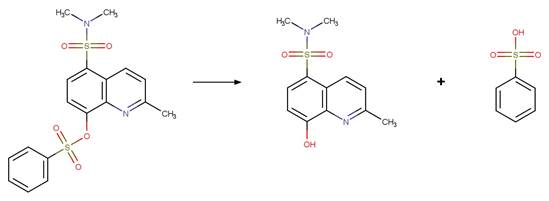
naphthalen‐1‐yl
benzenesulfonate (Kageyama et al. 2009)
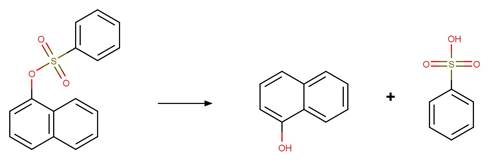
Bupirimate (EFSA)
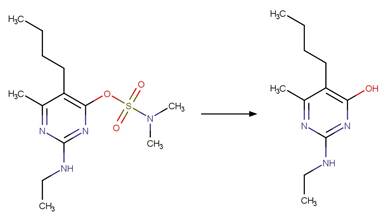
5-(dimethylsulfamoyl)-2-methylquinolin-8-yl
methanesulfonate (Kageyama et al. 2009)
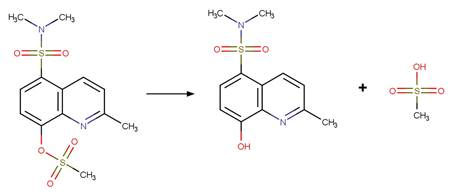
References:
Kageyama, Y., Ohshima, R., Sakurama, K., Fujiwara, Y., Tanimoto,
Y., Yamada, Y. and Aoki, S. 2009. Photochemical cleavage reactions of
8-quinolinyl sulfonates in aqueous solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 57(11),
1257-1266.
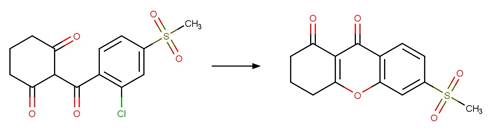
Scheme:
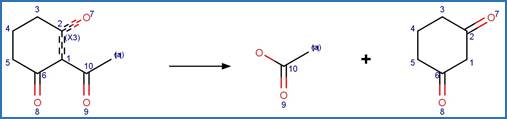
Examples:
Benzobicyclon
hydrolysate (Williams et al. 2018)

Sulcotrione (ter Halle et al. 2008) (EFSA)

Mesotrione (ter Halle and Richard 2006)
References:
ter Halle, A. and
Richard, C. 2006. Simulated solar light irradiation of mesotrione in natural
waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40(12), 3842-3847.
ter Halle, A.,
Wiszniowski, J., Hitmi, A., Ledoigt, G., Bonnemoy, F., Bonnet, J.L., Bohatier,
J. and Richard, C. 2008. Photolysis of the herbicide sulcotrione: Formation of
a major photoproduct and its toxicity evaluation. Pest Manage. Sci. 65(1),
14-18.
Williams, K.L., Kaur, R., McFall, A.S., Kalbfleisch, J.,
Gladfelder, J.J., Ball, D.B., Anastasio, C. and Tjeerdema, R.S. 2018. Aqueous
photolysis of benzobicyclon hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66(22),
5462-5472.
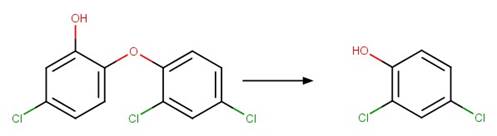
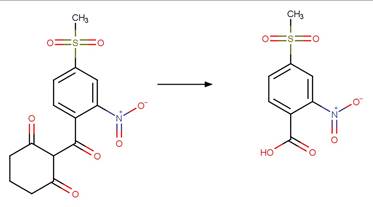
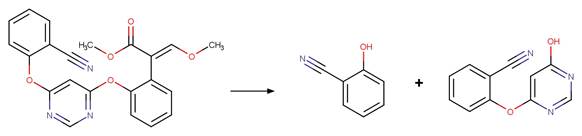
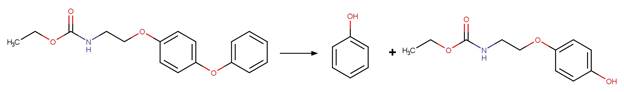
Scheme:

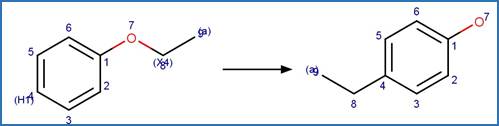
A reactivity is
included to specify that reactant atom 3 is not part of a ring. A selectivity
rule is included to avoid duplication of products for symmetric reactant by
specifying that reactant atom 1 needs to be the more sterically hindered atom
compared to atom 2. An exclusion rule is included to exclude reactants
susceptible to “Phenoxylphenol Ether Photocleavage” by specifying that reactant
atom 1 or 2 is not part of a phenoxyphenol functional group.
Examples:
Nitrofen (Nakagawa and Crosby 1974)
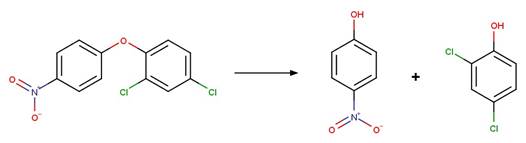
Acifluorfen (Vialaton et al. 2001)
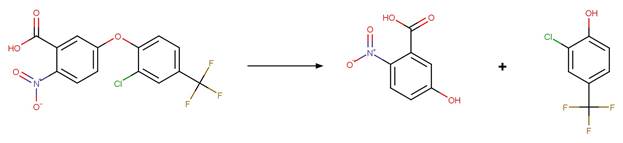
Permethrin
photo-product (3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol) (Holmstead et al. 1978)
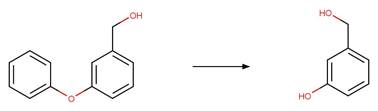
3-phenoxybenzoic
acid (Katagi 1992)
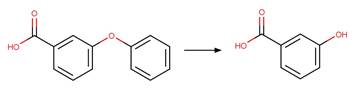
Flufenoxuron
(EFSA)
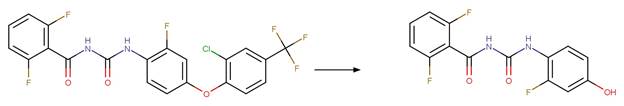
Azoxystrobin (Boudina et al. 2007)
Fenoxycarb
(EFSA)
Levothyroxine (Svanfelt et al. 2011)
Bifenox (EFSA)
haloxyfop-P
(EFSA)
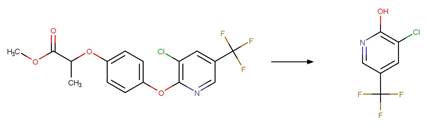
References:
Boudina, A.,
Emmelin, C., Baaliouamer, A., Païssé, O. and Chovelon, J.M. 2007. Photochemical
transformation of azoxystrobin in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 68(7),
1280-1288.
Holmstead, R.L.,
Casida, J.E., Ruzo, L.O. and Fullmer, D.G. 1978. Pyrethroid photodecomposition:
Permethrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26(3), 590-595.
Katagi, T. 1992.
Photodegradation of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid in water and on solid surfaces. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 40(7), 1269-1274.
Nakagawa, M. and
Crosby, D.G. 1974. Photodecomposition of nitrofen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 22(5),
849-853.
Svanfelt, J.,
Eriksson, J. and Kronberg, L. 2011. Photochemical transformation of the thyroid
hormone levothyroxine in aqueous solution. Environmental Science and Pollution
Research 18(6), 871-876.
Vialaton, D., Baglio, D., Paya-Perez, A. and Richard, C.
2001. Photochemical transformation of acifluorfen under laboratory and natural
conditions. Pest Manage. Sci. 57(4), 372-379.
Scheme:

Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude halogen substitution at reactant atom 8 and
(2) to exclude molecules with a lower electrophilicity at atom 6 than
norfloxacin. The electrophilicity of a specific unsaturated atom is calculated
using ChemAxon’s Huckel analysis plugin.
Examples:
Ciprofloxacin (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)

Enoxacin (Fasani et al. 1999)
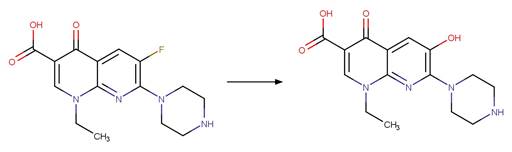
Lomefloxacin (Fasani et al. 1999)
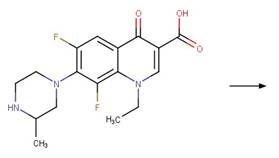
Flumequine (Sirtori et al. 2012)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
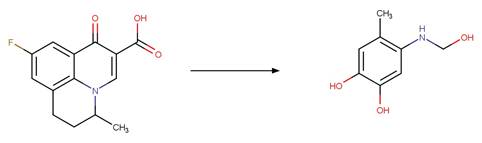
References:
Baena-Nogueras,
R.M., González-Mazo, E. and Lara-Martín, P.A. 2017. Photolysis of antibiotics
under simulated sunlight irradiation: Identification of photoproducts by
high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(6), 3148-3156.
Fasani, E.,
Barberis Negra, F.F., Mella, M., Monti, S. and Albini, A. 1999. Photoinduced
c−f bond cleavage in some fluorinated 7-amino-4-quinolone-3-carboxylic
acids. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 64(15), 5388-5395.
Sirtori, C., Zapata, A., Gernjak, W., Malato, S. and Agüera,
A. 2012. Photolysis of flumequine: Identification of the major
phototransformation products and toxicity measures. Chemosphere 88(5), 627-634.
Scheme:
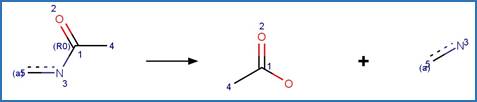
The bond
between atom 3 and 5 is single/aromatic.
Examples:
Niclosamide (McConville et al. 2016)
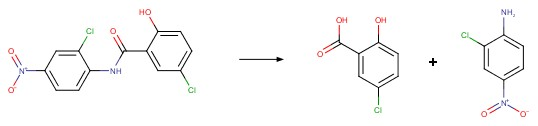
Flutolanil (Lam et al. 2005)

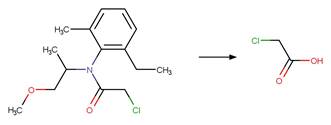
Metolachlor (Wilson and Mabury 2000)
Sedaxane (EFSA)

Isopyrazam (EFSA)

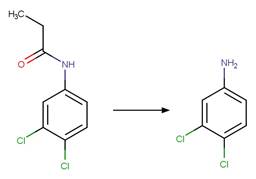
Propanil (Moilanen and Crosby 1972)
Indomethacin
photo-product (Temussi et al. 2011)
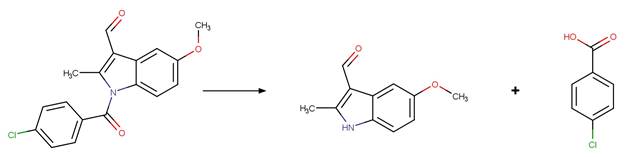
References:
Lam, M.W., Young,
C.J. and Mabury, S.A. 2005. Aqueous photochemical reaction kinetics and
transformations of fluoxetine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(2), 513-522.
McConville, M.B.,
Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016. Direct photolysis rates and transformation
pathways of the lampricides tfm and niclosamide in simulated sunlight. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Moilanen, K.W.
and Crosby, D.G. 1972. Photodecomposition of 3',4'-dichloropropionanilide
(propanil). J. Agric. Food Chem. 20(5), 950-953.
Temussi, F.,
Cermola, F., DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Passananti, M., Previtera, L. and
Zarrelli, A. 2011. Determination of photostability and photodegradation
products of indomethacin in aqueous media. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 56(4),
678-683.
Wilson, R.I. and Mabury, S.A. 2000. Photodegradation of
metolachlor: Isolation, identification, and quantification of
monochloroacetic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(3), 944-950.
Scheme:
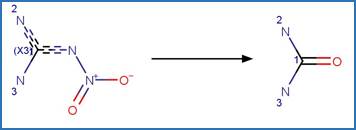
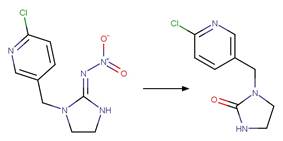
An exclusion
rule is included to exclude the exact chemical of nitroguanidine.
Examples:
Imidacloprid (Moza et al. 1998)
Thiamethoxam (Todey et al. 2018)
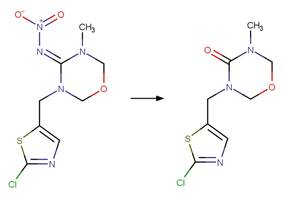
Clothianidin (Mulligan et al. 2015)
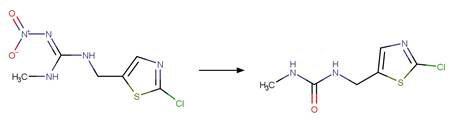
References:
Moza, P.N.,
Hustert, K., Feicht, E. and Kettrup, A. 1998. Photolysis of imidacloprid in
aqueous solution. Chemosphere 36(3), 497-502.
Mulligan, R.A.,
Redman, Z.C., Keener, M.R., Ball, D.B. and Tjeerdema, R.S. 2015.
Photodegradation of clothianidin under simulated california rice field
conditions. Pest Manage. Sci. 72(7), 1322-1327.
Todey, S.A., Fallon, A.M. and Arnold, W.A. 2018.
Neonicotinoid insecticide hydrolysis and photolysis: Rates and residual
toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 37(11), 2797-2809.
Scheme:
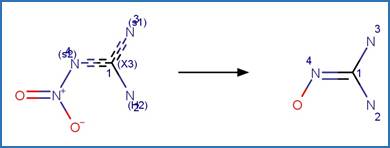
Examples:
Nitroguanidine (Haag et al. 1990)
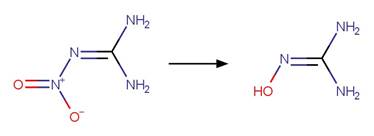
References:
Haag, W.R., Spanggord, R., Mill, T., Podoll, R.T., Chou, T.-W.,
Tse, D.S. and Harper, J.C. 1990. Aquatic environmental fate of nitroguanidine.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9(11), 1359-1367.
Rule
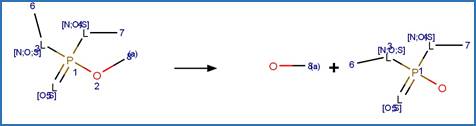
Examples:
Parathion-methyl
(Weber et al. 2009)
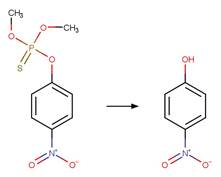
Fenitrothion (Weber et al. 2009)

Fenthion (Hirahara et al. 2003, Torrisi
and Sortino 2004)
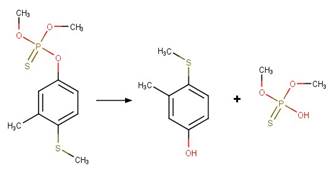
Butamifos (Katagi 1993)
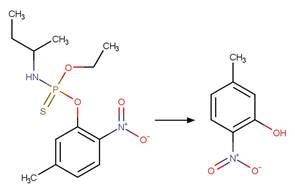
4-nitro
butamifos photo-product (Katagi 1993)

Isofenfos (Zamy et al. 2004)
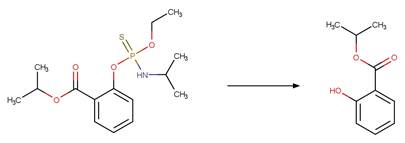
Profenofos (Zamy et al. 2004)
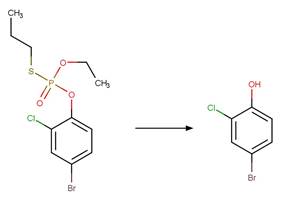
pirimiphos-methyl
(EFSA)
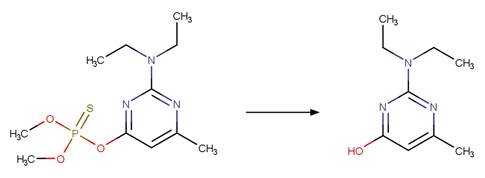
References:
Hirahara, Y.,
Ueno, H. and Nakamuro, K. 2003. Aqueous photodegradation of fenthion by
ultraviolet b irradiation: Contribution of singlet oxygen in photodegradation
and photochemical hydrolysis. Water Res. 37(2), 468-476.
Katagi, T. 1993.
Photochemistry of organophosphorus herbicide butamifos. J. Agric. Food Chem.
41(3), 496-501.
Torrisi, S. and
Sortino, S. 2004. New insights into the photoreactivity of the organophosphorus
pesticide fenthion: A σ aryl cation as a key intermediate in the
photodecomposition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52(19), 5943-5949.
Weber, J.,
Kurková, R., Klánová, J., Klán, P. and Halsall, C.J. 2009. Photolytic
degradation of methyl-parathion and fenitrothion in ice and water: Implications
for cold environments. Environ. Pollut. 157(12), 3308-3313.
Zamy, C., Mazellier, P. and Legube, B. 2004.
Phototransformation of selected organophosphorus pesticides in dilute aqueous
solutions. Water Res. 38(9), 2305-2314.
Scheme:

Examples:
Permethrin (Holmstead et al. 1978)
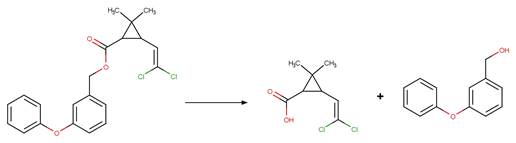
Metofluthrin (Nishiyama et al. 2010)
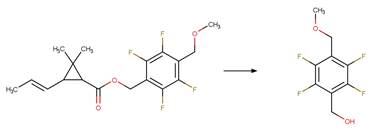
References:
Holmstead, R.L.,
Casida, J.E., Ruzo, L.O. and Fullmer, D.G. 1978. Pyrethroid photodecomposition:
Permethrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26(3), 590-595.
Nishiyama, M., Suzuki, Y. and Katagi, T. 2010. Hydrolysis
and photolysis of insecticide metofluthrin in water. J. Pestic. Sci. 35(4),
447-455.
Scheme:
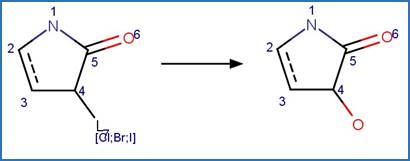
Examples:
Benoxacor
photo-product (Kral et al. 2019)
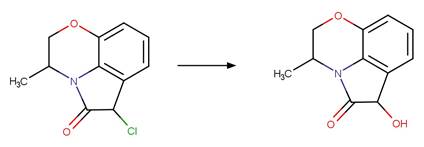
References:
Kral, A.E., Pflug, N.C., McFadden, M.E., LeFevre, G.H., Sivey,
J.D. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2019. Photochemical transformations of
dichloroacetamide safeners. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53(12), 6738-6746.
Scheme:

The bond
between atom 4 and 6 is single/aromatic.
Three exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude certain 4-nitro/4-nitroso sulfonamide
functional group (such as 4-nitro sulfamethoxazole), (2) to exclude
sulfonamides which have 6-membered ring in both atom 1 and atom 6, and (3) to
exclude reactants susceptible to “sulfonylurea” related reaction schemes by
specifying that reactant atom 6 is not a urea carbon.
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not part of an aromatic
sulfonate functional group.
Examples:
Sulfamethoxazole
(Boreen et al. 2004)
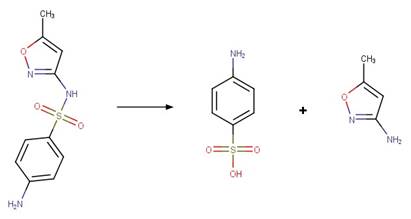
Sulfisoxazole (Boreen et al. 2004)
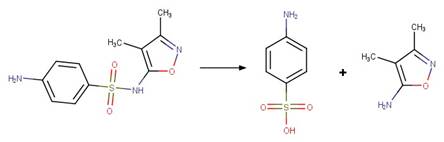
Sulfamethizole (Boreen et al. 2004)
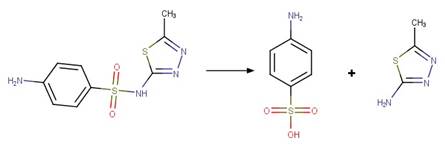
Sulfathiazole (Boreen et al. 2004)
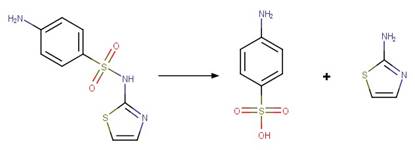
4-nitroso sulfamethoxazole
(Bonvin et al. 2013)

4-nitro sulfamethoxazole
(Bonvin et al. 2013)
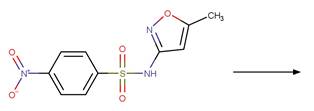
Penoxsulam (EFSA)
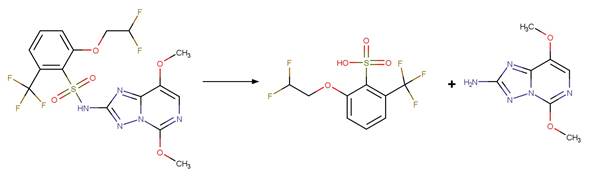
Pyroxsulam
(EFSA)
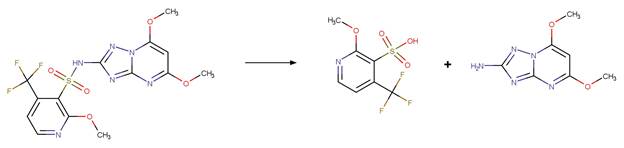
Florasulam (Krieger et al. 2000) (EFSA)
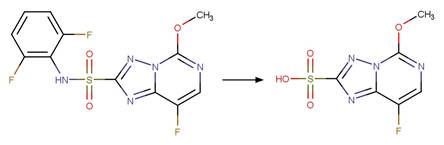
Amisulbrom
(EFSA)
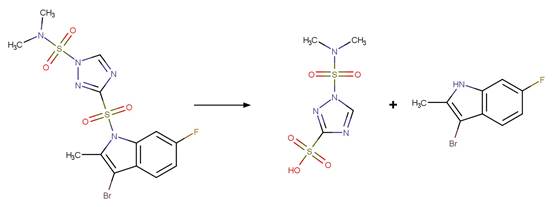
Argatroban (Secrétan et al. 2016)
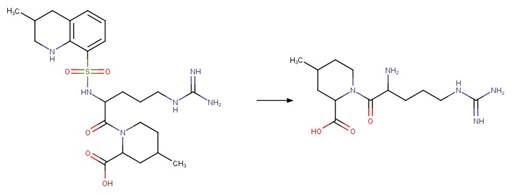
References:
Bonvin, F.,
Omlin, J., Rutler, R., Schweizer, W.B., Alaimo, P.J., Strathmann, T.J.,
McNeill, K. and Kohn, T. 2013. Direct photolysis of human metabolites of the antibiotic
sulfamethoxazole: Evidence for abiotic back-transformation. Environ. Sci.
Technol. 47(13), 6746-6755.
Boreen, A.L.,
Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2004. Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the
aquatic environment: Sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic
groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38(14), 3933-3940.
Krieger, M.S.,
Yoder, R.N. and Gibson, R. 2000. Photolytic degradation of florasulam on soil
and in water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(8), 3710-3717.
Secrétan, P.-H., Karoui, M., Bernard, M., Ghermani, N.,
Safta, F., Yagoubi, N. and Do, B. 2016. Photodegradation of aqueous argatroban
investigated by lc/msn: Photoproducts, transformation processes and potential
implications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 131, 223-232.
Scheme:

Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude certain 4-nitro sulfonamide functional group
(such as 4-nitro sulfamethoxazole) and (2) to exclude reactants susceptible to
“sulfonylurea” related reaction schemes by specifying that reactant atom 6 is
not a urea carbon.
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not part of an aromatic
sulfonate functional group.
Examples:
Sulfadimethoxine
(Guerard et al. 2009)

Sulfamethoxazole
(Bonvin et al. 2013)
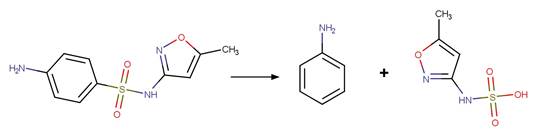
N-acetyl
sulfamethoxazole (Bonvin et al. 2013)
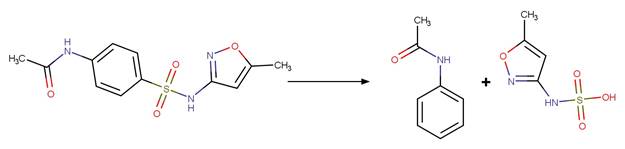
4-nitroso
sulfamethoxazole (Bonvin et al. 2013)

sulfamethoxazole
glucuronide (Bonvin et al. 2013)
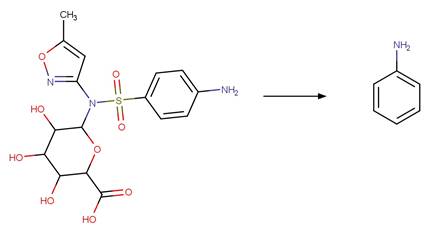
Penoxsulam (Jabusch and Tjeerdema 2006)
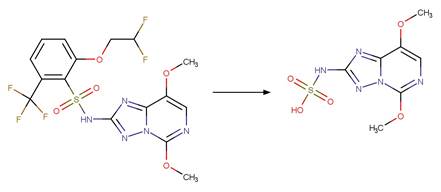
Argatroban (Secrétan et al. 2016)
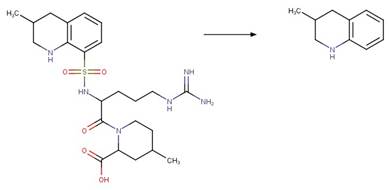
4-nitro
sulfamethoxazole (Bonvin et al. 2013)
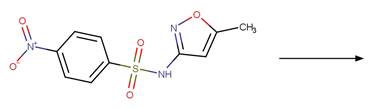
References:
Bonvin, F.,
Omlin, J., Rutler, R., Schweizer, W.B., Alaimo, P.J., Strathmann, T.J.,
McNeill, K. and Kohn, T. 2013. Direct photolysis of human metabolites of the
antibiotic sulfamethoxazole: Evidence for abiotic back-transformation. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 47(13), 6746-6755.
Guerard, J.J.,
Chin, Y.-P., Mash, H. and Hadad, C.M. 2009. Photochemical fate of
sulfadimethoxine in aquaculture waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(22),
8587-8592.
Jabusch, T.W. and
Tjeerdema, R.S. 2006. Photodegradation of penoxsulam. J. Agric. Food Chem.
54(16), 5958-5961.
Secrétan, P.-H., Karoui, M., Bernard, M., Ghermani, N.,
Safta, F., Yagoubi, N. and Do, B. 2016. Photodegradation of aqueous argatroban
investigated by lc/msn: Photoproducts, transformation processes and potential
implications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 131, 223-232.
Scheme:
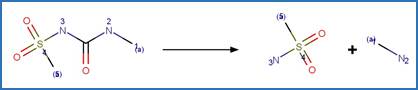
Examples:
Imazosulfuron (Rering et al. 2017)
Cinosulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
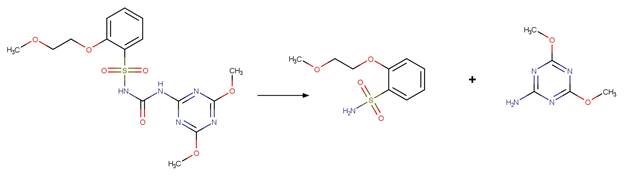
triasulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
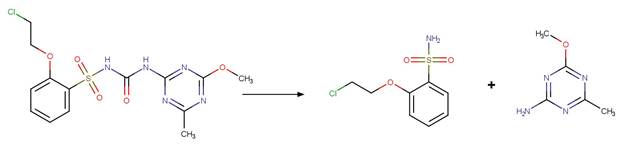
iodosulfuron-methyl
(Brigante et al. 2005)

thifensulfuron-methyl
(Aziz et al. 2010)
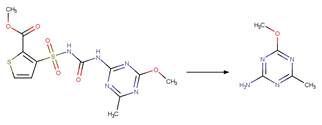
Sulfosulfuron
(EFSA)
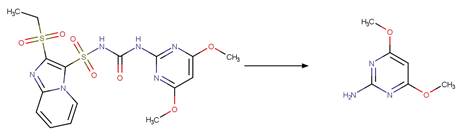
References:
Aziz, S., Dumas,
S., El Azzouzi, M., Sarakha, M. and Chovelon, J.-M. 2010. Photophysical and
photochemical studies of thifensulfuron-methyl herbicide in aqueous solution.
J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 209(2), 210-218.
Brigante, M.,
Emmelin, C., Previtera, L., Baudot, R. and Chovelon, J.M. 2005. Abiotic
degradation of iodosulfuron-methyl-ester in aqueous solution. J. Agric. Food
Chem. 53(13), 5347-5352.
Rering, C.,
Williams, K., Hengel, M. and Tjeerdema, R. 2017. Comparison of direct and
indirect photolysis in imazosulfuron photodegradation. J. Agric. Food Chem.
65(15), 3103-3108.
Vulliet, E., Emmelin, C., Grenier-Loustallot, M.F., Païssé,
O. and Chovelon, J.M. 2002. Simulated sunlight-induced photodegradations of
triasulfuron and cinosulfuron in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(5),
1081-1088.
Scheme:
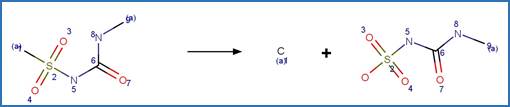
Examples:
Cinosulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
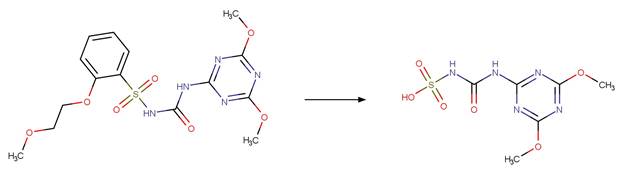
Triasulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
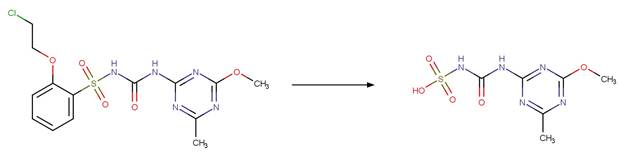
Sulfosulfuron
(EFSA)
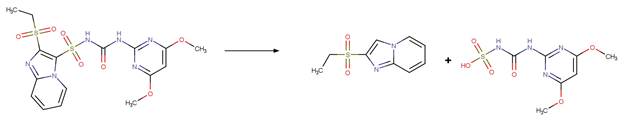
metsulfuron-methyl
(Caselli 2005) (EFSA)
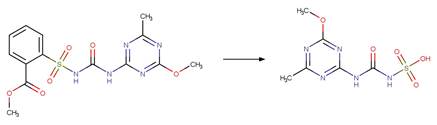
References:
Caselli, M.
2005. Light-induced degradation of metsulfuron-methyl in water. Chemosphere
59(8), 1137-1143.
Vulliet, E., Emmelin, C., Grenier-Loustallot, M.F., Païssé,
O. and Chovelon, J.M. 2002. Simulated sunlight-induced photodegradations of
triasulfuron and cinosulfuron in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(5),
1081-1088.
Scheme:
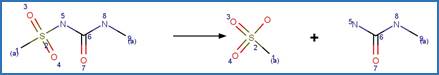
Examples:
Sulfosulfuron
(EFSA)
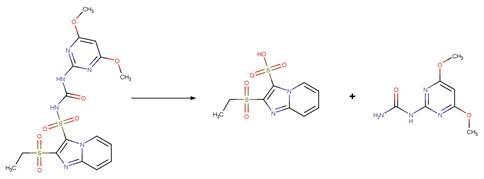
Imazosulfuron (Rering et al. 2017)
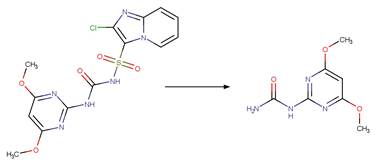
Cinosulfuron (Vulliet et al. 2002)
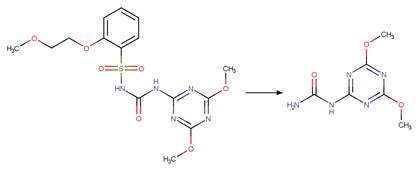
thifensulfuron-methyl
(Aziz et al. 2010)
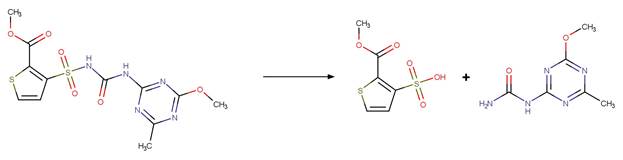
References:
Aziz, S., Dumas,
S., El Azzouzi, M., Sarakha, M. and Chovelon, J.-M. 2010. Photophysical and photochemical
studies of thifensulfuron-methyl herbicide in aqueous solution. J. Photochem.
Photobiol. A: Chem. 209(2), 210-218.
Rering, C.,
Williams, K., Hengel, M. and Tjeerdema, R. 2017. Comparison of direct and
indirect photolysis in imazosulfuron photodegradation. J. Agric. Food Chem.
65(15), 3103-3108.
Vulliet, E., Emmelin, C., Grenier-Loustallot, M.F., Païssé,
O. and Chovelon, J.M. 2002. Simulated sunlight-induced photodegradations of
triasulfuron and cinosulfuron in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(5),
1081-1088.
Scheme:
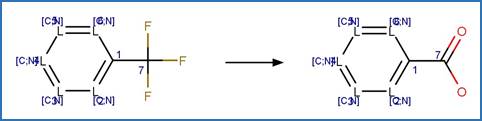
Two relative reasoning exclusion rules are included (1) by
specifying that reactant atoms 3 or 5 cannot be connected to a nitro group (2)
by specifying that the aromatic ring cannot be connected to a halide group.
Examples:
3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol
photo-product (trifluoromethylhydroquinone) (McConville et al. 2016)
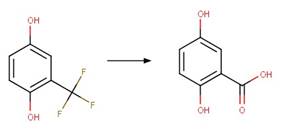
Flufenamic acid
(Rafqah and Sarakha 2016)
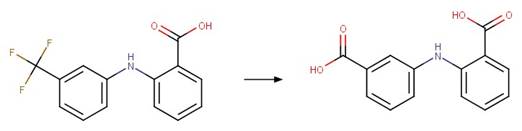
Fluoxetine (Lam et al. 2005)

Fluometuron (Halladja et al. 2007, Lam
et al. 2005)
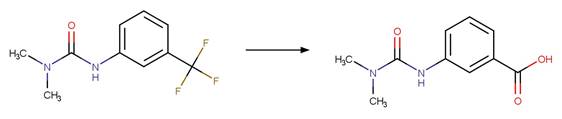
Flutolanil
photo-product (Lam et al. 2005)
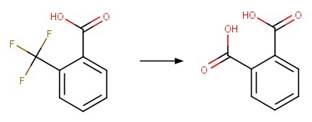
3-trifluoromethylphenol
(Ellis and Mabury 2000)
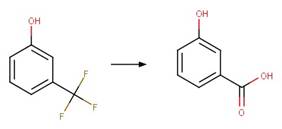
Fluazinam (EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
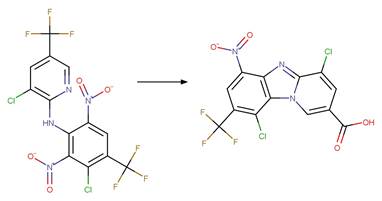
Penoxsulam photo-product
(EFSA)

2-chloro-5-trifluoromethylphenol
photo-product (Young et al. 2008)
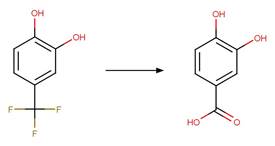
3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol
(Ellis and Mabury 2000)
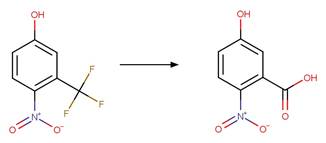
Oxyfluorfen
(EFSA)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
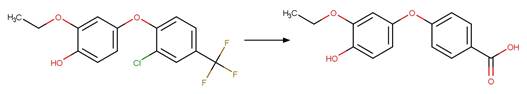
References:
Ellis, D.A. and
Mabury, S.A. 2000. The aqueous photolysis of tfm and related
trifluoromethylphenols. An alternate source of trifluoroacetic acid in the
environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(4), 632-637.
Halladja, S.,
Amine-Khodja, A., ter Halle, A., Boulkamh, A. and Richard, C. 2007. Photolysis
of fluometuron in the presence of natural water constituents. Chemosphere 69(10),
1647-1654.
Lam, M.W.,
Young, C.J. and Mabury, S.A. 2005. Aqueous photochemical reaction kinetics and
transformations of fluoxetine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(2), 513-522.
McConville,
M.B., Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016. Direct photolysis rates and
transformation pathways of the lampricides tfm and niclosamide in simulated
sunlight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Rafqah, S. and
Sarakha, M. 2016. Photochemical transformation of flufenamic acid by artificial
sunlight in aqueous solutions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 316, 1-6.
Young, C., J., Gómez Biagi, R., F., Hurley, M., D.,
Wallington, T., J. and Mabury, S., A. 2008. Paint solvent to food additive: An
environmental route of dehalogenation for 4‐chlorobenzotrifluoride.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27(11), 2233-2238.
Scheme:
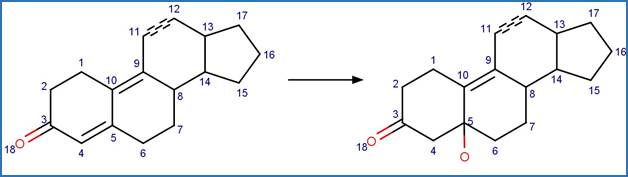
Examples:
17α-trenbolone
(Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)

17β-trenbolone
(Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)

Trendione (Qu et al. 2013)
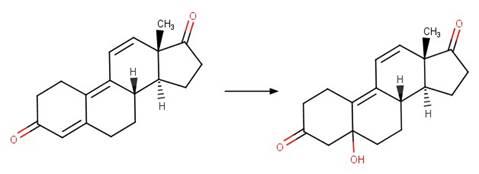
Altrenogest
photo-product (Wammer et al. 2016)
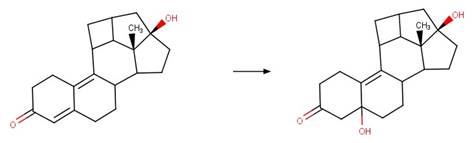
References:
Baltrusaitis,
J., Patterson, E.V., O’Connor, M., Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P. and Cwiertny, D.M.
2016. Reversible photohydration of trenbolone acetate metabolites: Mechanistic
understanding of product-to-parent reversion through complementary experimental
and theoretical approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(13), 6753-6761.
Qu, S.,
Kolodziej, E.P., Long, S.A., Gloer, J.B., Patterson, E.V., Baltrusaitis, J.,
Jones, G.D., Benchetler, P.V., Cole, E.A., Kimbrough, K.C., Tarnoff, M.D. and
Cwiertny, D.M. 2013. Product-to-parent reversion of trenbolone: Unrecognized
risks for endocrine disruption. Science 342(6156), 347.
Wammer, K.H., Anderson, K.C., Erickson, P.R., Kliegman, S.,
Moffatt, M.E., Berg, S.M., Heitzman, J.A., Pflug, N.C., McNeill, K.,
Martinovic-Weigelt, D., Abagyan, R., Cwiertny, D.M. and Kolodziej, E.P. 2016.
Environmental photochemistry of altrenogest: Photoisomerization to a bioactive
product with increased environmental persistence via reversible photohydration.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(14), 7480-7488.
Scheme:
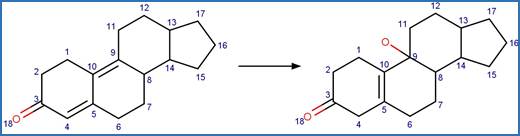
Examples:
Dienogest (Pflug et al. 2017)
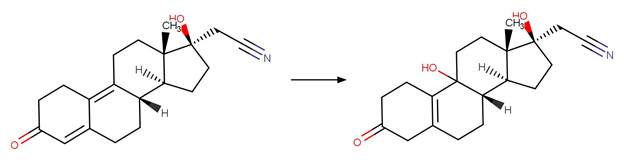
References:
Pflug, N.C., Hankard, M.K., Berg, Stephanie M., O'Connor,
M., Gloer, J.B., Kolodziej, E.P., Cwiertny, D.M. and Wammer, K.H. 2017.
Environmental photochemistry of dienogest: Phototransformation to estrogenic
products and increased environmental persistence via reversible photohydration.
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 19(11), 1414-1426.
Scheme:
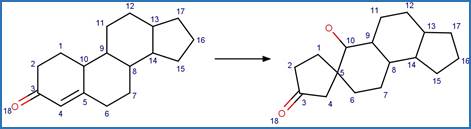
Examples:
Androstenedione
(Young et al. 2013)

Testosterone (Vulliet et al. 2010)
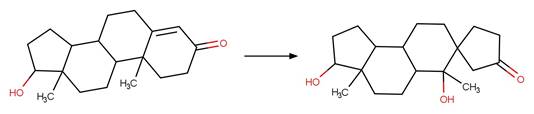
References:
Vulliet, E.,
Falletta, M., Marote, P., Lomberget, T., Païssé, J.-O. and Grenier-Loustalot,
M.-F. 2010. Light induced degradation of testosterone in waters. Sci. Total
Environ. 408(17), 3554-3559.
Young, R.B., Latch, D.E., Mawhinney, D.B., Nguyen, T.-H.,
Davis, J.C.C. and Borch, T. 2013. Direct photodegradation of androstenedione
and testosterone in natural sunlight: Inhibition by dissolved organic matter
and reduction of endocrine disrupting potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(15),
8416-8424.
Scheme:
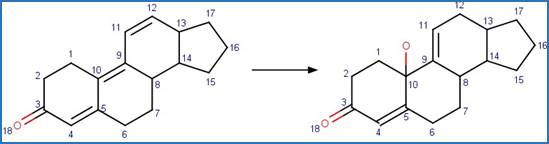
Examples:
17β-trenbolone
(Kolodziej et al. 2013)
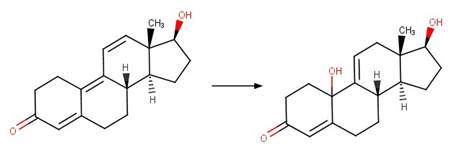
References:
Kolodziej, E.P., Qu, S., Forsgren, K.L., Long, S.A., Gloer,
J.B., Jones, G.D., Schlenk, D., Baltrusaitis, J. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2013.
Identification and environmental implications of photo-transformation products
of trenbolone acetate metabolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(10), 5031-5041.
Scheme:
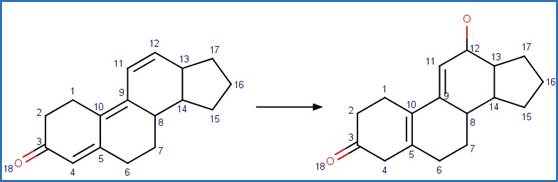
Examples:
17α-trenbolone
(Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)

17β-trenbolone
(Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)
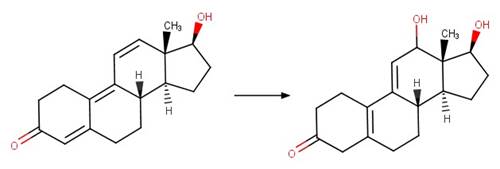
Trendione (Qu et al. 2013)
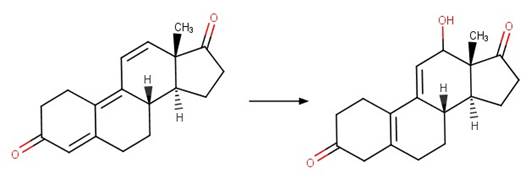
References:
Baltrusaitis,
J., Patterson, E.V., O’Connor, M., Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P. and Cwiertny, D.M.
2016. Reversible photohydration of trenbolone acetate metabolites: Mechanistic
understanding of product-to-parent reversion through complementary experimental
and theoretical approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(13), 6753-6761.
Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P., Long, S.A., Gloer, J.B.,
Patterson, E.V., Baltrusaitis, J., Jones, G.D., Benchetler, P.V., Cole, E.A.,
Kimbrough, K.C., Tarnoff, M.D. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2013. Product-to-parent
reversion of trenbolone: Unrecognized risks for endocrine disruption. Science
342(6156), 347.
Scheme:
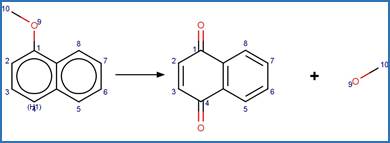
Examples:
Propranolol (Sortino et al. 2002)

Carbaryl (Brahmia and Richard 2003)
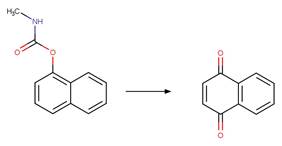
References:
Brahmia, O. and
Richard, C. 2003. Phototransformation of carbaryl in aqueous solution:
Laser-flash photolysis and steady-state studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A:
Chem. 156(1), 9-14.
Sortino, S., Petralia, S., Bosca, F. and Miranda, M.A.
2002. Irreversible photo-oxidation of propranolol triggered by
self-photogenerated singlet molecular oxygen. Photochemical &
Photobiological Sciences 1(2), 136-140.
Scheme:
Examples:
Anthracene (Sigman et al. 1991)

7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene
(Wood et al. 1979)
References:
Sigman, M.E.,
Zingg, S.P., Pagni, R.M. and Burns, J.H. 1991. Photochemistry of anthracene in
water. Tetrahedron Lett. 32(41), 5737-5740.
Wood, J.L., Barker, C.L. and Grubbs, C.J. 1979.
Photooxidation products of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a] anthracene. Chem. Biol.
Interact. 26(3), 339-347.
Scheme:
Examples:
4-nitro
butamifos (Katagi 1993)
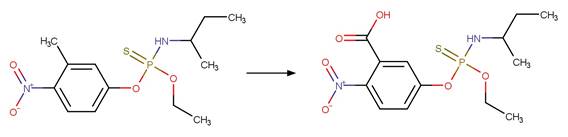
Fenitrothion (Mikami et al. 1985) (EFSA)
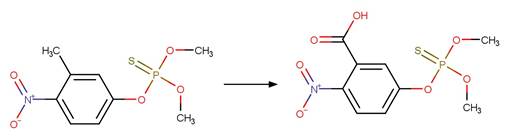
References:
Katagi, T. 1993.
Photochemistry of organophosphorus herbicide butamifos. J. Agric. Food Chem.
41(3), 496-501.
Mikami, N., Imanishi, K., Yamada, H. and Miyamoto, J. 1985.
Photodegradation of fenitrothion in water and on soil surface, and its
hydrolysis in water. J. Pestic. Sci. 10(2), 263-272.
Scheme:
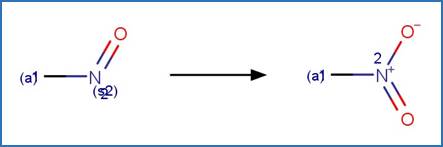
Examples:
4-nitroso
sulfamethoxazole (Bonvin et al. 2013), sulfamethoxazole
photo-product (Willach et al. 2018)

3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol photo-product (Carey and Fox 1981)
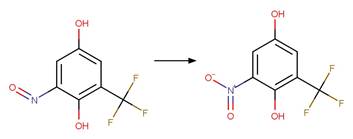
Butamifos
photo-product (Katagi 1993)
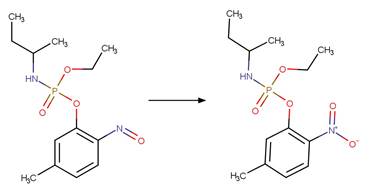
4-chloronitrosobenzene (Miller and Crosby 1983)
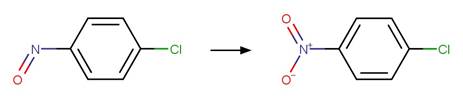
References:
Bonvin, F.,
Omlin, J., Rutler, R., Schweizer, W.B., Alaimo, P.J., Strathmann, T.J.,
McNeill, K. and Kohn, T. 2013. Direct photolysis of human metabolites of the
antibiotic sulfamethoxazole: Evidence for abiotic back-transformation. Environ.
Sci. Technol. 47(13), 6746-6755.
Carey, J.H. and
Fox, M.E. 1981. Photodegradation of the lampricide
3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol (tfm) 1. Pathway of the direct photolysis in
solution. J. Great Lakes Res. 7(3), 234-241.
Katagi, T. 1993.
Photochemistry of organophosphorus herbicide butamifos. J. Agric. Food Chem.
41(3), 496-501.
Miller, G.C. and
Crosby, D.G. 1983. Photooxidation of 4-chloroaniline and
n-(4-chlorophenyl)-benzenesulfonamide to nitroso- and nitro-products. Chemosphere
12(9), 1217-1227.
Willach, S., Lutze, H.V., Eckey, K., Löppenberg, K.,
Lüling, M., Wolbert, J.-B., Kujawinski, D.M., Jochmann, M.A., Karst, U. and
Schmidt, T.C. 2018. Direct photolysis of sulfamethoxazole using various
irradiation sources and wavelength ranges—insights from degradation product
analysis and compound-specific stable isotope analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol.
52(3), 1225-1233.
Scheme:
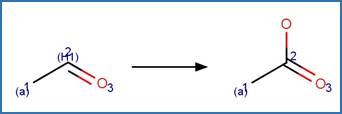
An exclusion
rule is included to exclude reactants susceptible to “2-Nitrobenzaldehyde Photorearrangement”
by specifying that there is no nitro functional group ortho to the
benzaldehyde.
Examples:
Permethrin
photo-product (Holmstead et al. 1978)
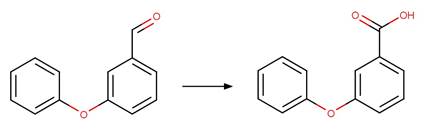
Methotrexate
photo-product (Chatterji and Gallelli 1978)

Diclofenac
photo-product (Agüera et al. 2005)

4-chlorobenzaldehyde
(Ware et al. 1980)
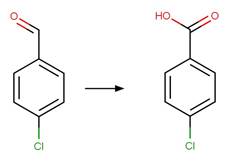
1-naphthaldehyde
(Crosby and Tang 1969)
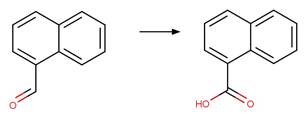
References:
Agüera, A.,
Pérez Estrada, L.A., Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Malato, S. and Fernández-Alba,
A.R. 2005. Application of time-of-flight mass spectrometry to the analysis of
phototransformation products of diclofenac in water under natural sunlight. J.
Mass Spectrom. 40(7), 908-915.
Chatterji, D.C.
and Gallelli, J.F. 1978. Thermal and photolytic decomposition of methotrexate
in aqueous solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 67(4), 526-531.
Crosby, D.G. and
Tang, C.-S. 1969. Photodecomposition of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid. J. Agric.
Food Chem. 17(6), 1291-1293.
Holmstead, R.L.,
Casida, J.E., Ruzo, L.O. and Fullmer, D.G. 1978. Pyrethroid photodecomposition:
Permethrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26(3), 590-595.
Ware, G.W., Crosby, D.G. and Giles, J.W. 1980.
Photodecomposition of dda. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9(2), 135-146.
Scheme:
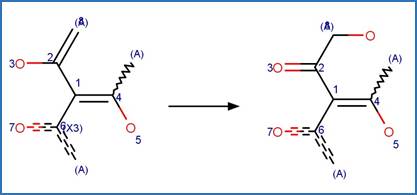
Examples:
myrigalone A (Khaled et al. 2019)
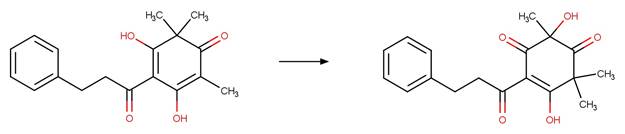
References:
Khaled, A., Sleiman, M., Darras, E., Trivella, A., Bertrand, C.,
Inguimbert, N., Goupil, P. and Richard, C. 2019. Photodegradation of myrigalone
a, an allelochemical from myrica gale: Photoproducts and effect of terpenes. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 67(26), 7258-7265.
Scheme:

Examples:
Isoleptospermone
(Trivella et al. 2015)
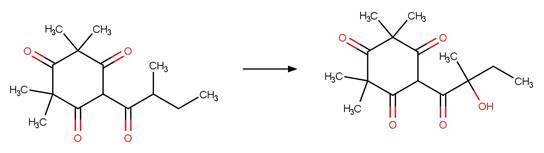
Grandiflorone (Trivella et al. 2015)
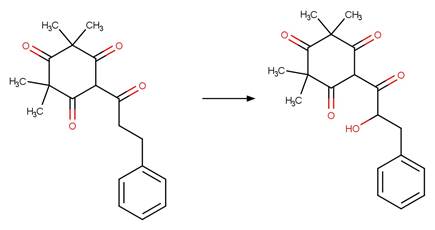
References:
Trivella, A., Stawinoga, M., Dayan, F.E., Cantrell, C.L.,
Mazellier, P. and Richard, C. 2015. Photolysis of natural β-triketonic
herbicides in water. Water Res. 78, 28-36.
Scheme:
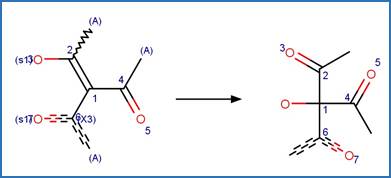
Examples:
myrigalone A (Khaled et al. 2019)
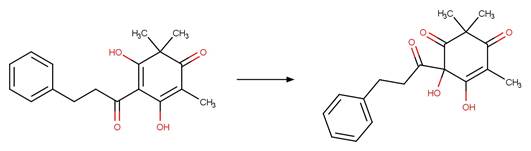
References:
Khaled, A., Sleiman, M., Darras, E., Trivella, A., Bertrand, C.,
Inguimbert, N., Goupil, P. and Richard, C. 2019. Photodegradation of myrigalone
a, an allelochemical from myrica gale: Photoproducts and effect of terpenes. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 67(26), 7258-7265.
Scheme:
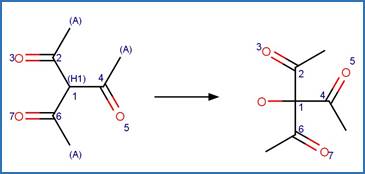
Examples:
Leptospermone (Trivella et al. 2015)
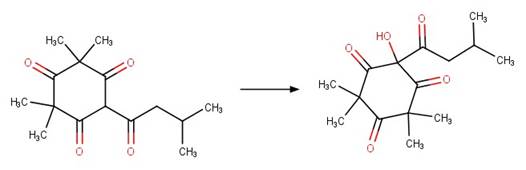
Grandiflorone (Trivella et al. 2015)
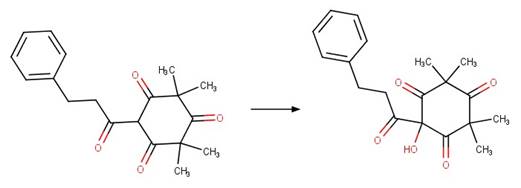
References:
Trivella, A., Stawinoga, M., Dayan, F.E., Cantrell, C.L.,
Mazellier, P. and Richard, C. 2015. Photolysis of natural β-triketonic
herbicides in water. Water Res. 78, 28-36.
Scheme:
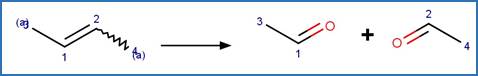
A selectivity
rule is included to avoid duplication of products for symmetric reactant by
specifying that reactant atom 3 needs to be the more sterically hindered atom.
Examples:
distyrylbiphenyl
disulfonate (Kramer et al. 1996)
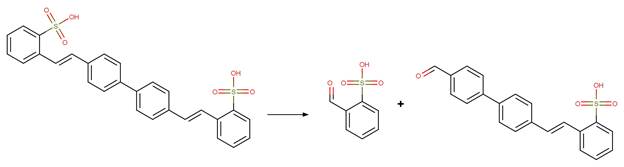
diaminostilbene
DAS 1 (Kramer et al. 1996)

Tamoxifen (DellaGreca et al. 2007)

References:
DellaGreca, M.,
Iesce, M.R., Isidori, M., Nardelli, A., Previtera, L. and Rubino, M. 2007.
Phototransformation products of tamoxifen by sunlight in water. Toxicity of the
drug and its derivatives on aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 67(10), 1933-1939.
Kramer, J.B., Canonica, S., Hoigné, J. and Kaschig, J.
1996. Degradation of fluorescent whitening agents in sunlit natural waters.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(7), 2227-2234.
Scheme:

Examples:
Amlodipine (DellaGreca et al. 2007)
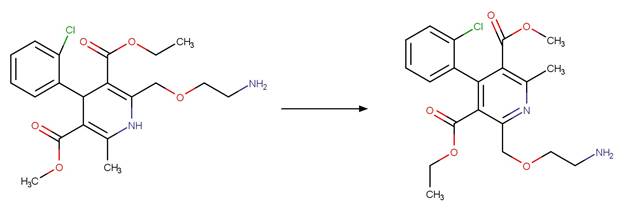
References:
DellaGreca, M., Iesce, M.R., Isidori, M., Montanaro, S.,
Previtera, L. and Rubino, M. 2007. Phototransformation of amlodipine in aqueous
solution: Toxicity of the drug and its photoproduct on aquatic organisms.
International Journal of Photoenergy 2007.
Scheme:
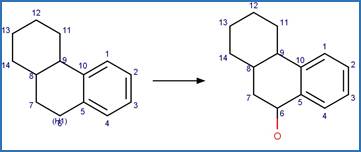
Examples:
17β-estradiol
(Mazellier et al. 2008)
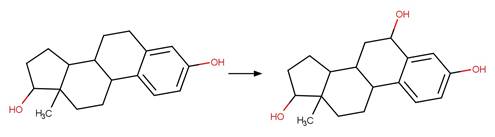
17α-ethinylestradiol
(Mazellier et al. 2008)
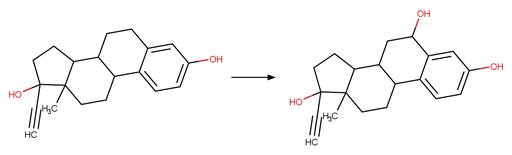
dehydroabietic
acid photo-product (Corin et al. 2000)

References:
Corin, N.S.,
Backlund, P.H. and Kulovaara, M.A.M. 2000. Photolysis of the resin acid
dehydroabietic acid in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(11), 2231-2236.
Mazellier, P., Méité, L. and Laat, J.D. 2008.
Photodegradation of the steroid hormones 17β-estradiol (e2) and
17α-ethinylestradiol (ee2) in dilute aqueous solution. Chemosphere 73(8),
1216-1223.
Scheme:
Examples:
17β-estradiol
(Mazellier et al. 2008)
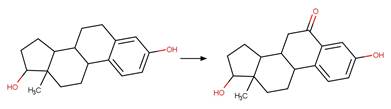
17α-ethinylestradiol
(Mazellier et al. 2008)
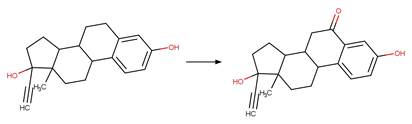
dehydroabietic
acid photo-product (Corin et al. 2000)
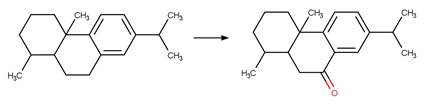
References:
Corin, N.S.,
Backlund, P.H. and Kulovaara, M.A.M. 2000. Photolysis of the resin acid
dehydroabietic acid in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(11), 2231-2236.
Mazellier, P., Méité, L. and Laat, J.D. 2008.
Photodegradation of the steroid hormones 17β-estradiol (e2) and
17α-ethinylestradiol (ee2) in dilute aqueous solution. Chemosphere 73(8),
1216-1223.
Scheme:

Examples:
Parathion-methyl
(Weber et al. 2009)
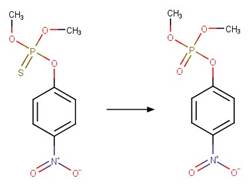
Fenitrothion (Weber et al. 2009) (EFSA)
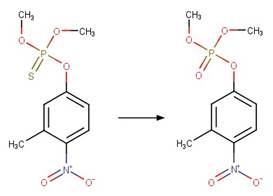
4-nitro
butamifos (Katagi 1993)
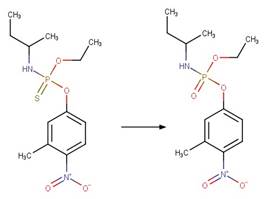
Parathion (Mansour et al. 1983)
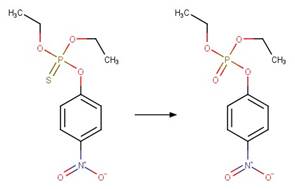
Isofenfos (Zamy et al. 2004)

References:
Katagi, T. 1993.
Photochemistry of organophosphorus herbicide butamifos. J. Agric. Food Chem.
41(3), 496-501.
Mansour, M.,
Thaller, S. and Korte, F. 1983. Action of sunlight on parathion. Bull. Environ.
Contam. Toxicol. 30(1), 358-364.
Weber, J.,
Kurková, R., Klánová, J., Klán, P. and Halsall, C.J. 2009. Photolytic
degradation of methyl-parathion and fenitrothion in ice and water: Implications
for cold environments. Environ. Pollut. 157(12), 3308-3313.
Zamy, C., Mazellier, P. and Legube, B. 2004.
Phototransformation of selected organophosphorus pesticides in dilute aqueous
solutions. Water Res. 38(9), 2305-2314.
Scheme:
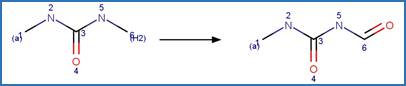
Examples:
Diuron (Tanaka et al. 1986)
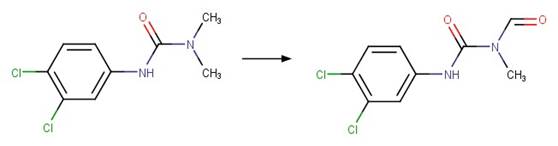
Monuron (Crosby and Tang 1969)
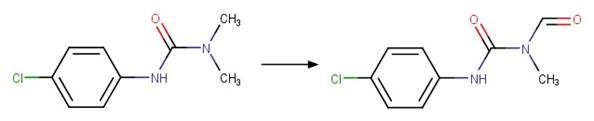
Monuron
photo-product (Crosby and Tang 1969)
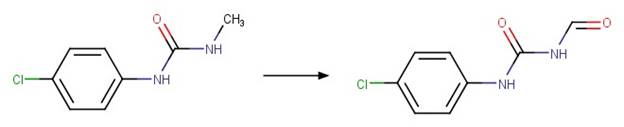
References:
Crosby, D.G. and
Tang, C.S. 1969. Photodecomposition of 3-(p-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
(monuron). J. Agric. Food Chem. 17(5), 1041-1044.
Tanaka, F.S., Hoffer, B.L. and Wien, R.G. 1986. Photolysis
of 3‐(3,4‐dichlorophenyl)‐1, 1 ‐dimethylurea
(diuron) in dilute aqueous solution. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 11(4), 261-269.
Scheme:

Examples:
Atrazine (Torrents et al. 1997)
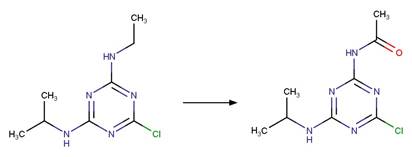
Pirimicarb (Pirisi et al. 1996) (EFSA)
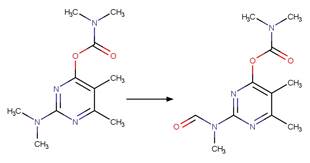
References:
Pirisi, F.M.,
Cabras, P., Garau, V.L., Melis, M. and Secchi, E. 1996. Photodegradation of
pesticides. Photolysis rates and half-life of pirimicarb and its metabolites in
reactions in water and in solid phase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 44(8), 2417-2422.
Torrents, A., Anderson, B.G., Bilboulian, S., Johnson, W.E.
and Hapeman, C.J. 1997. Atrazine photolysis: Mechanistic investigations
of direct and nitrate-mediated hydroxy radical processes and the influence of
dissolved organic carbon from the chesapeake bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31(5),
1476-1482.
Scheme:
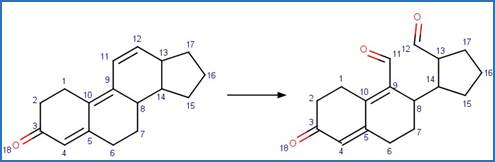
Examples:
17β-trenbolone
(Kolodziej et al. 2013)
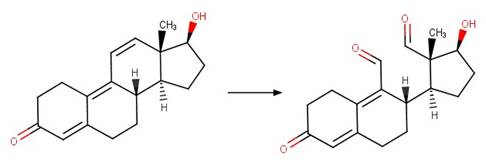
References:
Kolodziej, E.P., Qu, S., Forsgren, K.L., Long, S.A., Gloer,
J.B., Jones, G.D., Schlenk, D., Baltrusaitis, J. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2013.
Identification and environmental implications of photo-transformation products
of trenbolone acetate metabolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(10), 5031-5041.
Scheme:
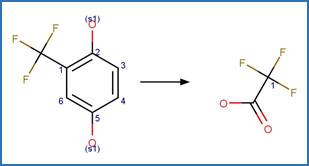
Examples:
3-trifluoromethyl-4-nitrophenol
photo-product (trifluoromethyl hydroquinone), 4-amino-3-trifluoromethylphenol
photo-product (Ellis and Mabury 2000,
McConville et al. 2016)
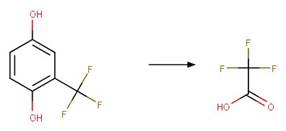
References:
Ellis, D.A. and
Mabury, S.A. 2000. The aqueous photolysis of tfm and related
trifluoromethylphenols. An alternate source of trifluoroacetic acid in the
environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(4), 632-637.
McConville, M.B., Hubert, T.D. and Remucal, C.K. 2016.
Direct photolysis rates and transformation pathways of the lampricides tfm and
niclosamide in simulated sunlight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(18), 9998-10006.
Scheme:
An exclusion
rule is added to differentiate this scheme from “Fluoroquinolone Photohydrodefluorination”
by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not part of a quinolone functional group.
A relative reasoning exclusion
rule is included by specifying that reactant atom 1 is not connected to a
benzoylphenylurea functional group.
Examples:
fipronil
photo-product (Ngim et al. 2000)
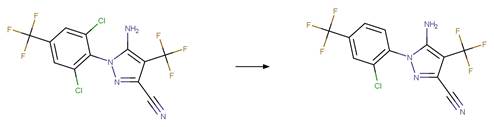
BDE-47 (Wei-Haas 2015)
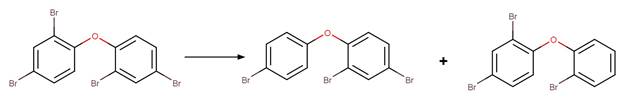
Profenofos (Zamy et al. 2004)
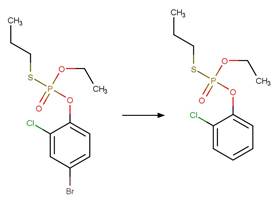
Diclofenac
photo-product (Moore et al. 1990)

Triclosan (Kliegman et al. 2013)

Iopromide (Pérez et al. 2009)
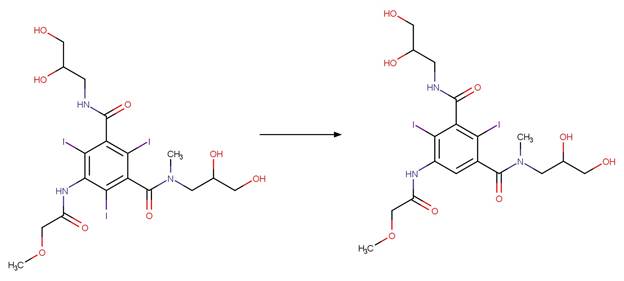
Proquinazid
(EFSA)

References:
Kliegman, S.,
Eustis, S.N., Arnold, W.A. and McNeill, K. 2013. Experimental and theoretical
insights into the involvement of radicals in triclosan phototransformation.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(13), 6756-6763.
Moore, D.E.,
Roberts-Thomson, S., Zhen, D. and Duke, C.C. 1990. Photochemical studies on the
antinelammatory drug diclofenac. Photochem. Photobiol. 52(4), 685-690.
Ngim, K.K.,
Mabury, S.A. and Crosby, D.G. 2000. Elucidation of fipronil photodegradation
pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(10), 4661-4665.
Pérez, S.,
Eichhorn, P., Ceballos, V. and Barceló, D. 2009. Elucidation of
phototransformation reactions of the x-ray contrast medium iopromide under
simulated solar radiation using uplc-esi-qqtof-ms. J. Mass Spectrom. 44(9),
1308-1317.
Wei-Haas, M.L.
2015. The influence of dissolved organic matter on the fate of polybrominated
diphenyl ethers (pbdes) in the environment, The Ohio State University.
Zamy, C., Mazellier, P. and Legube, B. 2004.
Phototransformation of selected organophosphorus pesticides in dilute aqueous
solutions. Water Res. 38(9), 2305-2314.
Scheme:
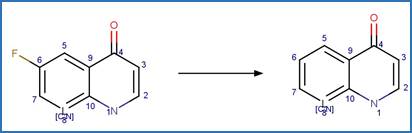
An exclusion
rules are included to exclude halogen substitution at reactant atom 8.
Examples:
Enrofloxacin (Wammer et al. 2013)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
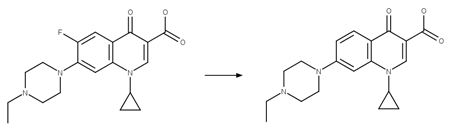
Ciprofloxacin (Baena-Nogueras et al. 2017)
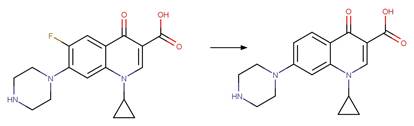
Balofloxacin
photo-product (Ge et al. 2018)
References:
Baena-Nogueras,
R.M., González-Mazo, E. and Lara-Martín, P.A. 2017. Photolysis of antibiotics
under simulated sunlight irradiation: Identification of photoproducts by
high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(6), 3148-3156.
Ge, L., Halsall,
C., Chen, C.-E., Zhang, P., Dong, Q. and Yao, Z. 2018. Exploring the aquatic photodegradation
of two ionisable fluoroquinolone antibiotics – gatifloxacin and balofloxacin:
Degradation kinetics, photobyproducts and risk to the aquatic environment. Sci.
Total Environ. 633, 1192-1197.
Wammer, K.H., Korte, A.R., Lundeen, R.A., Sundberg, J.E.,
McNeill, K. and Arnold, W.A. 2013. Direct photochemistry of three
fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water
Res. 47(1), 439-448.
Scheme:
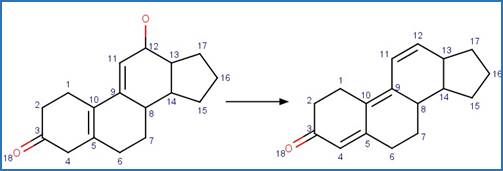
Examples:
17α-trenbolone
photo-product (12-OH-17α-trenbolone) (Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)
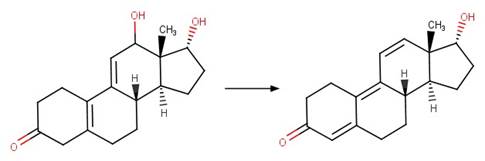
17β-trenbolone
photo-product (12-OH-17β-trenbolone) (Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)
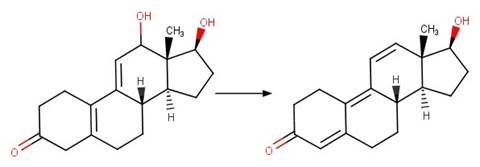
Trendione photo-product
(12-OH-trendione) (Qu et al. 2013)
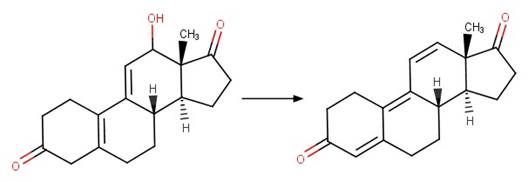
References:
Baltrusaitis,
J., Patterson, E.V., O’Connor, M., Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P. and Cwiertny, D.M.
2016. Reversible photohydration of trenbolone acetate metabolites: Mechanistic
understanding of product-to-parent reversion through complementary experimental
and theoretical approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(13), 6753-6761.
Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P., Long, S.A., Gloer, J.B.,
Patterson, E.V., Baltrusaitis, J., Jones, G.D., Benchetler, P.V., Cole, E.A.,
Kimbrough, K.C., Tarnoff, M.D. and Cwiertny, D.M. 2013. Product-to-parent
reversion of trenbolone: Unrecognized risks for endocrine disruption. Science
342(6156), 347.
Scheme:
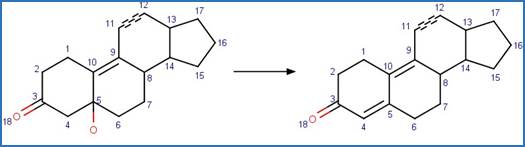
Examples:
17α-trenbolone
photo-product (5-OH-17α-trenbolone) (Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)

17β-trenbolone
photo-product (5-OH-17β-trenbolone) (Baltrusaitis et al. 2016)
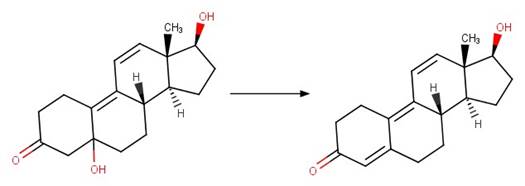
Trendione
photo-product (5-OH-trendione) (Qu et al. 2013)
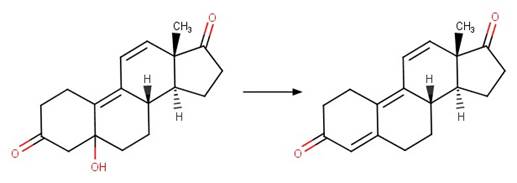
Altrenogest photo-product
(5-OH-altrenogest) (Wammer et al. 2016)
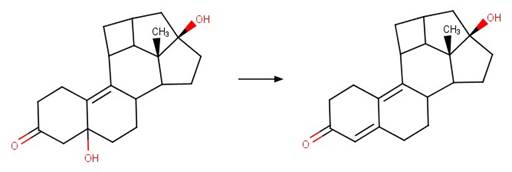
References:
Baltrusaitis,
J., Patterson, E.V., O’Connor, M., Qu, S., Kolodziej, E.P. and Cwiertny, D.M.
2016. Reversible photohydration of trenbolone acetate metabolites: Mechanistic
understanding of product-to-parent reversion through complementary experimental
and theoretical approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(13), 6753-6761.
Qu, S.,
Kolodziej, E.P., Long, S.A., Gloer, J.B., Patterson, E.V., Baltrusaitis, J.,
Jones, G.D., Benchetler, P.V., Cole, E.A., Kimbrough, K.C., Tarnoff, M.D. and
Cwiertny, D.M. 2013. Product-to-parent reversion of trenbolone: Unrecognized
risks for endocrine disruption. Science 342(6156), 347.
Wammer, K.H., Anderson, K.C., Erickson, P.R., Kliegman, S.,
Moffatt, M.E., Berg, S.M., Heitzman, J.A., Pflug, N.C., McNeill, K.,
Martinovic-Weigelt, D., Abagyan, R., Cwiertny, D.M. and Kolodziej, E.P. 2016.
Environmental photochemistry of altrenogest: Photoisomerization to a bioactive
product with increased environmental persistence via reversible photohydration.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(14), 7480-7488.
Scheme:
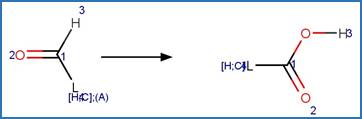
Examples:
N-nitrosodimethylamine
(Plumlee and Reinhard 2007)
The product is formed by the reaction scheme along with
other transformations.

Metofluthrin
photo-product (Nishiyama et al. 2010)
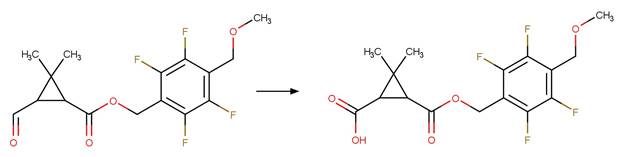
Cyphenothrin
photo-product (Suzuki et al. 2017)

References:
Nishiyama, M.,
Suzuki, Y. and Katagi, T. 2010. Hydrolysis and photolysis of insecticide
metofluthrin in water. J. Pestic. Sci. 35(4), 447-455.
Plumlee, M.H.
and Reinhard, M. 2007. Photochemical attenuation of n-nitrosodimethylamine
(ndma) and other nitrosamines in surface water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(17),
6170-6176.
Suzuki, Y., Yoshida, M., Sugano, T., Shibata, A., Kodaka,
R., Fujisawa, T. and Katagi, T. 2017. Behavior of cyphenothrin in aquatic
environment. J. Pestic. Sci. 42(2), 17-24.
Scheme:

Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to prevent the exact chemical of
N-[(nitroamino)methyl]formamide for reacting and (2) to constrain that the
reaction scheme does not happen to aromatic compounds.
Examples:
hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine
(RDX) photo-product (Hawari et al. 2002)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
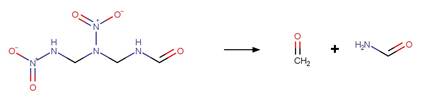
References:
Hawari, J., Halasz, A., Groom, C., Deschamps, S., Paquet, L.,
Beaulieu, C. and Corriveau, A. 2002. Photodegradation of rdx in aqueous
solution: A mechanistic probe for biodegradation with rhodococcus sp.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(23), 5117-5123.
Scheme:
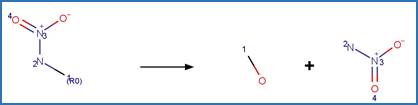
Two exclusion
rules are included (1) to exclude the exact chemical of
N-[(nitroamino)methyl]formamide and (2) to constrain that the reaction scheme
does not happen to aromatic compounds.
Examples:
hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine
(RDX) photo-product (Hawari et al. 2002)
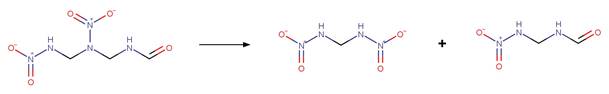
References:
Hawari, J., Halasz, A., Groom, C., Deschamps, S., Paquet, L.,
Beaulieu, C. and Corriveau, A. 2002. Photodegradation of rdx in aqueous
solution: A mechanistic probe for biodegradation with rhodococcus sp.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(23), 5117-5123.
Scheme:
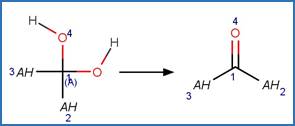
This scheme is
a duplicate of the same reaction scheme in the CTS abiotic hydrolysis library. The
reaction is actually an equilibrium between a geminal diol and a carbonyl compound,
where the carbonyl is usually the dominant form except for simple aldehydes (Bell and Evans 1966, Tebes-Stevens et al. 2017). Although the dominant form for simple
aldehydes (e.g., formaldehyde) is usually the diol, this reaction is still
allowed for simple aldehydes because the equilibrium is strongly dependent on
the solution chemistry and some analytical techniques do not differentiate
between the two forms.
Examples:
hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine
photo-product (Hawari et al. 2002)
The product is
formed by the reaction scheme along with other transformations.
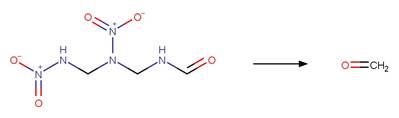
References:
Bell, R.P. and
Evans, P.G. 1966. Kinetics of the dehydration of methylene glycol in aqueous
solution. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical
and Physical Sciences 291(1426), 297-323.
Hawari, J.,
Halasz, A., Groom, C., Deschamps, S., Paquet, L., Beaulieu, C. and Corriveau,
A. 2002. Photodegradation of rdx in aqueous solution: A mechanistic
probe for biodegradation with rhodococcus sp. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(23),
5117-5123.
Tebes-Stevens, C., Patel, J.M., Jones, W.J. and Weber, E.J.
2017. Prediction of hydrolysis products of organic chemicals under
environmental ph conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51(9), 5008-5016.
Scheme:

Examples:
hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine
photo-product (Hawari et al. 2002)

References:
Hawari, J., Halasz, A., Groom, C., Deschamps, S., Paquet, L.,
Beaulieu, C. and Corriveau, A. 2002. Photodegradation of rdx in aqueous
solution: A mechanistic probe for biodegradation with rhodococcus sp.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(23), 5117-5123.
|
rank
|
equivalent mid-point half-life
|
range of geometric mean of t1/2,pr for rank
assignment
|
|
7
|
17 minutes
|
< 30 minutes
|
|
6
|
2.0 hours
|
30 minutes – 200 minutes
|
|
5
|
14 hours
|
200 minuts - 1 day
|
|
4
|
4.0 days
|
1 day - 1 week
|
|
3
|
0.93 month
|
1 week - 2 months
|
|
2
|
0.54 year
|
2 months - 1 year
|
|
1
|
3.8 year
|
> 1 year
|
|
#
|
reaction scheme name
|
rank
|
|
|
Photorearrangement
|
|
|
1
|
1-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C2)
|
4
|
|
2
|
1-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C4)
|
4
|
|
3
|
2-Naphthoxy Photorearrangement (C1)
|
4
|
|
4
|
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde Photorearrangement
|
4
|
|
5
|
Benzyl Phenyl Ether Photorearrangement (o)
|
3
|
|
6
|
Benzyl Phenyl Ether Photorearrangement (p)
|
3
|
|
7
|
Enone Steroid Photorearrangement to Cyclopentenone
|
4
|
|
8
|
Enone Steroid Photorearrangement to Lumiketone
|
4
|
|
9
|
O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangement (o)
|
4
|
|
10
|
O-aryl Carbamate Photorearrangement (p)
|
4
|
|
11
|
Organothiophosphorus Ester Photochemical Oxygen Transfer
|
4
|
|
12
|
Organothiophosphorus Ester Photorearrangement
|
4
|
|
13
|
Phenoxyphenol Dehalogenative Photorearrangement
|
4
|
|
|
Photodissociation
|
|
|
14
|
Aromatic Ketone Norrish II Photocleavage (C1_C4)
|
4
|
|
15
|
Aminobenzophenone Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
4
|
|
16
|
Benzyl Photodeamination to Alcohol
|
3
|
|
17
|
Benzyl Photodeamination to Carbonyl
|
3
|
|
18
|
Benzyl Thiocarbamate Photocleavage to Carbonyl
|
2
|
|
19
|
Cyclohexanedione Oxime N-O Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
20
|
Diazepam Ring Photocleavage
|
3
|
|
21
|
Dihydrophenanthrene Benzyl Photodealkylation
|
4
|
|
22
|
Dihydrophenanthrene Benzyl Oxidative Photodealkylation
|
4
|
|
23
|
Dinitroaniline Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
4
|
|
24
|
Fluoroquinolone Ethylenediamine Photochemical N-dealkylation
|
7
|
|
25
|
Fluoroquinolone Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
6
|
|
26
|
Fluoroquinolone Piperazine Photochemical Bis N-dealkylation
|
7
|
|
27
|
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to Aldehyde
|
4
|
|
28
|
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to Amide
|
4
|
|
29
|
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to Amidine
|
4
|
|
30
|
Imidazolinone Ring Photocleavage to Carboxylic Acid
|
4
|
|
31
|
Nitroenamine Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
32
|
Nitroenamine Photocleavage to Carbonyl
|
4
|
|
33
|
Nitrosamine N-C Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
34
|
p-Aminobenzoic Acid Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
4
|
|
35
|
Phenoxyphenol Ether Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
36
|
Phenylurea Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
1
|
|
37
|
Phenylurea Photochemical
N-demethoxylation
|
1
|
|
38
|
Phenylurea N-formyl Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
39
|
Pyridinium Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
4
|
|
40
|
s-Triazine Side Chain Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
3
|
|
41
|
Sulfonamide N-C Photocleavage (6-5)
|
4
|
|
42
|
Tetracycline Photochemical
N-dealkylation
|
4
|
|
|
Photoelimination
|
|
|
43
|
1_2_4-Triazine-5-one Photochemical
N-deamination
|
4
|
|
44
|
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation
|
4
|
|
45
|
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation to Alcohol
|
4
|
|
46
|
Aromatic Acetic Acid Photodecarboxylation to Carbonyl
|
4
|
|
47
|
Aromatic Carboxylic Acid Photodecarboxylation
|
4
|
|
48
|
Aromatic Carboxylic Acid Photodecarboxylation to Alcohol
|
4
|
|
49
|
Benzotriazole Photodenitrogenation
|
4
|
|
50
|
Benzotriazole Photodenitrogenation to Phenol (o)
|
4
|
|
51
|
Cephem Photodecarboxylation
|
4
|
|
52
|
Cyanohydrin Cyano Photoelimination to Aldehyde
|
4
|
|
53
|
Fipronil Sulfoxide Photoextrusion
|
4
|
|
54
|
Imidazolinone Amide Photoelimination
|
4
|
|
55
|
Imidazolinone Photodecarbonylation
|
4
|
|
56
|
Nitroguanidine Photochemical
N-denitration
|
4
|
|
57
|
Nitrosamine N-N Photocleavage
|
4
|
|
58
|
Phenoxyacetic Acid Photodecarboxylation
|
4
|
|
59
|
Phenoxyacetic Acid Photodecarboxylation to Carbonyl
|
4
|
|
60
|
Pyrrolinone Photodecarbonylation
|
4
|
|
61
|
RDX Photochemical N-denitration to Imine
|
4
|
|
62
|
Sulfonamide SO2 Extrusion Photorearrangement (6-6)
|
4
|
|
|
Photocyclization
|
|
|
63
|
Acetanilide Dehalogenative Photocyclization to Pyrrolinone
|
4
|
|
64
|
Acetanilide O-dealkyl Dehalogenative Photocyclization to
Morpholinone
|
4
|
|
65
|
Altrenogest Photocycloaddition
|
7
|
|
66
|
Aminobenzophenone Photocyclization to Acridinone
|
4
|
|
67
|
Anthranilic Diamide Dehalogenative Photocyclization to
Oxazine
|
4
|
|
68
|
Aromatic Ketone Norrish II Photocyclization (C1_C4)
|
4
|
|
69
|
beta-Triketone Dehalogenative Photocyclization to
Pyran
|
4
|
|
70
|
Diarylethene Photocyclization to Phenanthrene
|
4
|
|
71
|
Diarylethene Photocyclization to Phenanthrene (E isomer)
|
4
|
|
72
|
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to Benzimidazole (NOHOH)
|
4
|
|
73
|
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to Benzimidazole (NOHOH to NO)
|
7
|
|
74
|
Dinitroaniline Photocyclization to Benzimidazole (NO to N)
|
4
|
|
75
|
Diphenylamine Photocyclization to Carbazole
|
4
|
|
76
|
Diphenylamine Dehalogenative Photocyclization to
Carbazole
|
4
|
|
77
|
Fluoroquinolone Defluorinative Photocyclization
|
7
|
|
78
|
Lamotrigine Photocyclization to Carbazole
|
4
|
|
79
|
Lamotrigine Dehalogenative Photocyclization to Carbazole
|
4
|
|
80
|
o-Vinylbiphenyl Photocyclization to Dihydrophenanthrene
|
5
|
|
81
|
Phenoxyphenol Dehalogenative Photocyclization to
Dioxin
|
4
|
|
|
Photochemical Ring
Contraction
|
|
|
82
|
Zepine Photochemical Ring Contraction to Acridine
|
4
|
|
|
Photohydrolysis
|
|
|
83
|
Aromatic Amine Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
84
|
Aromatic Carbamate Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
85
|
Aromatic Ether Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
86
|
Aromatic Halide Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
87
|
Aromatic Nitro Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
88
|
Aromatic Sulfonate Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
89
|
Benzoylphenylurea Amide Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
90
|
Benzoylphenylurea Urea Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
91
|
beta-Triketone alpha Photocleavage to Carboxylic Acid
|
4
|
|
92
|
Diphenyl Ether Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
93
|
Fluoroquinolone Fluoride Photohydrolysis
|
7
|
|
94
|
N-aryl Amide Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
95
|
Nitrofuran Imine Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
96
|
Nitroguanidine Imine Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
97
|
Nitroguanidine Nitro Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
98
|
Organophosphorus Ester Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
99
|
Pyrethroid Carboxylic Acid Ester Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
100
|
Pyrrolinone Halide Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
101
|
Sulfonamide Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
102
|
Sulfonamide S-C Photohydrolysis
|
3
|
|
103
|
Sulfonylurea Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
104
|
Sulfonylurea S-C Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
105
|
Sulfonylurea S-N Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
106
|
Trifluoromethyl Photohydrolysis
|
4
|
|
|
Photohydration
|
|
|
107
|
Diarylethene Photohydration
|
5
|
|
108
|
Dienone Steroid Photohydration (C5)
|
4
|
|
109
|
Dienone Steroid Photohydration (C9)
|
4
|
|
110
|
Enone Steroid Photohydration and Photorearrangement to Spiro
|
4
|
|
111
|
Trienone Steroid Photohydration (C10)
|
4
|
|
112
|
Trienone Steroid Photohydration (C12)
|
4
|
|
|
Photooxidation
|
|
|
113
|
1_2-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation (C4)
|
4
|
|
114
|
1_4-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation (C5)
|
4
|
|
115
|
1_4-Naphthoquinone Photohydroxylation (C6)
|
4
|
|
116
|
1-Hydroxypyrene Photooxidation to Quinone (C1_C6)
|
4
|
|
117
|
1-Hydroxypyrene Photooxidation to Quinone (C1_C8)
|
4
|
|
118
|
1-Naphthol Photooxidation to 1_2-Benzoquinone
|
4
|
|
119
|
1-Naphthol Photooxidation to 1_4-Benzoquinone
|
4
|
|
120
|
1-Naphthoxy Oxidative Photocleavage to 1_4-Benzoquinone
|
4
|
|
121
|
Anthracene Photooxidation to Endoperoxide
|
4
|
|
122
|
Aromatic Methyl Photooxidation to Carboxylic Acid
|
4
|
|
123
|
Aromatic Nitroso Photooxidation
|
4
|
|
124
|
Aromatic Sulfoxide Photooxidation
|
4
|
|
125
|
Aromatic Thioether Photooxidation
|
4
|
|
126
|
Benzaldehyde Photooxidation to Carboxylic Acid
|
4
|
|
127
|
Benzyl Thio Photooxidation to Sulfoxide
|
2
|
|
128
|
beta-Triketone alpha Photohydroxylation (Dienol)
|
4
|
|
129
|
beta-Triketone alpha Photohydroxylation (Keto)
|
4
|
|
130
|
beta-Triketone Photohydroxylation (Enol)
|
4
|
|
131
|
beta-Triketone Photohydroxylation (Keto)
|
4
|
|
132
|
Carbamazepine Photoepoxidation
|
4
|
|
133
|
Diarylethene Photooxidation
|
4
|
|
134
|
Dihydrooxathiine Anilide Photooxidation to Sulfoxide
|
4
|
|
135
|
Dihydropyridine Photooxidation to Pyridine
|
4
|
|
136
|
Octahydrophenanthrene Benzyl Photohydroxylation
|
4
|
|
137
|
Octahydrophenanthrene Benzyl Photooxidation to Ketone
|
4
|
|
138
|
Organothiophosphorus Ester Photooxidation to Oxon
|
3
|
|
139
|
Phenylurea N-methyl Photooxidation to N-formyl
|
1
|
|
140
|
Pyrene Aromatic Photohydroxylation
|
4
|
|
141
|
s-Triazine Side Chain N-alkyl Photooxidation to
Carbonyl
|
3
|
|
142
|
s-Triazine Side Chain N-isopropyl Photooxidation to Ketone
|
2
|
|
143
|
Trienone Steroid Photooxidation to Dialdehyde
|
4
|
|
144
|
Trifluoroacetic Acid Photoformation
|
4
|
|
|
Photoreduction
|
|
|
145
|
Aromatic Photohydrodehalogenation
|
2
|
|
146
|
Dinitroaniline Nitro Photoreduction
|
4
|
|
147
|
Fluoroquinolone Photohydrodefluorination
|
7
|
|
|
Secondary Dark Reaction
|
|
|
148
|
12-OH Steroid Dehydration to Trienone
|
4
|
|
149
|
5-OH Steroid Dehydration to Dienone
|
4
|
|
150
|
Aldehyde Oxidation to Carboxylic Acid
|
4
|
|
151
|
C-NCO Hydrolysis
|
4
|
|
152
|
C-NNO2 Hydrolysis
|
4
|
|
153
|
Dehydration of Geminal Diols
|
7
|
|
154
|
Hydroxy Enal Tautomerization
|
4
|
|
155
|
Nitro Amidine Hydrolysis
|
4
|
![]() is a single
bond
is a single
bond![]() is a double
bond
is a double
bond![]() is an aromatic
bond unless otherwise stated underneath the reaction scheme to represent a single/aromatic
or a double/aromatic bond
is an aromatic
bond unless otherwise stated underneath the reaction scheme to represent a single/aromatic
or a double/aromatic bond![]() is a single or
double bond
is a single or
double bond![]() is a double cis
or trans bond
is a double cis
or trans bond